The IC 348 surface density in the Perseus molecular cloud L. Cambrésy Observatoire de Strasbourg, France
... Embedded clusters toward the North America Nebula ...
... Embedded clusters toward the North America Nebula ...
The Sun's Crowded Delivery Room
... My after initial solar system formation, have no evidence for 60Fe (low ε60Ni) www.psrd.hawaii.edu/July07/iron-60.html ...
... My after initial solar system formation, have no evidence for 60Fe (low ε60Ni) www.psrd.hawaii.edu/July07/iron-60.html ...
17Nov_2014
... • a. a low mass red giant that varies in size and brightness in an irregular way • b. a big planet • c. a high-mass giant or supergiant star that pulsates regularly in size and brightness • d. a variable emission nebula near a young star ...
... • a. a low mass red giant that varies in size and brightness in an irregular way • b. a big planet • c. a high-mass giant or supergiant star that pulsates regularly in size and brightness • d. a variable emission nebula near a young star ...
Introduction - Willmann-Bell
... Argo Navis. What can we say about this sprawling and incredibly bountiful constellation? Dennis has deemed it our masterpiece, and truth be told, there was no shortage of celestial marvels to chronicle and illustrate. We think it safe to say (as much as modesty allows) that our review of the uncanny ...
... Argo Navis. What can we say about this sprawling and incredibly bountiful constellation? Dennis has deemed it our masterpiece, and truth be told, there was no shortage of celestial marvels to chronicle and illustrate. We think it safe to say (as much as modesty allows) that our review of the uncanny ...
Consider Average Stars
... A Special Scale Stars with numerically larger magnitudes are fainter [this perplexes some people!] The scale measures ratios of brightness: if one star is 5 mag brighter than another, it is 100x as bright. ...
... A Special Scale Stars with numerically larger magnitudes are fainter [this perplexes some people!] The scale measures ratios of brightness: if one star is 5 mag brighter than another, it is 100x as bright. ...
Jeopardy 2015
... Type G2 star, middle of HR diagram-average size and luminosity, end of life will be white dwarf, only known star to support a planet with life. Why is our star (the sun) frequently referred to as an “average” star? Compare the important physical characteristics of the Sun with the most common types ...
... Type G2 star, middle of HR diagram-average size and luminosity, end of life will be white dwarf, only known star to support a planet with life. Why is our star (the sun) frequently referred to as an “average” star? Compare the important physical characteristics of the Sun with the most common types ...
Forces in stars
... The nuclear fusion reactions going on within the Sun generate huge amounts of energy in the form of radiation and this streams upwards through the Sun until it eventually leaves the surface and is radiated out into space. If the star is stable the gravitational forces acting inwards to the centre of ...
... The nuclear fusion reactions going on within the Sun generate huge amounts of energy in the form of radiation and this streams upwards through the Sun until it eventually leaves the surface and is radiated out into space. If the star is stable the gravitational forces acting inwards to the centre of ...
HR-diagram - Bakersfield College
... • two stars with the same absolute magnitude would not be the same apparent magnitude WHY? • To compare absolute brightness • use a standard distance of 32.6 light-years away from earth ...
... • two stars with the same absolute magnitude would not be the same apparent magnitude WHY? • To compare absolute brightness • use a standard distance of 32.6 light-years away from earth ...
Constellations, Star Names, and Magnitudes
... A huge globe of stars surrounding the Earth. An ancient concept of the Cosmos. IT IS A USEFUL CONCEPT TODAY BECAUSE: it is understandable in terms of spherical geometry. it can be used to extend map concepts for the Earth to the sky. it is useful in navigation. ...
... A huge globe of stars surrounding the Earth. An ancient concept of the Cosmos. IT IS A USEFUL CONCEPT TODAY BECAUSE: it is understandable in terms of spherical geometry. it can be used to extend map concepts for the Earth to the sky. it is useful in navigation. ...
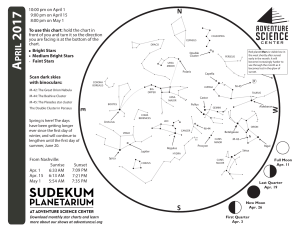
1704 chart front - Adventure Science Center
... constellations. Orion the Hunter stands out early in the month, but will be lost in the glow of sunset by May. Follow Orion’s belt to the left to find the brightest star in the night sky, Sirius, in Canis Major the Big Dog. Follow the belt stars to the right to find orange star Aldebaran, the eye of T ...
