Electrochemistry Oxidation – Reduction and Oxidation Numbers
... 5. Oxygen in a compound or ion usually has an oxidation state of –2. (Peroxides are the exception, in which case the oxidation number is –1.) 6. Hydrogen in a compound or ion usually has an oxidation state of +1. (Hydrides are the exception, in which case the oxidation number is –1.) 7. For covalent ...
... 5. Oxygen in a compound or ion usually has an oxidation state of –2. (Peroxides are the exception, in which case the oxidation number is –1.) 6. Hydrogen in a compound or ion usually has an oxidation state of +1. (Hydrides are the exception, in which case the oxidation number is –1.) 7. For covalent ...
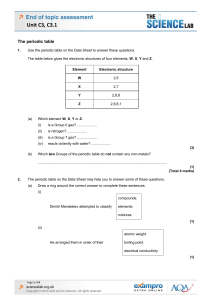
Unit C3, C3.1
... Use the periodic table on the Data Sheet to answer these questions. The table below gives the electronic structures of four elements, W, X, Y and Z. ...
... Use the periodic table on the Data Sheet to answer these questions. The table below gives the electronic structures of four elements, W, X, Y and Z. ...
syllabus details - hrsbstaff.ednet.ns.ca
... can extend to the whole of the periodic table. For example, students should know or be able to predict that K is in group I is using Z = 19, but need only know that since Cs is in group I, it has one electron in its outer shell. ...
... can extend to the whole of the periodic table. For example, students should know or be able to predict that K is in group I is using Z = 19, but need only know that since Cs is in group I, it has one electron in its outer shell. ...
Chemistry - NIC Karnataka
... Electronegativity. valence – periodicity of valence or oxidation states (s and p block elements). ...
... Electronegativity. valence – periodicity of valence or oxidation states (s and p block elements). ...
15anespp
... This Powerpoint show is one of several produced to help students understand selected topics at AS and A2 level Chemistry. It is based on the requirements of the AQA and OCR specifications but is suitable for other examination boards. Individual students may use the material at home for revision purp ...
... This Powerpoint show is one of several produced to help students understand selected topics at AS and A2 level Chemistry. It is based on the requirements of the AQA and OCR specifications but is suitable for other examination boards. Individual students may use the material at home for revision purp ...
CHEMISTRY 101 Name Mock Final Exam Spring 2014 Signature Dr
... Ionization energies are generally endothermic. “Lower in energy” also means “more stable”. The ground state is the lowest energy state. In an exothermic chemical reaction, the products are more stable than the reactants. All of the above statements (a-d) are true. ...
... Ionization energies are generally endothermic. “Lower in energy” also means “more stable”. The ground state is the lowest energy state. In an exothermic chemical reaction, the products are more stable than the reactants. All of the above statements (a-d) are true. ...
Sample pages 2 PDF
... For centuries, human beings have found inspiration in nature, from macro-scale to micro-scale. Animals have been inspiring designs of cars, robotics, and even computational algorithms based on their behaviors. Some new super tough materials got inspired in deer antlers. Environmental analysis of pre ...
... For centuries, human beings have found inspiration in nature, from macro-scale to micro-scale. Animals have been inspiring designs of cars, robotics, and even computational algorithms based on their behaviors. Some new super tough materials got inspired in deer antlers. Environmental analysis of pre ...
AS CHECKLISTS File
... Predict the shapes of, and bond angles in, molecules and ions analogous to those above. Describe the term electronegativity as the ability of an atom to attract the bonding electrons in a covalent bond. ...
... Predict the shapes of, and bond angles in, molecules and ions analogous to those above. Describe the term electronegativity as the ability of an atom to attract the bonding electrons in a covalent bond. ...
Redox Reactions - hrsbstaff.ednet.ns.ca
... Oxidation and reduction reaction = redox rxn Oxidation is loss of electrons and reduction is gain of electrons = transfer of electrons Those 2 reactions are occurring simultaneously ...
... Oxidation and reduction reaction = redox rxn Oxidation is loss of electrons and reduction is gain of electrons = transfer of electrons Those 2 reactions are occurring simultaneously ...
Year Review Booklet (optional)
... points. Increase in temperature until only one boils. Vapour condensed to liquid. Other substances stay in the flask. b. Small amounts of ink, pigments, etc. c. Spins quickly. Dense materials forced outward to the bottom of the test tube. 4. New chemical substances formed. Eg: Burning, photosynthesi ...
... points. Increase in temperature until only one boils. Vapour condensed to liquid. Other substances stay in the flask. b. Small amounts of ink, pigments, etc. c. Spins quickly. Dense materials forced outward to the bottom of the test tube. 4. New chemical substances formed. Eg: Burning, photosynthesi ...
