MYP 10 PeriodicityWS
... 5(a) Draw a diagram to show the structure of sodium chloride. Explain, in terms of bonding, why sodium chloride has a high melting point. (b) Lithium reacts with water. Write an equation for the reaction and state two observations that could be made during the reaction. [SL paper 2, Nov 05] 6 (a) Fo ...
... 5(a) Draw a diagram to show the structure of sodium chloride. Explain, in terms of bonding, why sodium chloride has a high melting point. (b) Lithium reacts with water. Write an equation for the reaction and state two observations that could be made during the reaction. [SL paper 2, Nov 05] 6 (a) Fo ...
chemical equation
... atoms as the right side for EACH element. 4. Check your answer to see if: – The numbers of atoms on both sides of the equation are now balanced. – The coefficients are in the lowest possible whole number ratios. (reduced) ...
... atoms as the right side for EACH element. 4. Check your answer to see if: – The numbers of atoms on both sides of the equation are now balanced. – The coefficients are in the lowest possible whole number ratios. (reduced) ...
www.tutor-homework.com (for tutoring, homework help, or help with
... b. compounds and elements. c. elements and homogeneous solutions. d. compounds and homogeneous solutions. e. elements and heterogeneous solutions. Chemistry 1411 General Chemistry I Chapter 2 Review ...
... b. compounds and elements. c. elements and homogeneous solutions. d. compounds and homogeneous solutions. e. elements and heterogeneous solutions. Chemistry 1411 General Chemistry I Chapter 2 Review ...
Review Unit - hrsbstaff.ednet.ns.ca
... - Exothermic reactions are accompanied by the release of heat into their surroundings. CH4 + 2O2 → CO2 + 2H2O + energy The release of energy is shown as a product in the equation. We can show this in an energy level diagram: ...
... - Exothermic reactions are accompanied by the release of heat into their surroundings. CH4 + 2O2 → CO2 + 2H2O + energy The release of energy is shown as a product in the equation. We can show this in an energy level diagram: ...
C6-Chemical Reactions
... Group- Vertical columns on the periodic table Elements within a group have similar chemical and physical ...
... Group- Vertical columns on the periodic table Elements within a group have similar chemical and physical ...
Solutions - Seattle Central
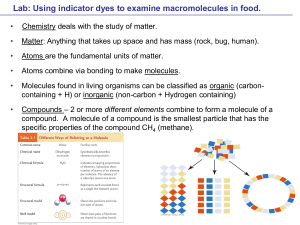
... Benedict's solution is a chemical indicator for simple sugars such as glucose: C6H12O6. Unlike some other indicators, Benedict’s solution does not work at room temperature - it must be heated first Details: ...
... Benedict's solution is a chemical indicator for simple sugars such as glucose: C6H12O6. Unlike some other indicators, Benedict’s solution does not work at room temperature - it must be heated first Details: ...
TDDFT as a tool in chemistry
... What’s quantum chemistry and photochemistry? From Wikipedia: Photochemistry, a sub-discipline of chemistry, is the study of the interactions between atoms, small molecules, and light (or electromagnetic radiation). […] Photochemistry may also be introduced to laymen as a reaction that proceeds with ...
... What’s quantum chemistry and photochemistry? From Wikipedia: Photochemistry, a sub-discipline of chemistry, is the study of the interactions between atoms, small molecules, and light (or electromagnetic radiation). […] Photochemistry may also be introduced to laymen as a reaction that proceeds with ...
Name Date Class Period ______
... Name ______________________________________ Date __________________ Class Period _________ Atoms, Elements, and Compound Test Study Guide I. ...
... Name ______________________________________ Date __________________ Class Period _________ Atoms, Elements, and Compound Test Study Guide I. ...
Topic2890 Thermodynamics and Kinetics A given system at
... water (l) , the solvent, together with n 0X and n 0Y moles of chemical substances X and Y respectively at time ‘t = 0’. The molalities of these solutes are m 0X (= n 0X / n 1 ⋅ M 1 = n 0X / w 1 ) and m 0Y (= n 0Y / n 1 ⋅ M 1 = n 0Y / w 1 ) respectively at time ‘t = 0’; the concentrations are c 0X (= ...
... water (l) , the solvent, together with n 0X and n 0Y moles of chemical substances X and Y respectively at time ‘t = 0’. The molalities of these solutes are m 0X (= n 0X / n 1 ⋅ M 1 = n 0X / w 1 ) and m 0Y (= n 0Y / n 1 ⋅ M 1 = n 0Y / w 1 ) respectively at time ‘t = 0’; the concentrations are c 0X (= ...
Honors Mid-Term Review Sheet
... 8. What is a compound? List an example. 9. What is an element? List an example. 10. List and define the four states of matter. 11. List and define the two methods for separating mixtures. 12. What is the law of conservation of mass and how does it apply to chemical reactions? 13. What is a precipita ...
