Veljko A. Vujicic PREPRINCIPLES OF MECHANICS
... small distances between the adjoining points; even so, only under the conditions that the backgrounds against which the distances are being observed are not degenerative. The positions of two bodies, no matter how small particles they can happen to be, cannot coincide; instead, their distance must b ...
... small distances between the adjoining points; even so, only under the conditions that the backgrounds against which the distances are being observed are not degenerative. The positions of two bodies, no matter how small particles they can happen to be, cannot coincide; instead, their distance must b ...
UNIT - I Review of the three laws of motion and vector algebra In this
... In this course on Engineering Mechanics, we shall be learning about mechanical interaction between bodies. That is we will learn how different bodies apply forces on one another and how they then balance to keep each other in equilibrium. That will be done in the first part of the course. So in the ...
... In this course on Engineering Mechanics, we shall be learning about mechanical interaction between bodies. That is we will learn how different bodies apply forces on one another and how they then balance to keep each other in equilibrium. That will be done in the first part of the course. So in the ...
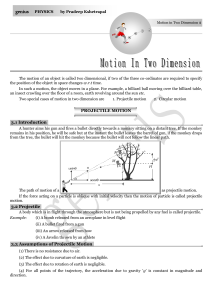
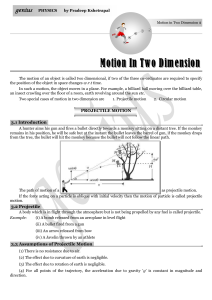
Motion In Two Dimension
... the position of the object in space changes w.r.t time. In such a motion, the object moves in a plane. For example, a billiard ball moving over the billiard table, an insect crawling over the floor of a room, earth revolving around the sun etc. Two special cases of motion in two dimension are 1. Pro ...
... the position of the object in space changes w.r.t time. In such a motion, the object moves in a plane. For example, a billiard ball moving over the billiard table, an insect crawling over the floor of a room, earth revolving around the sun etc. Two special cases of motion in two dimension are 1. Pro ...
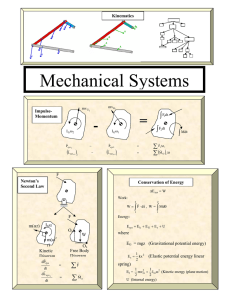
Impulse and Linear Momentum - Pearson-Global
... knock bowling pins down with a bowling ball, a similar transfer occurs. However, motion is not a physical quantity. What physical quantities describing motion are constant in an isolated system? Can we describe the changes in these quantities using a bar chart? Let’s conduct a few experiments to fin ...
... knock bowling pins down with a bowling ball, a similar transfer occurs. However, motion is not a physical quantity. What physical quantities describing motion are constant in an isolated system? Can we describe the changes in these quantities using a bar chart? Let’s conduct a few experiments to fin ...
Chapter 5: Conservation of Linear momentum
... entering/leaving the system would account for the change in the mass of the system. This is what makes mass a conserved quantity. To understand this idea better, think of an analogy. The system of interest will be the money in your pocket. When you go to a supermarket to buy groceries, the money in ...
... entering/leaving the system would account for the change in the mass of the system. This is what makes mass a conserved quantity. To understand this idea better, think of an analogy. The system of interest will be the money in your pocket. When you go to a supermarket to buy groceries, the money in ...
Module 2 UNDERSTANDING MOTION 2
... around. The speed (or the magnitude of the velocity) of the merry-go-round will be constant but the velocity will be changing because of the changing direction, so therefore there is an acceleration. (As long as one component is changing, be it the magnitude or the direction of the velocity.) Suppos ...
... around. The speed (or the magnitude of the velocity) of the merry-go-round will be constant but the velocity will be changing because of the changing direction, so therefore there is an acceleration. (As long as one component is changing, be it the magnitude or the direction of the velocity.) Suppos ...
Motion, Forces, and Energy in More Than One Dimension
... in the vertical component of velocity. So if there is no horizontal motion to start with, gravity can’t produce any. But suppose the object is moving with some initial horizontal component of velocity; what does gravity do then? It can only change the vertical component of velocity, so the horizonta ...
... in the vertical component of velocity. So if there is no horizontal motion to start with, gravity can’t produce any. But suppose the object is moving with some initial horizontal component of velocity; what does gravity do then? It can only change the vertical component of velocity, so the horizonta ...