Chapter 6 - More on confidence intervals
... C) There is not enough information to find the margin of error. D) 0.42 Find the necessary sample size. 12) Weights of women in one age group are normally distributed with a standard deviation s of 15 lb. A researcher wishes to estimate the mean weight of all women in this age group. Find how large ...
... C) There is not enough information to find the margin of error. D) 0.42 Find the necessary sample size. 12) Weights of women in one age group are normally distributed with a standard deviation s of 15 lb. A researcher wishes to estimate the mean weight of all women in this age group. Find how large ...
Study Guide
... scores by subtracting the lowest score in your distribution from the highest, and adding one (i.e., range = highest score - lowest score + 1). Then divide the range by a convenient class width (a multiple of 5, or a number less than 5, if appropriate), and round up if there is any fraction, to find ...
... scores by subtracting the lowest score in your distribution from the highest, and adding one (i.e., range = highest score - lowest score + 1). Then divide the range by a convenient class width (a multiple of 5, or a number less than 5, if appropriate), and round up if there is any fraction, to find ...
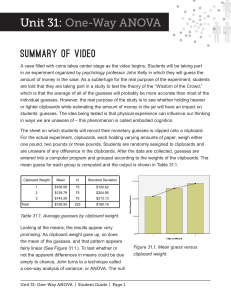
Unit 31: One
... jumping into running an ANOVA – there are some underlying assumptions that need to be checked in order for the results of the analysis to be valid. What 1. Each group’s data need to be an independent random sample from that we should ...
... jumping into running an ANOVA – there are some underlying assumptions that need to be checked in order for the results of the analysis to be valid. What 1. Each group’s data need to be an independent random sample from that we should ...
Chapter 12 iClicker Questions
... 1. A __________________ is a hypothesis test that includes two nominal independent variables and an interval dependent variable, and a __________________ is a statistical analysis used with one interval dependent variable and at least two nominal independent variables. a) factorial analysis of varia ...
... 1. A __________________ is a hypothesis test that includes two nominal independent variables and an interval dependent variable, and a __________________ is a statistical analysis used with one interval dependent variable and at least two nominal independent variables. a) factorial analysis of varia ...
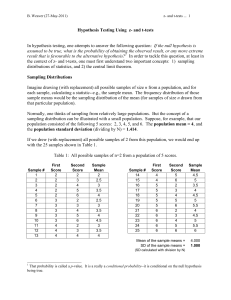
Hypothesis Testing Using z- and t-tests In hypothesis testing, one
... X < 100 or if X > 100 , provided the difference is large enough. Because differences in either direction can lead to rejection of H 0 , we must consider both tails of the standard normal distribution when calculating the p-value--i.e., the probability of the observed outcome, or a more extreme outco ...
... X < 100 or if X > 100 , provided the difference is large enough. Because differences in either direction can lead to rejection of H 0 , we must consider both tails of the standard normal distribution when calculating the p-value--i.e., the probability of the observed outcome, or a more extreme outco ...