11MONEY, INTEREST, REAL GDP, AND THE PRICE LEVEL*
... 19) In the above figure, suppose the economy is initially on the demand for money curve MD1. What is the effect of an increase in financial innovation such as the introduction of ATMs? A) The demand for money curve would shift rightward to MD2. B) The demand for money curve would shift leftward to M ...
... 19) In the above figure, suppose the economy is initially on the demand for money curve MD1. What is the effect of an increase in financial innovation such as the introduction of ATMs? A) The demand for money curve would shift rightward to MD2. B) The demand for money curve would shift leftward to M ...
Canada Deposit Insurance Corporation
... mandate, enacted in 1987, kept CDIC’s earlier role as paying agent and “work out” agent—overseeing the liquidation and other forms of closing down failed institutions—but added the responsibility of assessing and managing the risks it insured and minimizing its exposure to loss. This mandate was rec ...
... mandate, enacted in 1987, kept CDIC’s earlier role as paying agent and “work out” agent—overseeing the liquidation and other forms of closing down failed institutions—but added the responsibility of assessing and managing the risks it insured and minimizing its exposure to loss. This mandate was rec ...
abuse of structured financial products
... unspecified basket of assets placed in a designated account. The referenced account was opened in the name of the bank and operated as the bank’s own proprietary trading account. All assets were purchased in the name of the bank. To reduce trading risk, the option contract normally set a few basic p ...
... unspecified basket of assets placed in a designated account. The referenced account was opened in the name of the bank and operated as the bank’s own proprietary trading account. All assets were purchased in the name of the bank. To reduce trading risk, the option contract normally set a few basic p ...
IFRS - PwC
... Question A1 – Assessing power when different investors control activities in different periods ....................................................................................................... 5 Question A2 – Re-assessment of power .............................................................. ...
... Question A1 – Assessing power when different investors control activities in different periods ....................................................................................................... 5 Question A2 – Re-assessment of power .............................................................. ...
The Monetarist-Keynesian Debate and the Phillips Curve
... Speci…cally, the economist looks for event studies, that is, episodes in which he (she) has some information particular to the time period about the nature of causation. Because of the impossibility of controlling for extraneous forces in particular episodes, the ideal is one where metastudies gener ...
... Speci…cally, the economist looks for event studies, that is, episodes in which he (she) has some information particular to the time period about the nature of causation. Because of the impossibility of controlling for extraneous forces in particular episodes, the ideal is one where metastudies gener ...
Impact of Monetary Policy on Indian Economy in the Post
... Let me thank all of them at the very outset, with great gratitude and sincere heart. No few words can express my profound gratitude and indebtedness to my supervising guide, Dr. K.C. Sankaranarayanan, former Professor and Head of the Department, Department of Applied Economics and former Dean of Fac ...
... Let me thank all of them at the very outset, with great gratitude and sincere heart. No few words can express my profound gratitude and indebtedness to my supervising guide, Dr. K.C. Sankaranarayanan, former Professor and Head of the Department, Department of Applied Economics and former Dean of Fac ...
Business Integrated Account Terms and Conditions
... within each Account Status or sub-category under an Account Status at any time and from time to time. 2.03 Each Account Status may have a set of criteria and/or conditions that the Customer has to fulfill so as to maintain its Integrated Account in that Account Status and/or to enjoy the Services, ...
... within each Account Status or sub-category under an Account Status at any time and from time to time. 2.03 Each Account Status may have a set of criteria and/or conditions that the Customer has to fulfill so as to maintain its Integrated Account in that Account Status and/or to enjoy the Services, ...
annual report 2015 - RHB Banking Group
... focus towards achieving its vision of being a leading multinational financial services group. The wire links further symbolise our commitment to fostering greater ties with our customers and key stakeholders by placing them at the centre of what we do, as described by our revitalised Brand Promise, ...
... focus towards achieving its vision of being a leading multinational financial services group. The wire links further symbolise our commitment to fostering greater ties with our customers and key stakeholders by placing them at the centre of what we do, as described by our revitalised Brand Promise, ...
