lecture3
... However, the spread is more than that of the standard normal distribution. This is due to the fact that in formula 1, the denominator is s rather than sigma . Since s is a random quantity varying with various samples, the variability in t is more, resulting in a larger spread. The larger the degrees ...
... However, the spread is more than that of the standard normal distribution. This is due to the fact that in formula 1, the denominator is s rather than sigma . Since s is a random quantity varying with various samples, the variability in t is more, resulting in a larger spread. The larger the degrees ...
Document
... and we use the same “recipe” to construct confidence intervals. What is the real coverage probability? See meanCoverageOfConfidenceIntervals.R Answer: around 86%, lower than the 90% claimed. Doesn’t sound bad, but, the NON-coverage is 14% instead of 10%, which is 40% worse. The reason it’s off: ou ...
... and we use the same “recipe” to construct confidence intervals. What is the real coverage probability? See meanCoverageOfConfidenceIntervals.R Answer: around 86%, lower than the 90% claimed. Doesn’t sound bad, but, the NON-coverage is 14% instead of 10%, which is 40% worse. The reason it’s off: ou ...
chp12_section1_seta_answers
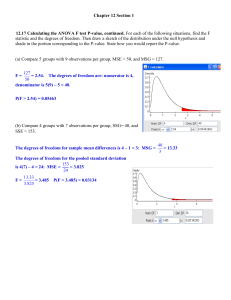
... As the means change in difference then the F –value starts to increase, which means that we are increasing the amount of evidence to support the alternative hypothesis that at least one of the means is different. We are trying to find if there is a difference in the means. If we continue to change t ...
... As the means change in difference then the F –value starts to increase, which means that we are increasing the amount of evidence to support the alternative hypothesis that at least one of the means is different. We are trying to find if there is a difference in the means. If we continue to change t ...
mean 2.3
... When reporting results obtained by replicate measurements the following quantities should be included: the number of observations, the arithmetic mean, the standard deviation, [or the range, see the comments to both terms], the confidence limits with the level of significance or confidence level, an ...
... When reporting results obtained by replicate measurements the following quantities should be included: the number of observations, the arithmetic mean, the standard deviation, [or the range, see the comments to both terms], the confidence limits with the level of significance or confidence level, an ...
Solution to MAS Applied exam May 2015
... There is no sufficient evidence to conclude that the newsletter’s strategy has a significantly higher winning odds than random selection given the available data at a 0.05 of significance. b. Type II error of this test is that one fails to conclude that the newsletter’s winning strategy is significant ...
... There is no sufficient evidence to conclude that the newsletter’s strategy has a significantly higher winning odds than random selection given the available data at a 0.05 of significance. b. Type II error of this test is that one fails to conclude that the newsletter’s winning strategy is significant ...
Lecture 8 - UCSB Department of Economics
... And taking the square root, the estimated standard deviation for b̂ is: 0.1268. V. Hypothesis Tests About the Slope Using the estimated CAPM as an example, the null hypothesis that the UC stock index fund does not depend on the market can be tested by the conjecture that the slope is zero, i.e. H0 : ...
... And taking the square root, the estimated standard deviation for b̂ is: 0.1268. V. Hypothesis Tests About the Slope Using the estimated CAPM as an example, the null hypothesis that the UC stock index fund does not depend on the market can be tested by the conjecture that the slope is zero, i.e. H0 : ...
Ex2_diane_F11 - Arizona State University
... e.) The formulas and tables are shown on the last page. You may take these pages off to help you during the exam f.) Part 1 of the exam is for free response. Show your work or explain the process for each problem to receive credit. g.) Part 2 is the multiple choice part of the exam. A table is given ...
... e.) The formulas and tables are shown on the last page. You may take these pages off to help you during the exam f.) Part 1 of the exam is for free response. Show your work or explain the process for each problem to receive credit. g.) Part 2 is the multiple choice part of the exam. A table is given ...
Test 2 SHORT ANSWER QUESTIONS Which hypothesis {Ho or Ha
... 23. In a right-hand tail the p-value is the area to the right of the test statistic. This is because this area represents the chance of getting stonger evidence against Ho, assuming Ho is _______. 24. In order to reject Ho, the p-value must be what compared to the significance level? 25. Which casts ...
... 23. In a right-hand tail the p-value is the area to the right of the test statistic. This is because this area represents the chance of getting stonger evidence against Ho, assuming Ho is _______. 24. In order to reject Ho, the p-value must be what compared to the significance level? 25. Which casts ...
PSYC60 Review
... Does statistics students eat less candy than that of other students here? (lower) ...
... Does statistics students eat less candy than that of other students here? (lower) ...
Review of basic concepts
... hypothesis that there is no difference. If the range in which the true mean for machine B lies does not overlap the range for machine A, the true mean of B lies outside the range and there is a significant difference between the two machines, i.e. we have 95% confidence that the means are different. ...
... hypothesis that there is no difference. If the range in which the true mean for machine B lies does not overlap the range for machine A, the true mean of B lies outside the range and there is a significant difference between the two machines, i.e. we have 95% confidence that the means are different. ...