QUANTUM NUMBERS
... For an electron in an atom with l=0 is said to be in an s state. For an electron in an atom with l=1 is said to be in an p state. For an electron in an atom with l=2 is said to be in an d state. For an electron in an atom with l=3 is said to be in an e state. ...
... For an electron in an atom with l=0 is said to be in an s state. For an electron in an atom with l=1 is said to be in an p state. For an electron in an atom with l=2 is said to be in an d state. For an electron in an atom with l=3 is said to be in an e state. ...
The Current Model of the Atom Name This Element Building on Bohr
... these orbitals and the electrons within them • This information provides the basis for our understanding of bonding ...
... these orbitals and the electrons within them • This information provides the basis for our understanding of bonding ...
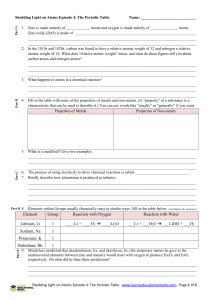
Element Group Reaction with Oxygen Reaction with Water Lithium
... 1. Zinc is made entirely of ____________ atoms and oxygen is made entirely of ______________ atoms. Zinc oxide (ZnO) is made of ______________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________________ ______________________ ...
... 1. Zinc is made entirely of ____________ atoms and oxygen is made entirely of ______________ atoms. Zinc oxide (ZnO) is made of ______________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________________ ______________________ ...
Ch. 8 Sections 8.1-8.3 Powerpoint
... •Any diatomic (two-atom) molecule that has a polar bond will show a molecular dipole moment. •In other words, if there is a difference in electronegativity between the two atoms the molecule is polar. ...
... •Any diatomic (two-atom) molecule that has a polar bond will show a molecular dipole moment. •In other words, if there is a difference in electronegativity between the two atoms the molecule is polar. ...
Example 27-1
... Bohr Model of the Atom •Niels Bohr was a Danish physicist who studied at the Rutherford lab. He decided to try to add the quantum effects of Planck and Einstein to the Rutherford planetary model of the atom ...
... Bohr Model of the Atom •Niels Bohr was a Danish physicist who studied at the Rutherford lab. He decided to try to add the quantum effects of Planck and Einstein to the Rutherford planetary model of the atom ...
quantum mechanical model
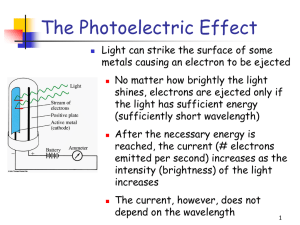
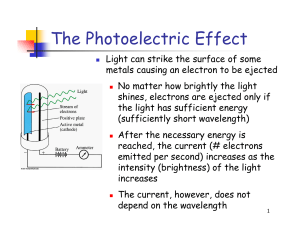
... Revising the Atomic Model • Rutherford’s atomic model could not explain the chemical properties of elements. • For example, why does iron first glow dull red, then yellow, then white when heated to higher and higher temperatures? ...
... Revising the Atomic Model • Rutherford’s atomic model could not explain the chemical properties of elements. • For example, why does iron first glow dull red, then yellow, then white when heated to higher and higher temperatures? ...
AP Semester I Review: Free Response Questions
... Calculate the number of Ne-22 atoms in a 12.55 g sample of naturally occurring neon. ...
... Calculate the number of Ne-22 atoms in a 12.55 g sample of naturally occurring neon. ...
Charged Particle Interactions with Matter: R Z M
... the incident particle needs to have more kinetic energy than this: T > mc 2α 2 . This implies that only about 53 keV is needed for the incident particle in this treatment. Other generalization beyond these assumptions will also be possible. Note we are using slightly different notations: T and m and ...
... the incident particle needs to have more kinetic energy than this: T > mc 2α 2 . This implies that only about 53 keV is needed for the incident particle in this treatment. Other generalization beyond these assumptions will also be possible. Note we are using slightly different notations: T and m and ...
Notes matter energy
... On the Periodic Table of the Elements (See Week 1 handout), gaseous elements have symbols with an italic font, liquid elements have symbols with an outline font, and solids have symbols with a Times-Roman font. The Law of Definite Composition states that compounds always contain the same proportions ...
... On the Periodic Table of the Elements (See Week 1 handout), gaseous elements have symbols with an italic font, liquid elements have symbols with an outline font, and solids have symbols with a Times-Roman font. The Law of Definite Composition states that compounds always contain the same proportions ...
Science-M2-Basic-Che..
... they correctly understand and answering any questions that come up. Having them answer each other’s questions is a great confidence builder, as they see that they have the skills to help each other. Finally, have each group come up to the board and lead the class through the process. Using the perio ...
... they correctly understand and answering any questions that come up. Having them answer each other’s questions is a great confidence builder, as they see that they have the skills to help each other. Finally, have each group come up to the board and lead the class through the process. Using the perio ...
Chemistry - Unit 6 What do you need to know?? This chapter is on
... Atoms are indestructible and unchangeable, so compounds, such as water and mercury calx, are formed when one atom chemically combines with other atoms. This was an extremely advanced concept for its time; while Dalton’s theory implied that atoms bonded together, it would be more than 100 years befor ...
... Atoms are indestructible and unchangeable, so compounds, such as water and mercury calx, are formed when one atom chemically combines with other atoms. This was an extremely advanced concept for its time; while Dalton’s theory implied that atoms bonded together, it would be more than 100 years befor ...
Chapter7 - FSU Chemistry
... (a) Balance this reaction and calculate !Hocomb for 1 mol of octane, assuming water forms as a gas; !Hof = -208.45 kJ/mol for octane !Hof = -393.5 kJ/mol for carbon dioxide !Hof = -241.8 kJ/mol for H2O (g) (b) How many liters of CO2 (at 25 oC and 1 atm, R = 0.0821 atm.L/mol.K) are formed when 1 kg o ...
... (a) Balance this reaction and calculate !Hocomb for 1 mol of octane, assuming water forms as a gas; !Hof = -208.45 kJ/mol for octane !Hof = -393.5 kJ/mol for carbon dioxide !Hof = -241.8 kJ/mol for H2O (g) (b) How many liters of CO2 (at 25 oC and 1 atm, R = 0.0821 atm.L/mol.K) are formed when 1 kg o ...
Lewis
... To understand the formation and structure of molecular compounds, first one has to learn, recognize, use, count, take into account: • the periodic table with groups and periods, • the number of electrons and valence electrons (i.e. count electrons), (2 (K), 8 (L) = 2 + 6, 18 (M) = 2 + 6 + 10, 32 (N) ...
... To understand the formation and structure of molecular compounds, first one has to learn, recognize, use, count, take into account: • the periodic table with groups and periods, • the number of electrons and valence electrons (i.e. count electrons), (2 (K), 8 (L) = 2 + 6, 18 (M) = 2 + 6 + 10, 32 (N) ...