General and Organic Chemistry Review Primer
... 2s and 2p orbitals). Chlorine has seven valence electrons because there are seven electrons in its 3s and 3p orbitals. For many elements, atoms will react so that their outermost energy level or valence shell is filled, which is the most stable configuration they can have. The term octet rule is use ...
... 2s and 2p orbitals). Chlorine has seven valence electrons because there are seven electrons in its 3s and 3p orbitals. For many elements, atoms will react so that their outermost energy level or valence shell is filled, which is the most stable configuration they can have. The term octet rule is use ...
MISE - Physical Basis of Chemistry
... Up to now, we’ve been talking about relative atomic weights and we have been working in ratio - using the “triangle”. Since individual weights appear in the periodic table, there has to be a mass standard, i.e., a reference mass - so that the ratio of atomic weights can become individual values. Sin ...
... Up to now, we’ve been talking about relative atomic weights and we have been working in ratio - using the “triangle”. Since individual weights appear in the periodic table, there has to be a mass standard, i.e., a reference mass - so that the ratio of atomic weights can become individual values. Sin ...
- TestbankU
... 36) Van der Waals interactions may result when _____. A) electrons are not symmetrically distributed in a molecule B) molecules held by ionic bonds react with water C) two polar covalent bonds react D) a hydrogen atom loses an electron Answer: A Bloom's Taxonomy: Knowledge/Comprehension Section: 2.3 ...
... 36) Van der Waals interactions may result when _____. A) electrons are not symmetrically distributed in a molecule B) molecules held by ionic bonds react with water C) two polar covalent bonds react D) a hydrogen atom loses an electron Answer: A Bloom's Taxonomy: Knowledge/Comprehension Section: 2.3 ...
Pauling Scale of Electronegativities for the Various Elements
... C. Changes in a few of the Pauling electronegativities improve predictions. 1. Chang Cu from 1.9 to 2.3. 2. When a transition element is at a nonmetal oxidation number (+4 → +7) increase its electronegativity by 1.1 units before adding .1 for each unit increase in oxidation number. (example Crs+ is ...
... C. Changes in a few of the Pauling electronegativities improve predictions. 1. Chang Cu from 1.9 to 2.3. 2. When a transition element is at a nonmetal oxidation number (+4 → +7) increase its electronegativity by 1.1 units before adding .1 for each unit increase in oxidation number. (example Crs+ is ...
doc: Oxidation Numbers
... that atom would have if the compound was composed of ions. 1. The oxidation number of an atom is zero in a neutral substance that contains atoms of only one element. Thus, the atoms in O2, O3, P4, S8, and aluminum metal all have an oxidation number of 0. 2. The oxidation number of simple ions is equ ...
... that atom would have if the compound was composed of ions. 1. The oxidation number of an atom is zero in a neutral substance that contains atoms of only one element. Thus, the atoms in O2, O3, P4, S8, and aluminum metal all have an oxidation number of 0. 2. The oxidation number of simple ions is equ ...
FREE Sample Here
... become oppositely charged B) protons and neutrons are shared by two atoms so as to satisfy the requirements of both atoms C) outer-shell electrons of two atoms are shared so as to satisfactorily fill their respective orbitals D) outer-shell electrons of one atom are transferred to fill the inner ele ...
... become oppositely charged B) protons and neutrons are shared by two atoms so as to satisfy the requirements of both atoms C) outer-shell electrons of two atoms are shared so as to satisfactorily fill their respective orbitals D) outer-shell electrons of one atom are transferred to fill the inner ele ...
Structure and Properties of Matter Jeopardy
... In group 1, the first column on the left In period 1, the first row across the top In group 13 through 16 near the right In periods 6 and 7 at the bottom ...
... In group 1, the first column on the left In period 1, the first row across the top In group 13 through 16 near the right In periods 6 and 7 at the bottom ...
FREE Sample Here
... D) hydrophobic interactions Answer: C Bloom's Taxonomy: Knowledge/Comprehension Section: 2.3 36) Van der Waals interactions may result when _____. A) electrons are not symmetrically distributed in a molecule B) molecules held by ionic bonds react with water C) two polar covalent bonds react D) a hyd ...
... D) hydrophobic interactions Answer: C Bloom's Taxonomy: Knowledge/Comprehension Section: 2.3 36) Van der Waals interactions may result when _____. A) electrons are not symmetrically distributed in a molecule B) molecules held by ionic bonds react with water C) two polar covalent bonds react D) a hyd ...
1 • Introduction The Scientific Method (1 of 20) 1
... 2•Stoichiometry: Chemical Arithmetic Writing Formula Equations Things To Remember (11 of 24) ...
... 2•Stoichiometry: Chemical Arithmetic Writing Formula Equations Things To Remember (11 of 24) ...
