Topic 1: Quantitative chemistry (12
... the pseudoscience of alchemy. Lavoisier’s work with oxygen, which overturned the phlogiston theory of heat, could be discussed as an example of a paradigm shift. Int: The discovery of the elements and the arrangement of them is a story that exemplifies how scientific progress is made across national ...
... the pseudoscience of alchemy. Lavoisier’s work with oxygen, which overturned the phlogiston theory of heat, could be discussed as an example of a paradigm shift. Int: The discovery of the elements and the arrangement of them is a story that exemplifies how scientific progress is made across national ...
in-class assignment - hrsbstaff.ednet.ns.ca
... non-metal. Sodium and potassium ions are always a plus one charge, so there's no need to indicate charge. Titanium however, can have a plus 2, plus 3, or a plus 4 charge, so there needs to be a way to indicate which one. The Roman numeral IV means this titanium has a plus 4 charge. To balance that c ...
... non-metal. Sodium and potassium ions are always a plus one charge, so there's no need to indicate charge. Titanium however, can have a plus 2, plus 3, or a plus 4 charge, so there needs to be a way to indicate which one. The Roman numeral IV means this titanium has a plus 4 charge. To balance that c ...
Introduction to Inorganic Chemistry
... order to achieve its ends. This means that a good chemist is one who not only has a mastery of chemical theory, but also a good knowledge of chemical facts. With such a knowledge, he can direct a trial and error approach to practical problems in the most promising directions. Inorganic Chemistry Org ...
... order to achieve its ends. This means that a good chemist is one who not only has a mastery of chemical theory, but also a good knowledge of chemical facts. With such a knowledge, he can direct a trial and error approach to practical problems in the most promising directions. Inorganic Chemistry Org ...
CH100: Fundamentals for Chemistry
... Determines the chemical properties of the atom During chemical processes, interactions occur between the outermost electrons of each atom The electron properties of the atom will define the type(s) of interaction ...
... Determines the chemical properties of the atom During chemical processes, interactions occur between the outermost electrons of each atom The electron properties of the atom will define the type(s) of interaction ...
hc1(8)notes
... • The ability of an element to react is referred to as the element’s activity or reactivity. • The more readily an element reacts with other substances, the greater its activity is. • An activity series is a list of elements organized according to the ease with which the elements undergo certain ch ...
... • The ability of an element to react is referred to as the element’s activity or reactivity. • The more readily an element reacts with other substances, the greater its activity is. • An activity series is a list of elements organized according to the ease with which the elements undergo certain ch ...
CLASS X carbon and its compound
... ascending order of molecular mass, such that they differ by 14 amu or a – CH2 group are called homologous. 16. Alkanes (saturated hydrocarbons) : Compounds of carbon and hydrogen, in which all the valencies of carbon atoms are satisfied by single covalent bonds are called saturated hydrocarbons or a ...
... ascending order of molecular mass, such that they differ by 14 amu or a – CH2 group are called homologous. 16. Alkanes (saturated hydrocarbons) : Compounds of carbon and hydrogen, in which all the valencies of carbon atoms are satisfied by single covalent bonds are called saturated hydrocarbons or a ...
Chapter 1 Chemistry: The Study of Matter
... Elements- simplest kind of matter, made of one type of atom An atom is the smallest unit of an element that maintains the properties of that element. Cannot be broken down into simpler substances by ordinary chemical means Ex. gold, copper, oxygen (on the periodic table) ...
... Elements- simplest kind of matter, made of one type of atom An atom is the smallest unit of an element that maintains the properties of that element. Cannot be broken down into simpler substances by ordinary chemical means Ex. gold, copper, oxygen (on the periodic table) ...
Redox - edl.io
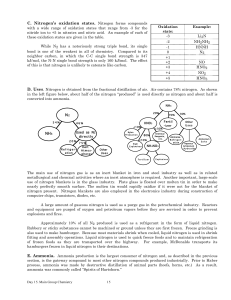
... 5. Oxygen is usually assigned an oxidation state of -2. Exceptions to this rule include peroxides (compound containing the O22- group), where each oxygen is assigned an oxidation state of -1, as in hydrogen peroxide (H2O2), and OF2 in which oxygen is assigned a +2 oxidation state. 6. In its covalent ...
... 5. Oxygen is usually assigned an oxidation state of -2. Exceptions to this rule include peroxides (compound containing the O22- group), where each oxygen is assigned an oxidation state of -1, as in hydrogen peroxide (H2O2), and OF2 in which oxygen is assigned a +2 oxidation state. 6. In its covalent ...
31 BIOMOLECULES Y MODULE - 7
... pH or in temperature, the hydrogen bonds are disturbed and broken. When attractions between and within protein molecules are destroyed, the chains separate from each other, globules unfold and helices uncoil. We say that the protein has been denatured. Denaturation is seen in our daily life in many ...
