General Physics I - University of Rochester
... • Light bulb: current heats up atoms, they collide with each other and emit EM waves – light • Incoherent source of light – a continuous spectrum, isotropic in direction, no correlation in ...
... • Light bulb: current heats up atoms, they collide with each other and emit EM waves – light • Incoherent source of light – a continuous spectrum, isotropic in direction, no correlation in ...
Monday, Mar. 23, 2015
... Importance of Bohr’s Model • Demonstrated the need for Plank’s constant in understanding the atomic structure • Assumption of quantized angular momentum which led to quantization of other quantities, r, v and E as ...
... Importance of Bohr’s Model • Demonstrated the need for Plank’s constant in understanding the atomic structure • Assumption of quantized angular momentum which led to quantization of other quantities, r, v and E as ...
Know (main topic)
... divide, add, and subtract, very large and very small numbers. -describe the difference bet. the four states of matter. ...
... divide, add, and subtract, very large and very small numbers. -describe the difference bet. the four states of matter. ...
Final Review Answers
... a) Water evaporates faster at 40oC than at 20oC. More hydrogen bonds are breaking due to higher T. b) Propane (C3H8) boils at a lower temperature than water. Propane held together by weaker dispersion forces (NP). c) Oil is not soluble in water. Propane is nonpolar & is not attracted to polarity of ...
... a) Water evaporates faster at 40oC than at 20oC. More hydrogen bonds are breaking due to higher T. b) Propane (C3H8) boils at a lower temperature than water. Propane held together by weaker dispersion forces (NP). c) Oil is not soluble in water. Propane is nonpolar & is not attracted to polarity of ...
File
... Quantum Mechanical Model • Each orbital can contain two electrons. • Since negative-negative repel, these electrons occupy the orbital with opposite spins. ...
... Quantum Mechanical Model • Each orbital can contain two electrons. • Since negative-negative repel, these electrons occupy the orbital with opposite spins. ...
Chemistry A - Montgomery County Public Schools
... illustrate the structure of the atom by using the Bohr model, including the charge, relative mass and location of the sub-atomic particles. use atomic mass, atomic number, and charge to identify neutral atoms, ions, and isotopes. analyze the structure of the atom and describe the characteristi ...
... illustrate the structure of the atom by using the Bohr model, including the charge, relative mass and location of the sub-atomic particles. use atomic mass, atomic number, and charge to identify neutral atoms, ions, and isotopes. analyze the structure of the atom and describe the characteristi ...
Electron Configuration
... Use the last noble gas that is located in the periodic table right before the element. Write the symbol of the noble gas in brackets. Write the remaining configuration after the brackets. Ex: Fluorine: [He] 2s2 2p5 ...
... Use the last noble gas that is located in the periodic table right before the element. Write the symbol of the noble gas in brackets. Write the remaining configuration after the brackets. Ex: Fluorine: [He] 2s2 2p5 ...
Document
... ACT: CheckPoint 3.2 Suppose the charge of the nucleus is doubled (+2e), but the e– charge remains the same ( the e remains the same (–e). e). How does r How does r for the for the ground state (n = 1) orbit compare to that in hydrogen? n2 2 For hydrogen: rn = ...
... ACT: CheckPoint 3.2 Suppose the charge of the nucleus is doubled (+2e), but the e– charge remains the same ( the e remains the same (–e). e). How does r How does r for the for the ground state (n = 1) orbit compare to that in hydrogen? n2 2 For hydrogen: rn = ...
Quantum Disentanglement Eraser
... • ‘Clicks’ at D1 or D2 erase the which path information (Fringes!!) • absence or restoration of interference can be arranged via an appropriately contrived photon correlation experiment. ...
... • ‘Clicks’ at D1 or D2 erase the which path information (Fringes!!) • absence or restoration of interference can be arranged via an appropriately contrived photon correlation experiment. ...
P202 Lecture 2
... Potential Barrier: Alpha Decay Alpha decay in radioactivity The narrow “squarish” well is provided by the STRONG force, but once the a particle gets far enough away from the other nucleons, it feels the Coulomb repulsion. The a particle ‘leaks’ through the triangle-like barrier. The energy level (ab ...
... Potential Barrier: Alpha Decay Alpha decay in radioactivity The narrow “squarish” well is provided by the STRONG force, but once the a particle gets far enough away from the other nucleons, it feels the Coulomb repulsion. The a particle ‘leaks’ through the triangle-like barrier. The energy level (ab ...
Chapter 5 Electrons in Atoms - Lakeland Regional High School
... A quantum is the amount of energy needed to move from one energy level to another. Since the energy of an atom is never “in between” there must be a quantum leap in energy. ...
... A quantum is the amount of energy needed to move from one energy level to another. Since the energy of an atom is never “in between” there must be a quantum leap in energy. ...
Unit 9 The p-Block Elements
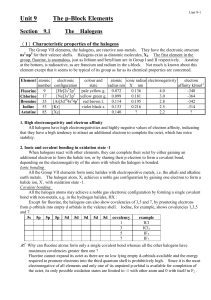
... Electron affinity decreases numerically with increasing atomic number. This is because the outer electrons become more shielded from the nucleus as the atomic size increases, so the tendency to attract another electron decreases as the group is descended. (d) Suggest a reason why the electron affini ...
... Electron affinity decreases numerically with increasing atomic number. This is because the outer electrons become more shielded from the nucleus as the atomic size increases, so the tendency to attract another electron decreases as the group is descended. (d) Suggest a reason why the electron affini ...
Document
... Like sound waves described by Newtonian mechanics, or electromagnetic waves by Maxwell’s equation, matter waves are described by an equation called Schrödinger’s equation (1926) ...
... Like sound waves described by Newtonian mechanics, or electromagnetic waves by Maxwell’s equation, matter waves are described by an equation called Schrödinger’s equation (1926) ...
Chapter 5 Mendeleev`s Periodic Table
... • When a particular element is heated and the light emitted is focused and passed through a prism, the resulting breakdown results in a non-continuous spectrum or a discrete line spectrum • This spectrum is called the element’s atomic spectrum • The discrete lines indicate a light is emitted or abso ...
... • When a particular element is heated and the light emitted is focused and passed through a prism, the resulting breakdown results in a non-continuous spectrum or a discrete line spectrum • This spectrum is called the element’s atomic spectrum • The discrete lines indicate a light is emitted or abso ...
Atomic structure
... potential V(r). The spin-orbit term is due to magnetic interaction. The spin-spin term describes the Pauli exclusion principal and has no classical interpretation. To determine the perturbed eigenfunctions, one needs to know whether all the above terms are of the same order, or not. In most cases, t ...
... potential V(r). The spin-orbit term is due to magnetic interaction. The spin-spin term describes the Pauli exclusion principal and has no classical interpretation. To determine the perturbed eigenfunctions, one needs to know whether all the above terms are of the same order, or not. In most cases, t ...
Unit 7 Chemical Composition: he Mole We Need to Count atoms
... 2. A certain sample of calcium carbonate contains 4.86 mol. What is the mass in grams of this sample? ...
... 2. A certain sample of calcium carbonate contains 4.86 mol. What is the mass in grams of this sample? ...