... 8. What is a compound? List an example. 9. What is an element? List an example. 10. List and define the four states of matter. 11. List and define the two methods for separating mixtures. 12. What is the law of conservation of mass and how does it apply to chemical reactions? 13. What is a precipita ...
THE CHEMICAL BASIS OF LIFE
... Matter is composed of 92 naturally occurring elements, each composed of atoms. Atoms have subatomic particles: neutrons, protons, and electrons. Atoms of the same type that differ by the number of neutrons are called isotopes. Atoms react with one another by giving up, gaining, and sharing electrons ...
... Matter is composed of 92 naturally occurring elements, each composed of atoms. Atoms have subatomic particles: neutrons, protons, and electrons. Atoms of the same type that differ by the number of neutrons are called isotopes. Atoms react with one another by giving up, gaining, and sharing electrons ...
110 exam i material
... the space shuttle lifting off __________________________ c. Indicate which of the following is a chemical or physical change Burning of a log __________________________ Rusting of a nail __________________________ melting of ice __________________________ The odor of a skunk ________________________ ...
... the space shuttle lifting off __________________________ c. Indicate which of the following is a chemical or physical change Burning of a log __________________________ Rusting of a nail __________________________ melting of ice __________________________ The odor of a skunk ________________________ ...
Chapter 2: Chemistry Level
... High heat capacity – absorbs and releases large amounts of heat before changing temperature High heat of vaporization – changing from a liquid to a gas requires large amounts of heat Polar solvent properties – dissolves ionic substances, forms hydration layers around large charged molecules, a ...
... High heat capacity – absorbs and releases large amounts of heat before changing temperature High heat of vaporization – changing from a liquid to a gas requires large amounts of heat Polar solvent properties – dissolves ionic substances, forms hydration layers around large charged molecules, a ...
Science Olympiad
... ______ 5. In the lanthanide elements, which orbitals are only partially filled? (A) 5s and 4d (B) 5d and 4f (C) 6s and 5d (D) 6p and 5f (E) 4f only ______ 6. Ions with the electronic structure 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 would not be present in which aqueous solution? (A) NaF(aq) (B) NaCl(aq) (C) KBr(aq) ( ...
... ______ 5. In the lanthanide elements, which orbitals are only partially filled? (A) 5s and 4d (B) 5d and 4f (C) 6s and 5d (D) 6p and 5f (E) 4f only ______ 6. Ions with the electronic structure 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 would not be present in which aqueous solution? (A) NaF(aq) (B) NaCl(aq) (C) KBr(aq) ( ...
Chapter 3
... – identity of reactants [R] and products [P]; use study of nomenclature to write equations – Identify the state of matter for each [R] and [P] – identify reaction type ...
... – identity of reactants [R] and products [P]; use study of nomenclature to write equations – Identify the state of matter for each [R] and [P] – identify reaction type ...
Chemistry- CST Review
... people in the back of the room eventually be able to smell it? Why? Explain completely. ...
... people in the back of the room eventually be able to smell it? Why? Explain completely. ...
Atoms, Molecules and Ions
... (c) nitrous oxide (N2O), used as an anesthetic gas (“laughing gas”) and as an aerosol propellant for whipped creams. Because the subscripts in N2O are already the smallest possible whole numbers, the empirical formula for nitrous oxide is the same as its molecular formula. ...
... (c) nitrous oxide (N2O), used as an anesthetic gas (“laughing gas”) and as an aerosol propellant for whipped creams. Because the subscripts in N2O are already the smallest possible whole numbers, the empirical formula for nitrous oxide is the same as its molecular formula. ...
History of chemistry

The history of chemistry represents a time span from ancient history to the present. By 1000 BC, civilizations used technologies that would eventually form the basis to the various branches of chemistry. Examples include extracting metals from ores, making pottery and glazes, fermenting beer and wine, extracting chemicals from plants for medicine and perfume, rendering fat into soap, making glass, and making alloys like bronze.The protoscience of chemistry, alchemy, was unsuccessful in explaining the nature of matter and its transformations. However, by performing experiments and recording the results, alchemists set the stage for modern chemistry. The distinction began to emerge when a clear differentiation was made between chemistry and alchemy by Robert Boyle in his work The Sceptical Chymist (1661). While both alchemy and chemistry are concerned with matter and its transformations, chemists are seen as applying scientific method to their work.Chemistry is considered to have become an established science with the work of Antoine Lavoisier, who developed a law of conservation of mass that demanded careful measurement and quantitative observations of chemical phenomena. The history of chemistry is intertwined with the history of thermodynamics, especially through the work of Willard Gibbs.