ap quick review
... Metallic carbonates metal oxides + carbon dioxide Hydrolysis = compound reacting with water. Watch for soluble salts that contain anions of weak acid the anion is a conjugate base and cations of weak bases that are conjugate acids. Reactions of coordinate compounds and complex Complex format ...
... Metallic carbonates metal oxides + carbon dioxide Hydrolysis = compound reacting with water. Watch for soluble salts that contain anions of weak acid the anion is a conjugate base and cations of weak bases that are conjugate acids. Reactions of coordinate compounds and complex Complex format ...
Electron Configurations
... the electron cannot go up or down a partial energy level, and the more energy it has the higher the energy level it can be in. ...
... the electron cannot go up or down a partial energy level, and the more energy it has the higher the energy level it can be in. ...
Quantum Physics Part II Quantum Physics in three units Bright Line
... • A new quantum number was used. It was called the l quantum number or the azimuthal quantum number. • These were called subshells. • For any given quantum number n, the possible subshells range from l=0 to l=n-1 • Again, the angular momentum was determined by the value according to ...
... • A new quantum number was used. It was called the l quantum number or the azimuthal quantum number. • These were called subshells. • For any given quantum number n, the possible subshells range from l=0 to l=n-1 • Again, the angular momentum was determined by the value according to ...
orbital
... be any integer between 0 and n - 1. For n = 3, l can be either 0, 1, or 2. The magnetic quantum number (m) can be any integer between -l and +l. For l = 2, m can be either -2, -1, 0, +1, or ...
... be any integer between 0 and n - 1. For n = 3, l can be either 0, 1, or 2. The magnetic quantum number (m) can be any integer between -l and +l. For l = 2, m can be either -2, -1, 0, +1, or ...
Chemistry Mid-Term Review Sheet
... 13. What are the 5 signs that a chemical reaction has taken place? Chapter 3 14. Express the following number in scientific notation: a. 4380000 b. 0.000274 15. List the SI units for the following quantities: length, mass, temperature, time, amount of substance, luminous intensity, and electric curr ...
... 13. What are the 5 signs that a chemical reaction has taken place? Chapter 3 14. Express the following number in scientific notation: a. 4380000 b. 0.000274 15. List the SI units for the following quantities: length, mass, temperature, time, amount of substance, luminous intensity, and electric curr ...
CHEM1611 Worksheet 2: Atomic Accountancy Model 1
... Throughout history, the model of the atom and how/where the electrons exist and move has changed as our scientific knowledge has increased. The current model describes the motions of electrons using atomic orbitals. Orbitals gives us information about the probability of an electron being in a partic ...
... Throughout history, the model of the atom and how/where the electrons exist and move has changed as our scientific knowledge has increased. The current model describes the motions of electrons using atomic orbitals. Orbitals gives us information about the probability of an electron being in a partic ...
Document
... never involved in the bond as they are too close to their own nucleus. 2 He atoms will never form a bond because Energy of He2 > 2 He. ...
... never involved in the bond as they are too close to their own nucleus. 2 He atoms will never form a bond because Energy of He2 > 2 He. ...
Section 9: Forces, Potentials, and the Shell Model , and
... modifications of the Bohr atom picture that results in the periodic table. In contrast, for nuclei, strong pairing should be observed, since if both nucleons are in the same orbital, the attractive nuclear force is maximized. For this reason more compact orbitals should also be favored (i.e. l = 2 d ...
... modifications of the Bohr atom picture that results in the periodic table. In contrast, for nuclei, strong pairing should be observed, since if both nucleons are in the same orbital, the attractive nuclear force is maximized. For this reason more compact orbitals should also be favored (i.e. l = 2 d ...
Ionic Bonding
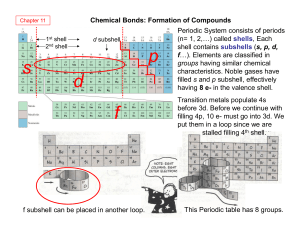
... eight electrons in their outer energy levels (or two in the case of helium). These noble gas structures are thought of as being in some way a "desirable" thing for an atom to have. You may well have been left with the strong impression that when other atoms react, they try to organize things such th ...
