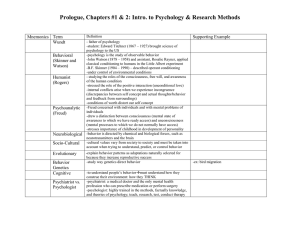
Psychologists and Their Contributions
... Alfred Binet: general I.Q. tests. A Frenchman designed a test that would identify slow learners in need of remedial help. It was not that valuable in America as it was too culture bound. Lewis Terman: Revised Binet’s I.Q. test and established norms for American children David Weschler: he establishe ...
... Alfred Binet: general I.Q. tests. A Frenchman designed a test that would identify slow learners in need of remedial help. It was not that valuable in America as it was too culture bound. Lewis Terman: Revised Binet’s I.Q. test and established norms for American children David Weschler: he establishe ...
1 - CBSD.org
... H0: 2 – 1 = 0, Ha: 2 – 1 0 Based on our data, the value of the two-sample t is A) 14.60 B) 7.80 C) 3.43 D) 2.54 25. Referring to the information above, suppose we wished to determine if there tended to be a difference in height for the seedlings treated with the different herbicides. To answer ...
... H0: 2 – 1 = 0, Ha: 2 – 1 0 Based on our data, the value of the two-sample t is A) 14.60 B) 7.80 C) 3.43 D) 2.54 25. Referring to the information above, suppose we wished to determine if there tended to be a difference in height for the seedlings treated with the different herbicides. To answer ...
Test 10A - Princeton High School
... (c) Describe a Type II error in the context of this problem. Give two ways to reduce the probability of a Type II error. ...
... (c) Describe a Type II error in the context of this problem. Give two ways to reduce the probability of a Type II error. ...
A First Look at Empirical Testing: Creating a Valid Research Design
... and a control group. These two groups are designed identically except for the treatment. Thus, if the experiment between the two groups yields different outcomes, then that difference can be attributed to the treatment. ...
... and a control group. These two groups are designed identically except for the treatment. Thus, if the experiment between the two groups yields different outcomes, then that difference can be attributed to the treatment. ...
Statistical hypothesis testing – Inferential statistics I.
... • Hypothesis testing (or significance test): a procedure of assessing whether sample data is consistent with statements (hypotheses) made about the statistical population. Briefly, we make a decision about the hypothesis on the basis of our sample data. We want to get answers to questions starting t ...
... • Hypothesis testing (or significance test): a procedure of assessing whether sample data is consistent with statements (hypotheses) made about the statistical population. Briefly, we make a decision about the hypothesis on the basis of our sample data. We want to get answers to questions starting t ...
Hwk 3
... 1. A bowl contains seven marbles of which θ are red while the others are blue. In order to test the null hypothesis θ = 2 against the alternative θ = 4, two of the marbles are randomly drawn without replacement and the null is rejected if and only if both are red. Find the probabilities of Type I an ...
... 1. A bowl contains seven marbles of which θ are red while the others are blue. In order to test the null hypothesis θ = 2 against the alternative θ = 4, two of the marbles are randomly drawn without replacement and the null is rejected if and only if both are red. Find the probabilities of Type I an ...
department of - Faculty of Arts and Sciences - EMU
... another student’s paper or from another text without written acknowledgement is plagiarism. According to University’s bylaws cheating and plagiarism are serious offences resulting in a failure from exam or project and disciplinary action (which includes an official warning may appear in student’s tr ...
... another student’s paper or from another text without written acknowledgement is plagiarism. According to University’s bylaws cheating and plagiarism are serious offences resulting in a failure from exam or project and disciplinary action (which includes an official warning may appear in student’s tr ...
Trying to find critical value for test statistics of 2
... Conclusion: Since calculated value is more than critical value (2.69 > 1.703) we reject H0 and conclude that girls are smarter than boys. No. We cannot reject null hypothesis just if mean of boys are lower than the mean of girls. We should also consider variation in score. We have to calculate the t ...
... Conclusion: Since calculated value is more than critical value (2.69 > 1.703) we reject H0 and conclude that girls are smarter than boys. No. We cannot reject null hypothesis just if mean of boys are lower than the mean of girls. We should also consider variation in score. We have to calculate the t ...
Statistical Concepts for Disease Detectives Division C
... Z-test - compares sample and population means to determine if there is a significant difference. It requires a simple random sample from a population with a Normal distribution and where the mean is known. The Z-test is preferable when the sample number n is greater than 30. The Z value indicates th ...
... Z-test - compares sample and population means to determine if there is a significant difference. It requires a simple random sample from a population with a Normal distribution and where the mean is known. The Z-test is preferable when the sample number n is greater than 30. The Z value indicates th ...
Chemistry 6.2 - Conversions - Notes Teacher
... *Example: A scale may read a person’s weight as 135 lbs. Another scale may read the person’s weight as 135.13 lbs. The ___________ second more significant figures in the scale is more precise. It also has ______ measurement. ...
... *Example: A scale may read a person’s weight as 135 lbs. Another scale may read the person’s weight as 135.13 lbs. The ___________ second more significant figures in the scale is more precise. It also has ______ measurement. ...
Review for Elementary Statistics Exam 1 Dr. Schultz 1. Consider the
... a. Find the probability of a wrong test result for a person who does not use marijuana. Is it “unusual” for the test result to be wrong for those not using marijuana? b. Find the probability of a wrong test result for a person who does use marijuana. Is it “unusual” for the test result to be wrong f ...
... a. Find the probability of a wrong test result for a person who does not use marijuana. Is it “unusual” for the test result to be wrong for those not using marijuana? b. Find the probability of a wrong test result for a person who does use marijuana. Is it “unusual” for the test result to be wrong f ...
The Class
... • Ivan Pavlov – salivating dog study – classical conditioning • John Watson – founded Behaviorism and “Little Albert” experiment • B. F. Skinner – operant conditioning (reinforcement and punishment) ...
... • Ivan Pavlov – salivating dog study – classical conditioning • John Watson – founded Behaviorism and “Little Albert” experiment • B. F. Skinner – operant conditioning (reinforcement and punishment) ...
Hypothesis testing
... • H1: Law school admission rates were higher for those participating in a pre-law advising program. • H0:There is no difference in law school admission rates between those who participate in an advising program and those who do not. • Note: This is a one-tailed hypothesis. One mean is higher than th ...
... • H1: Law school admission rates were higher for those participating in a pre-law advising program. • H0:There is no difference in law school admission rates between those who participate in an advising program and those who do not. • Note: This is a one-tailed hypothesis. One mean is higher than th ...