Sun, Stars, HR Diagram
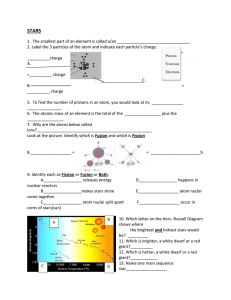
... 4. Approximately how many times larger is the diameter of the sun compared to the earth? A) 10 times C) 1000 times ...
... 4. Approximately how many times larger is the diameter of the sun compared to the earth? A) 10 times C) 1000 times ...
Introduction to Accretion Phenomena in Astrophysics
... star.This binary is 35 times brighter than the Sun. • Orbital period ~20 days. • There exist double-lined (SB2) and single-lined (SB1) spectroscopic binaries. • Famous SB1 - Cygnus X-1 System. ...
... star.This binary is 35 times brighter than the Sun. • Orbital period ~20 days. • There exist double-lined (SB2) and single-lined (SB1) spectroscopic binaries. • Famous SB1 - Cygnus X-1 System. ...
Life cycle of Stars Notes
... stars run out of fuel gravity quickly crushes the core. • The atmosphere is ripped apart by shock waves in a cataclysmic ...
... stars run out of fuel gravity quickly crushes the core. • The atmosphere is ripped apart by shock waves in a cataclysmic ...
Jupiter-Sized Star Smallest Ever Detected
... stars, caused by the regular transit of small orbiting objects (small stars, brown dwarfs or Jupiter-size planets). The OGLE team has since announced 177 "planetary transit candidates" from their survey of several hundred thousand stars in three southern sky fields, one in the direction of the Galac ...
... stars, caused by the regular transit of small orbiting objects (small stars, brown dwarfs or Jupiter-size planets). The OGLE team has since announced 177 "planetary transit candidates" from their survey of several hundred thousand stars in three southern sky fields, one in the direction of the Galac ...
t2 images part 1
... begins to crush the star. Stars die in spectacular fashion, either by expelling their outer layers or as huge super nova explosions. So much heat and energy is produced by these events that all of the heavier elements are formed. Large stars burn through their fuel faster. ...
... begins to crush the star. Stars die in spectacular fashion, either by expelling their outer layers or as huge super nova explosions. So much heat and energy is produced by these events that all of the heavier elements are formed. Large stars burn through their fuel faster. ...
WK10revisedoneweek
... 1. Each planet moves in an ellipse, with the sun at one focus. 2. The line between the sun and the planet sweeps out equal areas in equal times. 3. The ratio of the cube of the average radius of a planets orbit to the square of its orbital period of revolution is the same for each planet. (Harmonic ...
... 1. Each planet moves in an ellipse, with the sun at one focus. 2. The line between the sun and the planet sweeps out equal areas in equal times. 3. The ratio of the cube of the average radius of a planets orbit to the square of its orbital period of revolution is the same for each planet. (Harmonic ...
E5 stellar processes and stellar evolution (HL only)
... • The neutrons get too close to each other (this time it is “neutron degeneracy pressure” caused by neutrons not being allowed to occupy the same quantum state) and the entire core rebounds to a larger equilibrium size. • The causes a catastophic shock wave which explodes the star in a SUPERNOVA ...
... • The neutrons get too close to each other (this time it is “neutron degeneracy pressure” caused by neutrons not being allowed to occupy the same quantum state) and the entire core rebounds to a larger equilibrium size. • The causes a catastophic shock wave which explodes the star in a SUPERNOVA ...
Skymapper and Kepler K2: Finding the Origin of Hot Gas Giants
... Planet formation with migraiton where one set of initial conditions gives the solar system and another gives a solitary hot Jupiter. ...
... Planet formation with migraiton where one set of initial conditions gives the solar system and another gives a solitary hot Jupiter. ...
AST 207 Homework 5 Due 14 October 2011
... 2. Life on Deneb. Here you will find out what it means to live near a giant like Deneb. Recall that the luminosity of a star, where T is its temperature and R is its radius. Star ...
... 2. Life on Deneb. Here you will find out what it means to live near a giant like Deneb. Recall that the luminosity of a star, where T is its temperature and R is its radius. Star ...
Mon Jul 4, 2011 4TH OF JULY COSMIC FIREWORKS On the 4th of
... There’s been a pretty crescent moon in our evening skies this week; lots of folks noticed it during the 4 th of July fireworks a few days ago. The moon is waxing, and it’s now at first quarter, which looks like a half moon in the southern sky after sunset. Half moons and first quarter moons are the ...
... There’s been a pretty crescent moon in our evening skies this week; lots of folks noticed it during the 4 th of July fireworks a few days ago. The moon is waxing, and it’s now at first quarter, which looks like a half moon in the southern sky after sunset. Half moons and first quarter moons are the ...
