Atoms, compounds and elements - Mrs. Tes de Luna`s Science Class
... ◦ The first part of his theory states that all matter is made of atoms, which are indivisible. ◦ The second part of the theory says all atoms of a given element are identical in mass and properties. ◦ The third part says compounds are combinations of two or more different types of atoms. ◦ The fourt ...
... ◦ The first part of his theory states that all matter is made of atoms, which are indivisible. ◦ The second part of the theory says all atoms of a given element are identical in mass and properties. ◦ The third part says compounds are combinations of two or more different types of atoms. ◦ The fourt ...
chapter 7 quiz
... 10._T__The number of protons and neutrons in the nucleus L) cathode of an atom. M) electron cloud 11._Y__Discovered radioactivity. N) Darth Vader 12._C__Discovered three types of radiation. O) chemical symbol 13._J__The charge on an “beta” particle. P) 0 14._A__The charge on an “alpha” particle. Q) ...
... 10._T__The number of protons and neutrons in the nucleus L) cathode of an atom. M) electron cloud 11._Y__Discovered radioactivity. N) Darth Vader 12._C__Discovered three types of radiation. O) chemical symbol 13._J__The charge on an “beta” particle. P) 0 14._A__The charge on an “alpha” particle. Q) ...
Types of Measurement
... 1. Components of two or more components that can be separated by physical means, such as chromatography, filtration, or distillation 2. No chemical bonds between the separate ...
... 1. Components of two or more components that can be separated by physical means, such as chromatography, filtration, or distillation 2. No chemical bonds between the separate ...
SEPARATION OF MATTER - Los Angeles City College
... • Tends to lose electrons to form cations • Has low ionization energies & electronegativity values • Forms compounds with nonmetals but not other metals • Good conduction of heat and electricity • Lustrous & malleable solids excepts Hg which is a liquid • Ductile ...
... • Tends to lose electrons to form cations • Has low ionization energies & electronegativity values • Forms compounds with nonmetals but not other metals • Good conduction of heat and electricity • Lustrous & malleable solids excepts Hg which is a liquid • Ductile ...
Analysis of a Matter
... • Tends to lose electrons to form cations • Has low ionization energies & electronegativity values • Forms compounds with nonmetals but not other metals • Good conduction of heat and electricity • Lustrous & malleable solids excepts Hg which is a liquid • Ductile ...
... • Tends to lose electrons to form cations • Has low ionization energies & electronegativity values • Forms compounds with nonmetals but not other metals • Good conduction of heat and electricity • Lustrous & malleable solids excepts Hg which is a liquid • Ductile ...
Document
... spontaneous decay called radioactivity 11. Identification of Isotopes http://images.encarta.msn.com/xrefmedia/aencm ed/targets/illus/ilt/T046738A.gif 12. Molecules and Compounds Molecule – two or more atoms held together by chemical bonds Compound – two or more different kinds of atoms chemically bo ...
... spontaneous decay called radioactivity 11. Identification of Isotopes http://images.encarta.msn.com/xrefmedia/aencm ed/targets/illus/ilt/T046738A.gif 12. Molecules and Compounds Molecule – two or more atoms held together by chemical bonds Compound – two or more different kinds of atoms chemically bo ...
Atomic Theories- Part I - Tenafly Public Schools
... Thompson showed that the production of the cathode ray was not dependent on the type of gas in the tube, or the type of metal used for the electrodes. He concluded that these particles were part of every atom. ...
... Thompson showed that the production of the cathode ray was not dependent on the type of gas in the tube, or the type of metal used for the electrodes. He concluded that these particles were part of every atom. ...
Ch. 02 - HCC Learning Web
... Hydrogen Bonds • A hydrogen bond forms when a hydrogen atom covalently bonded to one electronegative atom is also attracted to another electronegative atom • In living cells, the electronegative partners are usually oxygen or nitrogen atoms ...
... Hydrogen Bonds • A hydrogen bond forms when a hydrogen atom covalently bonded to one electronegative atom is also attracted to another electronegative atom • In living cells, the electronegative partners are usually oxygen or nitrogen atoms ...
Bonding Notes
... Its easy to see that the Cl is more than 3 times the electronegativity of Na. Because of this large difference in electronegativity its easy see that Cl will pluck an electron from Na. Also one can see that the difference between the two atoms electronegativity is 2.3 . *This is important to note be ...
... Its easy to see that the Cl is more than 3 times the electronegativity of Na. Because of this large difference in electronegativity its easy see that Cl will pluck an electron from Na. Also one can see that the difference between the two atoms electronegativity is 2.3 . *This is important to note be ...
