Point Estimation
... Ex. One wants to estimate population mean . Person A uses a sample of size 10, and person B uses a sample of size 100. Which estimate is better? Recall: If a continuous numerical variable X has mean and SD , the sampling variability (variance) of sample mean X is ...
... Ex. One wants to estimate population mean . Person A uses a sample of size 10, and person B uses a sample of size 100. Which estimate is better? Recall: If a continuous numerical variable X has mean and SD , the sampling variability (variance) of sample mean X is ...
(7) In the graph below, the solid line is the true population
... A. 568 B. 823 C. 895 D. 1150 9. What is the equation for the regression line predicting number of doctors from population for the South region? A. Doctors = -338 + 2.3 pop B. Doctors = -255 + 83 pop C. Doctors = -172 + 2.3 pop D. Doctors = -255 + 2.3 pop 10. Based on this model, in which region is t ...
... A. 568 B. 823 C. 895 D. 1150 9. What is the equation for the regression line predicting number of doctors from population for the South region? A. Doctors = -338 + 2.3 pop B. Doctors = -255 + 83 pop C. Doctors = -172 + 2.3 pop D. Doctors = -255 + 2.3 pop 10. Based on this model, in which region is t ...
Problem 2.21 last part of the table has the years mixed up. You can
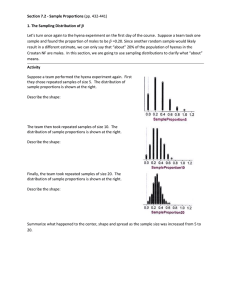
... 1. Which type of sampling must be used to select the samples used for constructing confidence intervals and performing hypothesis tests? 2. Which condition(s) needs to be checked to determine if A) a sampling distribution of sample proportions is approximately normally distributed? B) a sampling dis ...
... 1. Which type of sampling must be used to select the samples used for constructing confidence intervals and performing hypothesis tests? 2. Which condition(s) needs to be checked to determine if A) a sampling distribution of sample proportions is approximately normally distributed? B) a sampling dis ...
9.53 Sampling Distributions for Self study Suppose that we have two
... 9.53 Sampling Distributions for Self study Suppose that we have two normal populations with the means and standard deviations listed here. If random samples of size 25 are drawn from each population, what is the probability that the mean of sample 1 is greater than the mean of sample 2? Population 1 ...
... 9.53 Sampling Distributions for Self study Suppose that we have two normal populations with the means and standard deviations listed here. If random samples of size 25 are drawn from each population, what is the probability that the mean of sample 1 is greater than the mean of sample 2? Population 1 ...
If the data is shown to be statistically significant then the data
... variables. In order to determine that the patterns we observe are real, and not due to chance and our own preconceived notions, we must test the perceived pattern for significance. Statistical analysis allows scientists to test whether or not patterns are real, and not due to chance or preconceived ...
... variables. In order to determine that the patterns we observe are real, and not due to chance and our own preconceived notions, we must test the perceived pattern for significance. Statistical analysis allows scientists to test whether or not patterns are real, and not due to chance or preconceived ...
Chapter 1: Statistics
... 1. t is distributed with a mean of 0. 2. t is distributed symmetrically about its mean. 3. t is distributed so as to form a family of distributions, a separate distribution for each different number of degrees of freedom (df 1) 4. The t-distribution approaches the normal distribution as the number ...
... 1. t is distributed with a mean of 0. 2. t is distributed symmetrically about its mean. 3. t is distributed so as to form a family of distributions, a separate distribution for each different number of degrees of freedom (df 1) 4. The t-distribution approaches the normal distribution as the number ...