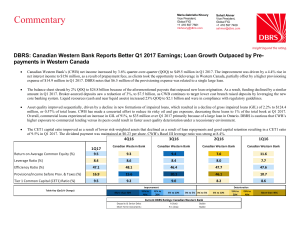
Canadian Western Bank Reports Better Q1 2017
... million, or 0.57% of total loans. CWB has made a concerted effort to reduce its risky oil and gas exposure, decreasing these loans to 1% of the total book at Q1 2017. Overall, commercial loans experienced an increase in GIL of 91%, to $35 million over Q1 2017 primarily because of a large loan in Ont ...
... million, or 0.57% of total loans. CWB has made a concerted effort to reduce its risky oil and gas exposure, decreasing these loans to 1% of the total book at Q1 2017. Overall, commercial loans experienced an increase in GIL of 91%, to $35 million over Q1 2017 primarily because of a large loan in Ont ...
Macroeconomics, 10e, Global Edition (Parkin) Chapter 25 Money
... Question history: Previous edition, Chapter 8 AACSB: Reflective Thinking 25) Suppose prices are quoted in dollars and transactions are conducted in pesos. The peso serves as a A) medium of exchange. B) store of value. C) unit of account. D) all of the above Answer: A Topic: Medium of Exchange Skill: ...
... Question history: Previous edition, Chapter 8 AACSB: Reflective Thinking 25) Suppose prices are quoted in dollars and transactions are conducted in pesos. The peso serves as a A) medium of exchange. B) store of value. C) unit of account. D) all of the above Answer: A Topic: Medium of Exchange Skill: ...
Risk and Capital Management
... The Group Supervisory Board lays down the general principles for risk and capital management as well as for the Group's risk profile, and implements these in the Group by adopting a number of risk policies and instructions. Together with the Group Executive Board, the Group Supervisory Board is resp ...
... The Group Supervisory Board lays down the general principles for risk and capital management as well as for the Group's risk profile, and implements these in the Group by adopting a number of risk policies and instructions. Together with the Group Executive Board, the Group Supervisory Board is resp ...
A Microfoundation of Monetary Economics
... son (1958). Lucas’ (1972) pioneering work on the neutrality of money stirred interest in this model for macroeconomists. Although Lucas focused on the positive implications of the model, he did specify the physical environment explicitly to support a role of money. The main friction in the overlapp ...
... son (1958). Lucas’ (1972) pioneering work on the neutrality of money stirred interest in this model for macroeconomists. Although Lucas focused on the positive implications of the model, he did specify the physical environment explicitly to support a role of money. The main friction in the overlapp ...
3 National Income: Where It Comes
... One goal of this chapter is to determine how the money supply affects the economy; we turn to that problem in the next section.As background for that analysis, let’s first discuss how economists measure the quantity of money. Because money is the stock of assets used for transactions, the quantity o ...
... One goal of this chapter is to determine how the money supply affects the economy; we turn to that problem in the next section.As background for that analysis, let’s first discuss how economists measure the quantity of money. Because money is the stock of assets used for transactions, the quantity o ...
The optimal quantity of money over the business cycle and at the
... To study these questions, this paper …rst presents a simple general equilibrium model to derive formal proof. Then, it provides a quantitative framework to study optimal monetary policy with heterogeneous agents and aggregate shocks. Analyzing the simple model, one …rst …nds that the distortions gen ...
... To study these questions, this paper …rst presents a simple general equilibrium model to derive formal proof. Then, it provides a quantitative framework to study optimal monetary policy with heterogeneous agents and aggregate shocks. Analyzing the simple model, one …rst …nds that the distortions gen ...
CONTENTS - National Bank of Pakistan
... interest income by Rs. 1,671 million (13%) through growth in the loan portfolio which increased by Rs. 60 billion (37%). The growth was across all sectors, in particular the high yielding consumer and retail banking sector. Interest rates started to climb up in the latter half of 2004, however, the ...
... interest income by Rs. 1,671 million (13%) through growth in the loan portfolio which increased by Rs. 60 billion (37%). The growth was across all sectors, in particular the high yielding consumer and retail banking sector. Interest rates started to climb up in the latter half of 2004, however, the ...