Chapter 08
... When there is more than one possible structure, the best arrangement is determined by the following guidelines: 1) A Lewis structure in which all formal charges are zero is preferred. 2) Small formal charges are preferred to large formal charges. ...
... When there is more than one possible structure, the best arrangement is determined by the following guidelines: 1) A Lewis structure in which all formal charges are zero is preferred. 2) Small formal charges are preferred to large formal charges. ...
The Chemical Basis of Life
... Chemical reactions involve making and breaking bonds. Making bonds requires the input of energy. Energy is stored in molecules in the chemical bonds. Breaking bonds usually releases energy. ...
... Chemical reactions involve making and breaking bonds. Making bonds requires the input of energy. Energy is stored in molecules in the chemical bonds. Breaking bonds usually releases energy. ...
Elements and Atoms
... • All matter is made of atoms • Atoms are the building blocks of matter, sort of how bricks are the building blocks of houses. ...
... • All matter is made of atoms • Atoms are the building blocks of matter, sort of how bricks are the building blocks of houses. ...
Study Guide (Semester 2)
... 2. How do reactions occur, and what part of the atom interacts? ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ 3. Reactions between atoms involve only their __________________________. 4. D ...
... 2. How do reactions occur, and what part of the atom interacts? ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ 3. Reactions between atoms involve only their __________________________. 4. D ...
objectives chm 1025 - Miami Dade College
... b. Using the structure of the periodic table to classify elements (e.g., metal, nonmetal, metalloid, noble gas, representative element, transition element, inner transition element, alkali metal, alkaline earth metal, and/or halogen). c. Using the periodic table to identify common patterns such as a ...
... b. Using the structure of the periodic table to classify elements (e.g., metal, nonmetal, metalloid, noble gas, representative element, transition element, inner transition element, alkali metal, alkaline earth metal, and/or halogen). c. Using the periodic table to identify common patterns such as a ...
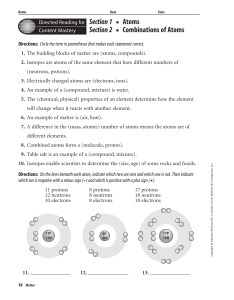
Chapter 18 Resource: Matter
... 1. The building blocks of matter are (atoms, compounds). 2. Isotopes are atoms of the same element that have different numbers of (neutrons, protons). 3. Electrically charged atoms are (electrons, ions). 4. An example of a (compound, mixture) is water. 5. The (chemical, physical) properties of an el ...
... 1. The building blocks of matter are (atoms, compounds). 2. Isotopes are atoms of the same element that have different numbers of (neutrons, protons). 3. Electrically charged atoms are (electrons, ions). 4. An example of a (compound, mixture) is water. 5. The (chemical, physical) properties of an el ...
Chemistry (CP) Final Exam Study Guide 1
... ____ 23. A vapor is which state of matter? a. solid c. gas b. liquid d. all of the above ____ 24. Which state of matter takes both the shape and volume of its container? a. solid c. gas b. liquid d. both b and c ____ 25. Which of the following CANNOT be classified as a substance? a. table salt c. ni ...
... ____ 23. A vapor is which state of matter? a. solid c. gas b. liquid d. all of the above ____ 24. Which state of matter takes both the shape and volume of its container? a. solid c. gas b. liquid d. both b and c ____ 25. Which of the following CANNOT be classified as a substance? a. table salt c. ni ...
CHEMISTRY FALL FINAL PRACTICE 2016
... How many significant digits does each of the following have: 45000 ____ 0.00320 ______ ...
... How many significant digits does each of the following have: 45000 ____ 0.00320 ______ ...
Chemistry Mid-Term Review Sheet
... 55. The radius of a cation is ___________ than its neutral atom. 56. The radius of an anion is ___________than its neutral atom. 57. What are 2 characteristics of noble gases? 58. List the charges formed by the groups on the periodic table. 59. What charges do the following elements have when they f ...
... 55. The radius of a cation is ___________ than its neutral atom. 56. The radius of an anion is ___________than its neutral atom. 57. What are 2 characteristics of noble gases? 58. List the charges formed by the groups on the periodic table. 59. What charges do the following elements have when they f ...
The Periodic Table of Elements and Atoms…
... •Neutrons, also found in the nucleus, have no electrical charge. They are neutral. They have about the same mass as a proton. •The nucleus is the central core of an atom that contains most of the mass of an atom because it contains both the neutrons and protons. ...
... •Neutrons, also found in the nucleus, have no electrical charge. They are neutral. They have about the same mass as a proton. •The nucleus is the central core of an atom that contains most of the mass of an atom because it contains both the neutrons and protons. ...