Star Life Cycle
... When a star has burned between 10% and 20% of its hydrogen, its core will to run out of fuel. At this stage, the star is entering the end of its life. The diameter of the star can increase by a factor of 200, while its cooling is translated into a reddening of its radiation : the star is becoming wh ...
... When a star has burned between 10% and 20% of its hydrogen, its core will to run out of fuel. At this stage, the star is entering the end of its life. The diameter of the star can increase by a factor of 200, while its cooling is translated into a reddening of its radiation : the star is becoming wh ...
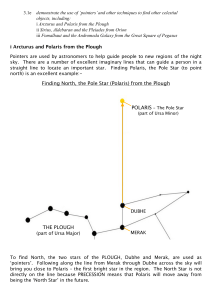
3.1e Finding Polaris and Sirius
... Star hopping is used to find the Andromeda Galaxy (M31). If you live where you have very dark skies, the Andromeda Galaxy is the furthest object that you can see with your naked eye – 2.4 million light years away! The galaxy appears as a small, white, fuzzy patch. When you have found the Great Squar ...
... Star hopping is used to find the Andromeda Galaxy (M31). If you live where you have very dark skies, the Andromeda Galaxy is the furthest object that you can see with your naked eye – 2.4 million light years away! The galaxy appears as a small, white, fuzzy patch. When you have found the Great Squar ...
CHAPTER 2 NOTES (STARS AND GALAXIES)
... Siruis (Dog Star)- middle sized star, which is the brightest star in the night sky Nova- a star that suddenly increases in brightness up to 100 times in just a few hours to days then grows dim again (maybe because of a companion star’s gases that strike its surface, causing explosions) ...
... Siruis (Dog Star)- middle sized star, which is the brightest star in the night sky Nova- a star that suddenly increases in brightness up to 100 times in just a few hours to days then grows dim again (maybe because of a companion star’s gases that strike its surface, causing explosions) ...
solutions
... The Hertzsprung-Russell diagram (usually referred to by the abbreviation HR diagram or a Color-Magnitude diagram abbreviated by CMD) shows the relationship between absolute magnitude, luminosity, classification, and effective temperature of stars. The diagram was proposed by Ejnar Hertzsprung and He ...
... The Hertzsprung-Russell diagram (usually referred to by the abbreviation HR diagram or a Color-Magnitude diagram abbreviated by CMD) shows the relationship between absolute magnitude, luminosity, classification, and effective temperature of stars. The diagram was proposed by Ejnar Hertzsprung and He ...
Chapter 21
... The sun is a medium-sized star. Stars that are much larger than the sun are called ______________ or __________________. Composition – The chemical composition of most stars is about 73 % ______________ and 25 % ____________________. How can astronomers infer which elements are found in stars? ___ ...
... The sun is a medium-sized star. Stars that are much larger than the sun are called ______________ or __________________. Composition – The chemical composition of most stars is about 73 % ______________ and 25 % ____________________. How can astronomers infer which elements are found in stars? ___ ...
Star Life Cycle Review 1. What is the first stage of star creation? A
... B. A star requires a continual supply of material from other stars in order to survive for long periods of time. C. ...
... B. A star requires a continual supply of material from other stars in order to survive for long periods of time. C. ...
Virtual Sky II (Rev 10/11)
... Give the two dates when the Sun is at the position where the path crosses itself. ___________ _________________ ...
... Give the two dates when the Sun is at the position where the path crosses itself. ___________ _________________ ...
Lyra

Lyra (/ˈlaɪərə/; Latin for lyre, from Greek λύρα) is a small constellation. It is one of 48 listed by the 2nd century astronomer Ptolemy, and is one of the 88 constellations recognized by the International Astronomical Union. Lyra was often represented on star maps as a vulture or an eagle carrying a lyre, and hence sometimes referred to as Aquila Cadens or Vultur Cadens. Beginning at the north, Lyra is bordered by Draco, Hercules, Vulpecula, and Cygnus. Lyra is visible from the northern hemisphere from spring through autumn, and nearly overhead, in temperate latitudes, during the summer months. From the southern hemisphere, it is visible low in the northern sky during the winter months.The lucida or brightest star—and one of the brightest stars in the sky—is the white main sequence star Vega, a corner of the Summer Triangle. Beta Lyrae is the prototype of a class of stars known as Beta Lyrae variables, binary stars so close to each other that they become egg-shaped and material flows from one to the other. Epsilon Lyrae, known informally as the Double Double, is a complex multiple star system. Lyra also hosts the Ring Nebula, the second-discovered and best-known planetary nebula.