Galaxies - cloudfront.net
... billions of stars. Galaxies are divided into three types according to shape: spiral, elliptical, and irregular galaxies. • Spiral galaxies spin and appear as a rotating disk of stars and dust, with a bulge in the middle. Several spiral arms reach outward from the central bulge like the arms of a pin ...
... billions of stars. Galaxies are divided into three types according to shape: spiral, elliptical, and irregular galaxies. • Spiral galaxies spin and appear as a rotating disk of stars and dust, with a bulge in the middle. Several spiral arms reach outward from the central bulge like the arms of a pin ...
Sky-High 2015 - Irish Astronomical Society
... can look gibbous, i.e. not quite full. Jupiter can show very slightly less than full at quadrature (i.e. when 90° from the Sun) in amateur telescopes. The outer planets exhibit a phenomenon known as retrograding. A consequence of their lying further from the Sun than us is that they orbit more slowl ...
... can look gibbous, i.e. not quite full. Jupiter can show very slightly less than full at quadrature (i.e. when 90° from the Sun) in amateur telescopes. The outer planets exhibit a phenomenon known as retrograding. A consequence of their lying further from the Sun than us is that they orbit more slowl ...
Activity and rotation of Kepler-17
... Kepler-17 is a G2V star (Tef f = 5781 K), the same spectral type as our Sun, with a mass of 1.16 M and radius of 1.05 R , that was observed by the Kepler satellite for almost 4 years. It is a young star with less than 1.78 Gyr (Bonomo et al. 2012), that rotates with an average period of 12.4 ± 0.1 ...
... Kepler-17 is a G2V star (Tef f = 5781 K), the same spectral type as our Sun, with a mass of 1.16 M and radius of 1.05 R , that was observed by the Kepler satellite for almost 4 years. It is a young star with less than 1.78 Gyr (Bonomo et al. 2012), that rotates with an average period of 12.4 ± 0.1 ...
Spectral classification of O–M stars on the basis of UBV photometry
... analyzed stars have been assigned to a single or two rather close estimates of spectra. In the last case an average value was adopted. Another 40% of stars have obtained two substantially different estimates of spectra. Double results of the classifying process based on U BV data originates as a rul ...
... analyzed stars have been assigned to a single or two rather close estimates of spectra. In the last case an average value was adopted. Another 40% of stars have obtained two substantially different estimates of spectra. Double results of the classifying process based on U BV data originates as a rul ...
Stellar Spectroscopy (GA 3.0) - National Optical Astronomy
... surface of the star, but most of what is known about stars is determined from the many spectral lines seen in their spectrum. A close inspection of a starʼs spectrum will reveal many absorption lines, and for some stars, emission lines as well. These spectral lines can be used to determine an incred ...
... surface of the star, but most of what is known about stars is determined from the many spectral lines seen in their spectrum. A close inspection of a starʼs spectrum will reveal many absorption lines, and for some stars, emission lines as well. These spectral lines can be used to determine an incred ...
Document
... 1999: using ASCA, X-1 in M82 was found to vary by up to a factor of four, confirming that this bright source was indeed a single object. *Over half of ULXs are known to be variable, ruling out the multiple source or SNR hypothesis. ...
... 1999: using ASCA, X-1 in M82 was found to vary by up to a factor of four, confirming that this bright source was indeed a single object. *Over half of ULXs are known to be variable, ruling out the multiple source or SNR hypothesis. ...
Stars Stars All Around - Columbus City Schools
... Sizing Up The Stars (Day 3) Prepare for the activity Sizing Up The Stars. (adapted from Meghan Webb, Huntington, WV) Students will use spheres on a flat table to discover the difference in size and distance of stars. Teacher will have students stop after each round object has been moved to bend down ...
... Sizing Up The Stars (Day 3) Prepare for the activity Sizing Up The Stars. (adapted from Meghan Webb, Huntington, WV) Students will use spheres on a flat table to discover the difference in size and distance of stars. Teacher will have students stop after each round object has been moved to bend down ...
Archaeoastronomical Study of the Main Pyramids of Giza
... that time, while Alnitak, the lowest star of the Belt at its culmination, corresponded to the Khufu pyramid, the lowest one in the maps. Obviously this choice is opposite to that adopted by the cartographers of the XVII century who decided to put North on the top of their maps, a convention that we ...
