Clicker_chapter20
... Margin of error (answer) Suppose you want to estimate the proportion of adults in Vermont (population 0.6 million) that approve of the new health care bill. You also want to estimate the proportion of adults in New York (population 19 million) that approve the new health care bill. To achieve the s ...
... Margin of error (answer) Suppose you want to estimate the proportion of adults in Vermont (population 0.6 million) that approve of the new health care bill. You also want to estimate the proportion of adults in New York (population 19 million) that approve the new health care bill. To achieve the s ...
iclicker_chapter_19
... Margin of error (answer) Suppose you want to estimate the proportion of adults in Vermont (population 0.6 million) that approve of the new health care bill. You also want to estimate the proportion of adults in New York (population 19 million) that approve the new health care bill. To achieve the s ...
... Margin of error (answer) Suppose you want to estimate the proportion of adults in Vermont (population 0.6 million) that approve of the new health care bill. You also want to estimate the proportion of adults in New York (population 19 million) that approve the new health care bill. To achieve the s ...
Worksheet 8 (Chapter 5): Confidence Intervals 1. File MPG.xlsx
... 3. A simple random sample of 100 customers were surveyed to determine the satisfaction with the updated version of the automatic teller machine at the bank. Of those surveyed 12 were unsatisfied with the updated machine. Use the appropriate methods to construct a 98% confidence interval for the popu ...
... 3. A simple random sample of 100 customers were surveyed to determine the satisfaction with the updated version of the automatic teller machine at the bank. Of those surveyed 12 were unsatisfied with the updated machine. Use the appropriate methods to construct a 98% confidence interval for the popu ...
sampling - AuroEnergy
... error, and represents the probability (i.e., the pre-selected significance level) of erroneously rejecting the null hypothesis. This is also called the “false negative” or “false alarm” rate. The flip side, i.e. concluding that the null hypothesis is true when in fact it is false, is called a Type I ...
... error, and represents the probability (i.e., the pre-selected significance level) of erroneously rejecting the null hypothesis. This is also called the “false negative” or “false alarm” rate. The flip side, i.e. concluding that the null hypothesis is true when in fact it is false, is called a Type I ...
Section 1
... • Confidence Interval – for an unknown parameter is an interval of numbers (that the unknown falls between) • Level of Confidence – represents the expected proportion of intervals that will contain the parameter if a large number of samples is obtained. The level of confidence is denoted by (1- α) * ...
... • Confidence Interval – for an unknown parameter is an interval of numbers (that the unknown falls between) • Level of Confidence – represents the expected proportion of intervals that will contain the parameter if a large number of samples is obtained. The level of confidence is denoted by (1- α) * ...
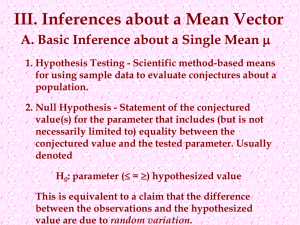
Inference about a Mean Vector
... 2. Null Hypothesis - Statement of the conjectured value(s) for the parameter that includes (but is not necessarily limited to) equality between the conjectured value and the tested parameter. Usually ...
... 2. Null Hypothesis - Statement of the conjectured value(s) for the parameter that includes (but is not necessarily limited to) equality between the conjectured value and the tested parameter. Usually ...