PSI AP Chemistry Name Unit 4: Chemical Bonding MC Review Part
... 48. SF4 will have ______ lone pair(s) and a __________ molecular geometry. (A) one; seesaw (B) two; square pyramidal (C) one; T-shaped (D) two; square planar 49. Which of the five basic geometries for molecules and ions has the smallest bond angle? (A) linear (B) planar triangular (C) tetrahedral ( ...
... 48. SF4 will have ______ lone pair(s) and a __________ molecular geometry. (A) one; seesaw (B) two; square pyramidal (C) one; T-shaped (D) two; square planar 49. Which of the five basic geometries for molecules and ions has the smallest bond angle? (A) linear (B) planar triangular (C) tetrahedral ( ...
Year 9 Chemical Sciences Program Term 3 Course 2 2017
... Chemical reactions, including combustion and the reactions of acids, are important in both non-living and living systems and involve energy transfer. (ACSSU179) investigating reactions of acids with metals, bases, and carbonates investigating a range of different reactions to classify them as ex ...
... Chemical reactions, including combustion and the reactions of acids, are important in both non-living and living systems and involve energy transfer. (ACSSU179) investigating reactions of acids with metals, bases, and carbonates investigating a range of different reactions to classify them as ex ...
Chapter 4:Chemical Quantities and Aqueous Reactions:
... (D-D) double displacement: AB + CD AD + CB (P) precipitation: a solid is formed (N) neutralization or acid-base: water is formed (G) gas evolution: gas is formed (Syn) synthesis or combination: A + B AB (D) decomposition: AB A + B (R) redox or oxidation-reduction: electrons are transferred (C) ...
... (D-D) double displacement: AB + CD AD + CB (P) precipitation: a solid is formed (N) neutralization or acid-base: water is formed (G) gas evolution: gas is formed (Syn) synthesis or combination: A + B AB (D) decomposition: AB A + B (R) redox or oxidation-reduction: electrons are transferred (C) ...
Honors Mid-Term Review Sheet
... 62. The radius of a cation is ___________ than its neutral atom. 63. The radius of an anion is ___________than its neutral atom. 64. What are 2 characteristics of noble gases? 65. List the charges formed by the groups on the periodic table. 66. What charges do the following elements have when they f ...
... 62. The radius of a cation is ___________ than its neutral atom. 63. The radius of an anion is ___________than its neutral atom. 64. What are 2 characteristics of noble gases? 65. List the charges formed by the groups on the periodic table. 66. What charges do the following elements have when they f ...
Chapter 1: Matter and Measurement
... Metals tend to lose electrons (lose negative charge) to form positively charged ions called cations. Non-metals tend to gain electrons (gain negative charge) to form negatively charged ions called anions. Chemistry 140 Fall 2002 Dutton ...
... Metals tend to lose electrons (lose negative charge) to form positively charged ions called cations. Non-metals tend to gain electrons (gain negative charge) to form negatively charged ions called anions. Chemistry 140 Fall 2002 Dutton ...
Export To Word
... Standard: Matter A. A working definition of matter is that it takes up space, has mass, and has measurable properties. Matter is comprised of atomic, subatomic, and elementary particles. B. Electrons are key to defining chemical and some physical properties, reactivity, and molecular structures. Rep ...
... Standard: Matter A. A working definition of matter is that it takes up space, has mass, and has measurable properties. Matter is comprised of atomic, subatomic, and elementary particles. B. Electrons are key to defining chemical and some physical properties, reactivity, and molecular structures. Rep ...
BS5-Ch 2.
... • Are symbols used to describe other elements in a compound • elements and compounds • Free elements are not combined with another element in a compound. Examples: Fe (iron), Na (sodium), and K (potassium) Many non-metals occur in groups of 2 (as diatomic molecules)- H, O, N, F, Cl, I, Br Some e ...
... • Are symbols used to describe other elements in a compound • elements and compounds • Free elements are not combined with another element in a compound. Examples: Fe (iron), Na (sodium), and K (potassium) Many non-metals occur in groups of 2 (as diatomic molecules)- H, O, N, F, Cl, I, Br Some e ...
Chemical Compounds
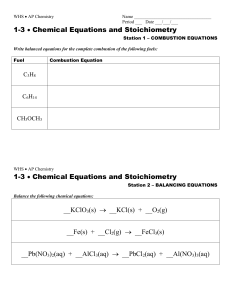
... The total number of atoms of each element must be the same in the products and reactants. When this condition is satisfied we say the equation is balanced. CH4(g)+O2(g) → CO2(g) +H2 O(g) (unbalanced!) CH4(g)+2O2(g) → CO2(g)+2H2 O(g) ...