TIME SERIES ANALYSIS OF DEMAND FOR MONEY IN
... which, in tum, is governed by three motives for holding money: the transactions motive, the speculativemotive and the prewtionary motive. Keynesian theory recognizes the firnction of money not only as a medium of exchange but also as a store of value. The transactions demand for money ,which consume ...
... which, in tum, is governed by three motives for holding money: the transactions motive, the speculativemotive and the prewtionary motive. Keynesian theory recognizes the firnction of money not only as a medium of exchange but also as a store of value. The transactions demand for money ,which consume ...
MONETARY THEORY AND POLICY
... demonstrate that you have read and researched more widely than the required minimum. You should use other references to have a broad viewpoint of the subject and also to give you a deeper understanding of the subject. When you have completed each assignment, send it, together with a TMA form, to you ...
... demonstrate that you have read and researched more widely than the required minimum. You should use other references to have a broad viewpoint of the subject and also to give you a deeper understanding of the subject. When you have completed each assignment, send it, together with a TMA form, to you ...
Money and Inflation
... What is Money? Definition: the stock of assets that can be readily used to make transaction The functions of money The types of money How the quantity of money is measured How the quantity of money is controlled Delegated to a partially independent institution ...
... What is Money? Definition: the stock of assets that can be readily used to make transaction The functions of money The types of money How the quantity of money is measured How the quantity of money is controlled Delegated to a partially independent institution ...
Report of Bank Pekao SA Group for the three quarters of
... corporate loans and non-quoted securities. Such increase in lending was financed by higher volumes of retail deposits growing 11.6% year on year. The solid liquidity structure of Bank Pekao S.A. Group is reflected by net loans to deposits ratio at 94.6% as at the end of September 2016. This, togethe ...
... corporate loans and non-quoted securities. Such increase in lending was financed by higher volumes of retail deposits growing 11.6% year on year. The solid liquidity structure of Bank Pekao S.A. Group is reflected by net loans to deposits ratio at 94.6% as at the end of September 2016. This, togethe ...
ING PP Example Reference 16x9
... • We continued to invest in business growth in Industry Lending, Retail Germany and other Retail Challengers & Growth Markets • Expenses in Retail Netherlands and Retail Belgium excluding regulatory costs have remained roughly flat • 1Q15 included a release from a legal provision • The first quarter ...
... • We continued to invest in business growth in Industry Lending, Retail Germany and other Retail Challengers & Growth Markets • Expenses in Retail Netherlands and Retail Belgium excluding regulatory costs have remained roughly flat • 1Q15 included a release from a legal provision • The first quarter ...
Money Laundering Using New Payment Methods
... 2006 has been accompanied by an increase in the number of detected cases where such payment systems were misused for ML/TF purposes. The NPM report in 2006 identified potential legitimate and illegitimate uses for the various NPMs but there was little evidence to support this. The current report wil ...
... 2006 has been accompanied by an increase in the number of detected cases where such payment systems were misused for ML/TF purposes. The NPM report in 2006 identified potential legitimate and illegitimate uses for the various NPMs but there was little evidence to support this. The current report wil ...
BANCOLOMBIA SA
... the U.S. Private Securities Litigation Reform Act of 1995. These forward-looking statements are not based on historical facts but instead represent only the Bank’s belief regarding future events, many of which, by their nature, are inherently uncertain and outside the Bank’s control. The words “anti ...
... the U.S. Private Securities Litigation Reform Act of 1995. These forward-looking statements are not based on historical facts but instead represent only the Bank’s belief regarding future events, many of which, by their nature, are inherently uncertain and outside the Bank’s control. The words “anti ...
NBER WORKING PAPER SERIES ON THE ORIGINS OF "A MONETARY HISTORY"
... diffuse widely through the economy, automatically produced forces – falling profits resulting from the pressure of costs on prices and tensions in the money market – that inevitably produced a contraction. The contraction, which would also diffuse widely, then produced changes in relative prices, su ...
... diffuse widely through the economy, automatically produced forces – falling profits resulting from the pressure of costs on prices and tensions in the money market – that inevitably produced a contraction. The contraction, which would also diffuse widely, then produced changes in relative prices, su ...