... that time, while Alnitak, the lowest star of the Belt at its culmination, corresponded to the Khufu pyramid, the lowest one in the maps. Obviously this choice is opposite to that adopted by the cartographers of the XVII century who decided to put North on the top of their maps, a convention that we ...
Circumstellar Disks: IRAS to ALMA (by way of HST) Dr. Karl Stapelfeldt
... Planet orbits still being defined ...
... Planet orbits still being defined ...
Chapter17.2
... • This double shell–burning stage never reaches equilibrium—fusion rate periodically spikes upward in a series of thermal pulses. • With each spike, convection dredges carbon up from core and transports it to surface. © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. ...
... • This double shell–burning stage never reaches equilibrium—fusion rate periodically spikes upward in a series of thermal pulses. • With each spike, convection dredges carbon up from core and transports it to surface. © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. ...
Precision age indicators that exploit chemically peculiar stars
... lines, including Fe, and therefore again containing a very healthy sum of total absorption. In the Am case, complete disambiguation of the Am signature may require measuring Ca K accurately, worrisome because it is a single spectral feature. To ease the worry, however, we note that this is a strong ...
... lines, including Fe, and therefore again containing a very healthy sum of total absorption. In the Am case, complete disambiguation of the Am signature may require measuring Ca K accurately, worrisome because it is a single spectral feature. To ease the worry, however, we note that this is a strong ...
Multiwavelength properties of γ-ray loud binary systems.
... Cyg X-3 and PSR B1259-63. Remarkably, there are no signatures of weaker variability which could be clearly associated to other binary systems with black holes and /or neutron stars. Recent discovery of the γ-ray flaring activity of the Crab pulsar shows that pulsars (or the inner compact parts of th ...
... Cyg X-3 and PSR B1259-63. Remarkably, there are no signatures of weaker variability which could be clearly associated to other binary systems with black holes and /or neutron stars. Recent discovery of the γ-ray flaring activity of the Crab pulsar shows that pulsars (or the inner compact parts of th ...
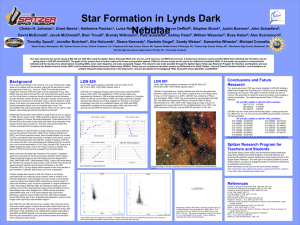
SciPoster_Jan2009
... initially from massive short-lived stars such as Cassiopeia A (e.g., Rho 2008). Dust can also be formed from old, dying stars that used to be like our Sun. Dust found in molecular clouds is crucial to the star formation process because it allows the gas to cool down enough so that clumps of the clou ...
... initially from massive short-lived stars such as Cassiopeia A (e.g., Rho 2008). Dust can also be formed from old, dying stars that used to be like our Sun. Dust found in molecular clouds is crucial to the star formation process because it allows the gas to cool down enough so that clumps of the clou ...
Aldebaran
... contracted, a protostar was formed. Gravity caused the protostar to condense further and heat up. Nuclear reactions occurred when the temperature in the center of the protostar reached about 10 million degrees, and the star was born. Further expansion and heating of the star’s exterior then led to t ...
... contracted, a protostar was formed. Gravity caused the protostar to condense further and heat up. Nuclear reactions occurred when the temperature in the center of the protostar reached about 10 million degrees, and the star was born. Further expansion and heating of the star’s exterior then led to t ...
The HERMES GALAH survey: overview
... over which the two disk components overlap (about 0.7 to 0.1), the thick disk stars are distinctly more ↵-enhanced, indicating that their chemical evolution occurred more rapidly. Near the sun, the stars of the thick disk appear to be old, with ages in excess of about 10 Gyr. We know that the Galact ...
... over which the two disk components overlap (about 0.7 to 0.1), the thick disk stars are distinctly more ↵-enhanced, indicating that their chemical evolution occurred more rapidly. Near the sun, the stars of the thick disk appear to be old, with ages in excess of about 10 Gyr. We know that the Galact ...