... The total number of atoms of each element must be the same in the products and reactants. When this condition is satisfied we say the equation is balanced. CH4(g)+O2(g) → CO2(g) +H2 O(g) (unbalanced!) CH4(g)+2O2(g) → CO2(g)+2H2 O(g) ...
base hydrolysis of cobalt(iii)
... I was pleased to be invited by Professor D. A. Davenport to present a paper at the symposium C. K. Ingold: Master and Mandarin of Physical Organic Chemistry to honor Professor Sir Christopher Ingold on the centennial year of his birth. The chemistry community recalls that he was one of the giants of ...
... I was pleased to be invited by Professor D. A. Davenport to present a paper at the symposium C. K. Ingold: Master and Mandarin of Physical Organic Chemistry to honor Professor Sir Christopher Ingold on the centennial year of his birth. The chemistry community recalls that he was one of the giants of ...
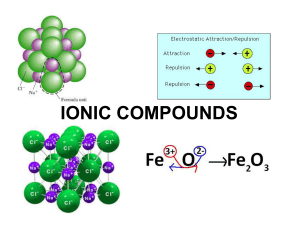
Section 8.3 Names and Formulas of Ionic Compounds Formula Unit
... • Binary Ionic Compounds- contain only two different elements (one metallic cation and one nonmetallic anion). ...
... • Binary Ionic Compounds- contain only two different elements (one metallic cation and one nonmetallic anion). ...
Chapter 1 - TamAPChemistryHart
... Chapter 1 “Introduction: Matter and Measurement” Assignments Classification and Properties of Matter: Exercises: p.31: #11,15,16 11. Classify each of the following as a pure substance or a mixture; if a mixture, indicate whether it is homogeneous or heterogeneous: a) rice pudding b) seawater c) magn ...
... Chapter 1 “Introduction: Matter and Measurement” Assignments Classification and Properties of Matter: Exercises: p.31: #11,15,16 11. Classify each of the following as a pure substance or a mixture; if a mixture, indicate whether it is homogeneous or heterogeneous: a) rice pudding b) seawater c) magn ...
Ch. 3 9-Station Review
... Hydrogen gas was generated according to the equation: Zn(s) + 2HCl(aq) H2(g) + ZnCl2(aq) When 25.00 grams of Zn metal reacted with excess HCl 7.50 L H2(g) was collected at STP. The theoretical yield of H2(g) for this reaction is: (show work) ...
... Hydrogen gas was generated according to the equation: Zn(s) + 2HCl(aq) H2(g) + ZnCl2(aq) When 25.00 grams of Zn metal reacted with excess HCl 7.50 L H2(g) was collected at STP. The theoretical yield of H2(g) for this reaction is: (show work) ...
Chapter 2 PPT - Richsingiser.com
... empirical formula that uses the smallest whole number subscripts to express the relative numbers of ions. • The relative numbers of ions in the empirical formula balances the charges to zero. • The formula of sodium chloride is NaCl, because the 1+ ions have to be present in a 1:1 ...
... empirical formula that uses the smallest whole number subscripts to express the relative numbers of ions. • The relative numbers of ions in the empirical formula balances the charges to zero. • The formula of sodium chloride is NaCl, because the 1+ ions have to be present in a 1:1 ...
Name__________________________________________ Answers to Sample Exam Questions #1 Chemistry 112
... b) They account for the fact that roses are red and violets are blue. c) They are found in pH paper. d) They form the basis of the Scott test for cocaine. 13. Isomers are molecules with the same a) kinds and number of atoms but a different arrangement of these atoms b) number of electrons and proton ...
... b) They account for the fact that roses are red and violets are blue. c) They are found in pH paper. d) They form the basis of the Scott test for cocaine. 13. Isomers are molecules with the same a) kinds and number of atoms but a different arrangement of these atoms b) number of electrons and proton ...
Inorganic chemistry

Inorganic chemistry deals with the synthesis and behavior of inorganic and organometallic compounds. This field covers all chemical compounds except the myriad organic compounds (carbon based compounds, usually containing C-H bonds), which are the subjects of organic chemistry. The distinction between the two disciplines is far from absolute, and there is much overlap, most importantly in the sub-discipline of organometallic chemistry. It has applications in every aspect of the chemical industry–including catalysis, materials science, pigments, surfactants, coatings, medicine, fuel, and agriculture.