Random samples from two age groups of brides (200 brides under
... 16. The standard deviation of the sampling distribution for a sample mean depends on the value(s) of A. the sample size and the population standard deviation. B. the sample size but not the population standard deviation. C. the population standard deviation but not the sample size D. neither the sam ...
... 16. The standard deviation of the sampling distribution for a sample mean depends on the value(s) of A. the sample size and the population standard deviation. B. the sample size but not the population standard deviation. C. the population standard deviation but not the sample size D. neither the sam ...
x - Wiserd
... the next election, based on a national survey The mean earnings of African American males, based on a national survey The mean SAT score of applicants to the UW, based on a randomly drawn sample of 250 applications The average mpg of a production run of 10,000 autos of a particular make produced dur ...
... the next election, based on a national survey The mean earnings of African American males, based on a national survey The mean SAT score of applicants to the UW, based on a randomly drawn sample of 250 applications The average mpg of a production run of 10,000 autos of a particular make produced dur ...
Repeated Measures ANOVA
... For the paired t test, which estimates the population correlation with the sample correlation coefficient, we have Var(difference) Var(Yi1 Yi 2 ) 12 22 2 1 2 so we get to substract off something to provide a smaller variance, which in turn produces a smaller standard error, which i ...
... For the paired t test, which estimates the population correlation with the sample correlation coefficient, we have Var(difference) Var(Yi1 Yi 2 ) 12 22 2 1 2 so we get to substract off something to provide a smaller variance, which in turn produces a smaller standard error, which i ...
View document - The Open University
... probability calculations for the binomial distribution B(n, 1.25/n) did not differ significantly. (However, note that whatever the value of n, the mean of the distribution remains unaltered at p = n p = 1.25.) Similarly, in Example 4.2, the actual value of n, at least in the two particular cases exa ...
... probability calculations for the binomial distribution B(n, 1.25/n) did not differ significantly. (However, note that whatever the value of n, the mean of the distribution remains unaltered at p = n p = 1.25.) Similarly, in Example 4.2, the actual value of n, at least in the two particular cases exa ...
Estimating with Confidence
... Explain what is meant by margin of error. State in nontechnical language what is meant by a “level C confidence interval.” State the three conditions that need to be present in order to construct a valid confidence interval. List the four necessary steps in the creation of a confidence interval (see ...
... Explain what is meant by margin of error. State in nontechnical language what is meant by a “level C confidence interval.” State the three conditions that need to be present in order to construct a valid confidence interval. List the four necessary steps in the creation of a confidence interval (see ...
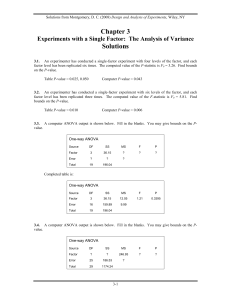
Chapter 3 Experiments with a Single Factor
... Critical value = 2.086 Intervals for (column level mean) - (row level mean) ...
... Critical value = 2.086 Intervals for (column level mean) - (row level mean) ...