... constellations. Orion the Hunter stands out early in the month, but will be lost in the glow of sunset by May. Follow Orion’s belt to the left to find the brightest star in the night sky, Sirius, in Canis Major the Big Dog. Follow the belt stars to the right to find orange star Aldebaran, the eye of T ...
LT 5: I can describe how astronomers determine the composition
... star a large celestial body that is composed of gas and that emits light. Nuclear fusion is the combination of light atomic nuclei to form heavier atomic nuclei Astronomers learn about stars by analyzing the light that the stars emit. ...
... star a large celestial body that is composed of gas and that emits light. Nuclear fusion is the combination of light atomic nuclei to form heavier atomic nuclei Astronomers learn about stars by analyzing the light that the stars emit. ...
Astronomy Fall 2013 Final Exam History of Astronomy Know: speed
... direction). Because to find longitude you would need a tool that measures 3D. 6. Who is credited with inventing the first telescope? When? Give two ways this tool helps to overcome difficulties of studying astronomy (how did this help). ...
... direction). Because to find longitude you would need a tool that measures 3D. 6. Who is credited with inventing the first telescope? When? Give two ways this tool helps to overcome difficulties of studying astronomy (how did this help). ...
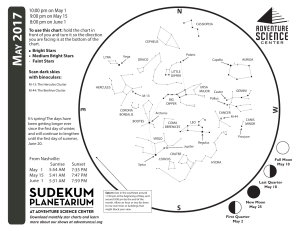
1705 chart front
... them orbit around their parent planet. If you have trouble steadying your binocular view on Jupiter, try leaning them up against the side of a building or another steady surface. A small telescope not only shows the moons of Jupiter, but also its cloud bands. Jupiter has stripes! Look for our own Mo ...
... them orbit around their parent planet. If you have trouble steadying your binocular view on Jupiter, try leaning them up against the side of a building or another steady surface. A small telescope not only shows the moons of Jupiter, but also its cloud bands. Jupiter has stripes! Look for our own Mo ...
Galaxies - C. Levesque
... • The Milky Way is a spiral galaxy • Our solar system is located on the Orion Arm of the Milky Way Galaxy ...
... • The Milky Way is a spiral galaxy • Our solar system is located on the Orion Arm of the Milky Way Galaxy ...
Lives and Deaths of Stars (middle school)
... Outer layers expand due to radiation pressure from a hot core • Surface temperature drops by a factor of ~ 2 • The radius increases by a factor of ~ 100 • Luminosity increases ~ R2 T4 ~ 100-1000 times ...
... Outer layers expand due to radiation pressure from a hot core • Surface temperature drops by a factor of ~ 2 • The radius increases by a factor of ~ 100 • Luminosity increases ~ R2 T4 ~ 100-1000 times ...
Lyra

Lyra (/ˈlaɪərə/; Latin for lyre, from Greek λύρα) is a small constellation. It is one of 48 listed by the 2nd century astronomer Ptolemy, and is one of the 88 constellations recognized by the International Astronomical Union. Lyra was often represented on star maps as a vulture or an eagle carrying a lyre, and hence sometimes referred to as Aquila Cadens or Vultur Cadens. Beginning at the north, Lyra is bordered by Draco, Hercules, Vulpecula, and Cygnus. Lyra is visible from the northern hemisphere from spring through autumn, and nearly overhead, in temperate latitudes, during the summer months. From the southern hemisphere, it is visible low in the northern sky during the winter months.The lucida or brightest star—and one of the brightest stars in the sky—is the white main sequence star Vega, a corner of the Summer Triangle. Beta Lyrae is the prototype of a class of stars known as Beta Lyrae variables, binary stars so close to each other that they become egg-shaped and material flows from one to the other. Epsilon Lyrae, known informally as the Double Double, is a complex multiple star system. Lyra also hosts the Ring Nebula, the second-discovered and best-known planetary nebula.