4.6 Oxidation-Reduction (Redox) Reactions Oxidation Reduction
... An atom in its elemental state has an oxidation number of ...
... An atom in its elemental state has an oxidation number of ...
Summaries of Review Topics for AP Chemistry
... made with a monatomic ion, use the prefix hydro + root + ic. Rule #2: Identify and name binary compounds (which consist of two elements only). ♦ The first element in the formula is named first using the name of the element (from the Periodic Table, PT) ♦ For the second element in the formula, use th ...
... made with a monatomic ion, use the prefix hydro + root + ic. Rule #2: Identify and name binary compounds (which consist of two elements only). ♦ The first element in the formula is named first using the name of the element (from the Periodic Table, PT) ♦ For the second element in the formula, use th ...
Document
... It will include questions on analysis and evaluation of practical work. Quality of written communication will also be assessed in this section. ...
... It will include questions on analysis and evaluation of practical work. Quality of written communication will also be assessed in this section. ...
Campbell Biology, 10e (Reece) Chapter 2 The Chemical Context of
... Bloom's Taxonomy: Application/Analysis Section: 2.2 6) In what way are elements in the same column of the periodic table the same? They have the same number of _____. A) protons B) electrons when neutral C) electrons in their valence shells when neutral D) electron shells when neutral Answer: C Bloo ...
... Bloom's Taxonomy: Application/Analysis Section: 2.2 6) In what way are elements in the same column of the periodic table the same? They have the same number of _____. A) protons B) electrons when neutral C) electrons in their valence shells when neutral D) electron shells when neutral Answer: C Bloo ...
CHAPTER-4 CHEMICAL BONDING AND
... (iii) High nuclear charge and small atomic size of the combining elements. POLAR COVALENT BOND: The bond between two unlike atoms which differ in their affinities for electrons is said to be polar covalent bond. E.g. H-Cl COORDINATE BOND: The bond formed when one sided sharing of electrons take plac ...
... (iii) High nuclear charge and small atomic size of the combining elements. POLAR COVALENT BOND: The bond between two unlike atoms which differ in their affinities for electrons is said to be polar covalent bond. E.g. H-Cl COORDINATE BOND: The bond formed when one sided sharing of electrons take plac ...
Electronegativity

Electronegativity, symbol χ, is a chemical property that describes the tendency of an atom or a functional group to attract electrons (or electron density) towards itself. An atom's electronegativity is affected by both its atomic number and the distance at which its valence electrons reside from the charged nucleus. The higher the associated electronegativity number, the more an element or compound attracts electrons towards it. The term ""electronegativity"" was introduced by Jöns Jacob Berzelius in 1811,though the concept was known even before that and was studied by many chemists including Avogadro.In spite of its long history, an accurate scale of electronegativity had to wait till 1932, when Linus Pauling proposed an electronegativity scale, which depends on bond energies, as a development of valence bond theory. It has been shown to correlate with a number of other chemical properties. Electronegativity cannot be directly measured and must be calculated from other atomic or molecular properties. Several methods of calculation have been proposed, and although there may be small differences in the numerical values of the electronegativity, all methods show the same periodic trends between elements. The most commonly used method of calculation is that originally proposed by Linus Pauling. This gives a dimensionless quantity, commonly referred to as the Pauling scale, on a relative scale running from around 0.7 to 3.98 (hydrogen = 2.20). When other methods of calculation are used, it is conventional (although not obligatory) to quote the results on a scale that covers the same range of numerical values: this is known as an electronegativity in Pauling units. As it is usually calculated, electronegativity is not a property of an atom alone, but rather a property of an atom in a molecule. Properties of a free atom include ionization energy and electron affinity. It is to be expected that the electronegativity of an element will vary with its chemical environment, but it is usually considered to be a transferable property, that is to say that similar values will be valid in a variety of situations.On the most basic level, electronegativity is determined by factors like the nuclear charge (the more protons an atom has, the more ""pull"" it will have on electrons) and the number/location of other electrons present in the atomic shells (the more electrons an atom has, the farther from the nucleus the valence electrons will be, and as a result the less positive charge they will experience—both because of their increased distance from the nucleus, and because the other electrons in the lower energy core orbitals will act to shield the valence electrons from the positively charged nucleus).The opposite of electronegativity is electropositivity: a measure of an element's ability to donate electrons.Caesium is the least electronegative element in the periodic table (=0.79), while fluorine is most electronegative (=3.98). (Francium and caesium were originally assigned both assigned 0.7; caesium's value was later refined to 0.79, but no experimental data allows a similar refinement for francium. However, francium's ionization energy is known to be slightly higher than caesium's, in accordance with the relativistic stabilization of the 7s orbital, and this in turn implies that caesium is in fact more electronegative than francium.)