Tutorial 1
... 1. Describe the four quantum numbers used to characterize an electron in an atom. 2. An electron in an atom is in the n = 3 quantum level. List the possible values of l and ml that it can have. 3. What is electron configuration? Describe the role that the Pauli Exclusion Principle and Hund’s rule pl ...
... 1. Describe the four quantum numbers used to characterize an electron in an atom. 2. An electron in an atom is in the n = 3 quantum level. List the possible values of l and ml that it can have. 3. What is electron configuration? Describe the role that the Pauli Exclusion Principle and Hund’s rule pl ...
Adv review key
... J) Draw the electron dot diagram (Lewis Dot Structure) and then tell if it would give up or take on electrons to get a full shell. Also tell what charge it would have (positive or negative and how much ex: +2) ...
... J) Draw the electron dot diagram (Lewis Dot Structure) and then tell if it would give up or take on electrons to get a full shell. Also tell what charge it would have (positive or negative and how much ex: +2) ...
APS 1st semester exam review 2016
... J) Draw the electron dot diagram (Lewis Dot Structure) and then tell if it would give up or take on electrons to get a full shell. Also tell what charge it would have (positive or negative and how much ex: +2) ...
... J) Draw the electron dot diagram (Lewis Dot Structure) and then tell if it would give up or take on electrons to get a full shell. Also tell what charge it would have (positive or negative and how much ex: +2) ...
bonding and geometry
... Very rare Tend to form harmful molecules Occurs when both of the bonding pair of electrons in a covalent bond come from only ONE of the atoms Example: CO ...
... Very rare Tend to form harmful molecules Occurs when both of the bonding pair of electrons in a covalent bond come from only ONE of the atoms Example: CO ...
Glowing Tubes for Signs, Television Sets, and Computers
... Thomson’s cathode ray tube has many modern applications. For example, “neon” signs consist of small-diameter cathode ray tubes containing different kinds of gases to produce various colors. For example, if the gas in the tube is neon, the tube glows with a red–orange color; if argon is present, a bl ...
... Thomson’s cathode ray tube has many modern applications. For example, “neon” signs consist of small-diameter cathode ray tubes containing different kinds of gases to produce various colors. For example, if the gas in the tube is neon, the tube glows with a red–orange color; if argon is present, a bl ...
Electronegativity

Electronegativity, symbol χ, is a chemical property that describes the tendency of an atom or a functional group to attract electrons (or electron density) towards itself. An atom's electronegativity is affected by both its atomic number and the distance at which its valence electrons reside from the charged nucleus. The higher the associated electronegativity number, the more an element or compound attracts electrons towards it. The term ""electronegativity"" was introduced by Jöns Jacob Berzelius in 1811,though the concept was known even before that and was studied by many chemists including Avogadro.In spite of its long history, an accurate scale of electronegativity had to wait till 1932, when Linus Pauling proposed an electronegativity scale, which depends on bond energies, as a development of valence bond theory. It has been shown to correlate with a number of other chemical properties. Electronegativity cannot be directly measured and must be calculated from other atomic or molecular properties. Several methods of calculation have been proposed, and although there may be small differences in the numerical values of the electronegativity, all methods show the same periodic trends between elements. The most commonly used method of calculation is that originally proposed by Linus Pauling. This gives a dimensionless quantity, commonly referred to as the Pauling scale, on a relative scale running from around 0.7 to 3.98 (hydrogen = 2.20). When other methods of calculation are used, it is conventional (although not obligatory) to quote the results on a scale that covers the same range of numerical values: this is known as an electronegativity in Pauling units. As it is usually calculated, electronegativity is not a property of an atom alone, but rather a property of an atom in a molecule. Properties of a free atom include ionization energy and electron affinity. It is to be expected that the electronegativity of an element will vary with its chemical environment, but it is usually considered to be a transferable property, that is to say that similar values will be valid in a variety of situations.On the most basic level, electronegativity is determined by factors like the nuclear charge (the more protons an atom has, the more ""pull"" it will have on electrons) and the number/location of other electrons present in the atomic shells (the more electrons an atom has, the farther from the nucleus the valence electrons will be, and as a result the less positive charge they will experience—both because of their increased distance from the nucleus, and because the other electrons in the lower energy core orbitals will act to shield the valence electrons from the positively charged nucleus).The opposite of electronegativity is electropositivity: a measure of an element's ability to donate electrons.Caesium is the least electronegative element in the periodic table (=0.79), while fluorine is most electronegative (=3.98). (Francium and caesium were originally assigned both assigned 0.7; caesium's value was later refined to 0.79, but no experimental data allows a similar refinement for francium. However, francium's ionization energy is known to be slightly higher than caesium's, in accordance with the relativistic stabilization of the 7s orbital, and this in turn implies that caesium is in fact more electronegative than francium.)