... pH or in temperature, the hydrogen bonds are disturbed and broken. When attractions between and within protein molecules are destroyed, the chains separate from each other, globules unfold and helices uncoil. We say that the protein has been denatured. Denaturation is seen in our daily life in many ...
Read the following text! TEXT A Organic chemistry is a subdiscipline
... Organic chemistry is a subdiscipline within chemistry involving the scientific study of the structure, properties, and reactions of organic compounds and organic materials, i.e., matter in its various forms that contain carbon atoms. In general any organic compound is anything compound that contains ...
... Organic chemistry is a subdiscipline within chemistry involving the scientific study of the structure, properties, and reactions of organic compounds and organic materials, i.e., matter in its various forms that contain carbon atoms. In general any organic compound is anything compound that contains ...
New substances are formed by chemical reactions. When elements
... Compounds formed from non-metals consist of molecules. The atoms in a molecule are joined together by covalent bonds. These bonds form when atoms share pairs of electrons. Chemical formulas The chemical formula of a compound shows how many of each type of atom join together to make the units which m ...
... Compounds formed from non-metals consist of molecules. The atoms in a molecule are joined together by covalent bonds. These bonds form when atoms share pairs of electrons. Chemical formulas The chemical formula of a compound shows how many of each type of atom join together to make the units which m ...
Balancing RedOx reactions handout
... Oxygen bonds follow previous rules, meaning other assignments take place first leaving oxygen to neutralize the charge. B1. ...
... Oxygen bonds follow previous rules, meaning other assignments take place first leaving oxygen to neutralize the charge. B1. ...
COMPOUNDS OF CARBON CONTAINING NITROGEN
... intermediates in drug synthesis. The quaternary ammonium salts derived from long chain aliphatic tertiary amines are widely used as detergents. Aromatic amines e.g. aniline and its derivatives, are used for the production of dyes, drugs and photographic developers. 1,4-Diaminobenzene is the main ing ...
... intermediates in drug synthesis. The quaternary ammonium salts derived from long chain aliphatic tertiary amines are widely used as detergents. Aromatic amines e.g. aniline and its derivatives, are used for the production of dyes, drugs and photographic developers. 1,4-Diaminobenzene is the main ing ...
Name ______ Period ______ 7th Grade Science Study Guide 1 7
... 52. Which of the following summarizes the Law of Conservation of Matter as applied to a chemical reaction? a. The total mass of the reactants is greater than the mass of the products. b. The total mass of the reactants is less than the total mass of the products. c. The total mass of the reactants e ...
... 52. Which of the following summarizes the Law of Conservation of Matter as applied to a chemical reaction? a. The total mass of the reactants is greater than the mass of the products. b. The total mass of the reactants is less than the total mass of the products. c. The total mass of the reactants e ...
Chapter 4 Reactions in Aqueous Solutions
... The oxidation number of Pb decreases; it is reduced; PbO is the oxidizing agent. ...
... The oxidation number of Pb decreases; it is reduced; PbO is the oxidizing agent. ...
CHEMICAL FORMULAE (ANSWERS) Molecule Empirical formula
... Organic compounds are composed of carbon and hydrogen and sometimes a few other elements. Many organic compounds contain carbon, hydrogen, oxygen and/or nitogen. Organic compounds may be divided into hydrocarbons containing carbon and hydrogen(e.g. methane CH4, ethene, C2H4) and functionalised hydro ...
... Organic compounds are composed of carbon and hydrogen and sometimes a few other elements. Many organic compounds contain carbon, hydrogen, oxygen and/or nitogen. Organic compounds may be divided into hydrocarbons containing carbon and hydrogen(e.g. methane CH4, ethene, C2H4) and functionalised hydro ...
Worksheet answers
... Organic compounds are composed of carbon and hydrogen and sometimes a few other elements. Many organic compounds contain carbon, hydrogen, oxygen and/or nitogen. Organic compounds may be divided into hydrocarbons containing carbon and hydrogen(e.g. methane CH4, ethene, C2H4) and functionalised hydro ...
... Organic compounds are composed of carbon and hydrogen and sometimes a few other elements. Many organic compounds contain carbon, hydrogen, oxygen and/or nitogen. Organic compounds may be divided into hydrocarbons containing carbon and hydrogen(e.g. methane CH4, ethene, C2H4) and functionalised hydro ...
Inorganic chemistry

Inorganic chemistry deals with the synthesis and behavior of inorganic and organometallic compounds. This field covers all chemical compounds except the myriad organic compounds (carbon based compounds, usually containing C-H bonds), which are the subjects of organic chemistry. The distinction between the two disciplines is far from absolute, and there is much overlap, most importantly in the sub-discipline of organometallic chemistry. It has applications in every aspect of the chemical industry–including catalysis, materials science, pigments, surfactants, coatings, medicine, fuel, and agriculture.