... eight electrons in their outer energy levels (or two in the case of helium). These noble gas structures are thought of as being in some way a "desirable" thing for an atom to have. You may well have been left with the strong impression that when other atoms react, they try to organize things such th ...
Lecture 17-PDF
... Here, we learnt that due to the orbital motion of the electron, the charge of the nucleus creates a magnetic field at the electron and this interacts with the spin of the electron. This interaction essentially couples the orbital and the spin angular momenta and the effect is the splitting of energy ...
... Here, we learnt that due to the orbital motion of the electron, the charge of the nucleus creates a magnetic field at the electron and this interacts with the spin of the electron. This interaction essentially couples the orbital and the spin angular momenta and the effect is the splitting of energy ...
Atomic Term Symbols and Energy Splitting
... The P0, P1, and P2 states are split in energy by a very small amount. This splitting is due to the coupling of spin angular momentum (S) with total orbital angular momentum (L). This spin-orbit coupling splits levels within the same term (that is, the same values of L and S) that have different valu ...
... The P0, P1, and P2 states are split in energy by a very small amount. This splitting is due to the coupling of spin angular momentum (S) with total orbital angular momentum (L). This spin-orbit coupling splits levels within the same term (that is, the same values of L and S) that have different valu ...
Identical Particles - Theory of Condensed Matter
... important physical implications. In particular, it determines the magnetic properties of atoms. The magnetic moment of the electron is aligned with its spin, and even though the spin variables do not appear in the Hamiltonian, the energy of the eigenstates depends on the relative spin orientation. T ...
... important physical implications. In particular, it determines the magnetic properties of atoms. The magnetic moment of the electron is aligned with its spin, and even though the spin variables do not appear in the Hamiltonian, the energy of the eigenstates depends on the relative spin orientation. T ...
Solution #3 - Temple University Department of Physics
... total angular momentum of the atom is F = J + I, where I is the nuclear spin. The eigenvalues of J 2 and F 2 are J(J + 1)~2 and F (F + 1)~2 respectively. a. What are the possible values of the quantum number J and F for a deuterium atom in the 1s ground state? In the 1s ground state of the deuterium ...
... total angular momentum of the atom is F = J + I, where I is the nuclear spin. The eigenvalues of J 2 and F 2 are J(J + 1)~2 and F (F + 1)~2 respectively. a. What are the possible values of the quantum number J and F for a deuterium atom in the 1s ground state? In the 1s ground state of the deuterium ...
rutherfords model
... states of hydrogen can also be used to describe (approximately) the allowed states of more complex atoms – This enables us to understand the periodic table • The hydrogen atom is an ideal system for performing precise comparisons of theory and experiment – Also for improving our understanding of ato ...
... states of hydrogen can also be used to describe (approximately) the allowed states of more complex atoms – This enables us to understand the periodic table • The hydrogen atom is an ideal system for performing precise comparisons of theory and experiment – Also for improving our understanding of ato ...
Chapter 2 - Chemistry
... acidic solutions when dissolved in water - name these solutions using the prefix hydro- and suffix ic with the stem name of the nonmetal, followed by the word acid - denote solution by formula of binary compound compound followed by (aq) aqueous (water ) solution ...
... acidic solutions when dissolved in water - name these solutions using the prefix hydro- and suffix ic with the stem name of the nonmetal, followed by the word acid - denote solution by formula of binary compound compound followed by (aq) aqueous (water ) solution ...
Chapter 2 power point
... For all ionic compounds, the name and formula lists the cation first and the anion second. In a binary ionic compound, both the cation and the anion are monatomic. The name of the cation is the same as the name of the metal. Many metal names end in -ium. The anion is named by adding the suffix -ide ...
... For all ionic compounds, the name and formula lists the cation first and the anion second. In a binary ionic compound, both the cation and the anion are monatomic. The name of the cation is the same as the name of the metal. Many metal names end in -ium. The anion is named by adding the suffix -ide ...