Evolution of stars
... The free-fall contraction of a molecular cloud a. can be initiated by shock waves from supernovae. b. can be initiated by nearby spectral type G stars. c. can be initiated by the rotation of the cloud. d. causes the cloud to become transparent to ultraviolet radiation. e. causes the particles in the ...
... The free-fall contraction of a molecular cloud a. can be initiated by shock waves from supernovae. b. can be initiated by nearby spectral type G stars. c. can be initiated by the rotation of the cloud. d. causes the cloud to become transparent to ultraviolet radiation. e. causes the particles in the ...
Astrophysical explosions: from solar flares to cosmic gamma
... of detonations and, in particular, the deflagration–detonation transition (DDT). Experimental and theoretical investigations of the propagation of terrestrial detonations have informed the study of astrophysical detonations, and examining the possibility of unconfined DDTs in astrophysical combustion ...
... of detonations and, in particular, the deflagration–detonation transition (DDT). Experimental and theoretical investigations of the propagation of terrestrial detonations have informed the study of astrophysical detonations, and examining the possibility of unconfined DDTs in astrophysical combustion ...
StellarManual
... -4.8) emits more energy than Alkaid (M = -1.8). Barnard’s Star (m = 9.5) appears brighter than Wolf 359 (13.4), and Barnard’s Star (M = 13.2) emits more energy than Wolf 359 (M = 16.6). Aldebaran (m = 0.9) appears brighter than Acrux (m = 1.6), but Acrux (M = -4.0) emits more energy than Aldebaran ( ...
... -4.8) emits more energy than Alkaid (M = -1.8). Barnard’s Star (m = 9.5) appears brighter than Wolf 359 (13.4), and Barnard’s Star (M = 13.2) emits more energy than Wolf 359 (M = 16.6). Aldebaran (m = 0.9) appears brighter than Acrux (m = 1.6), but Acrux (M = -4.0) emits more energy than Aldebaran ( ...
Age aspects of habitability - Cambridge University Press
... Abstract: A ‘habitable zone’ of a star is defined as a range of orbits within which a rocky planet can support liquid water on its surface. The most intriguing question driving the search for habitable planets is whether they host life. But is the age of the planet important for its habitability? If ...
... Abstract: A ‘habitable zone’ of a star is defined as a range of orbits within which a rocky planet can support liquid water on its surface. The most intriguing question driving the search for habitable planets is whether they host life. But is the age of the planet important for its habitability? If ...
- MNASSA Page
... axy, but on the other hand it is not very can be seen lurking in the nebulosity. Star centrally placed. The inner core consists splinters dot the surface of this outstanding of stars that are very hot and large, their object like dewdrops on frosted glass. combined radiation being responsible for it ...
... axy, but on the other hand it is not very can be seen lurking in the nebulosity. Star centrally placed. The inner core consists splinters dot the surface of this outstanding of stars that are very hot and large, their object like dewdrops on frosted glass. combined radiation being responsible for it ...
Lecture 7: Extrasolar Planets 01/08/2013 update: 725 exoplanets
... This is a measure of planetary radius, NOT the mass! The method suffers from a high rate of false detections. A transit detection requires additional confirmation, typically from the radial-velocity method. In practice, isolated planets with masses between ~ 0.1 MJ and 10 MJ, where MJ is the mass of ...
... This is a measure of planetary radius, NOT the mass! The method suffers from a high rate of false detections. A transit detection requires additional confirmation, typically from the radial-velocity method. In practice, isolated planets with masses between ~ 0.1 MJ and 10 MJ, where MJ is the mass of ...
Parallax
... Of course astronomers are not ones to use simple methods. They have goobered up this measurement just like the ones with magnitude. So keep reading and the enumeration as to how astronomers use parallax to measure the distance to a star will be given. Except for our sun, the stars are pretty far aw ...
... Of course astronomers are not ones to use simple methods. They have goobered up this measurement just like the ones with magnitude. So keep reading and the enumeration as to how astronomers use parallax to measure the distance to a star will be given. Except for our sun, the stars are pretty far aw ...
6.1 Introduction
... Figure 6.1: The globular cluster ω Centauri (at a distance of 5 kpc in the Galactic halo, with a mass of 107 M ) is unique among Galactic globular clusters in showing two distinct populations of stars, a bluer population and a redder one, with quite distinct main sequences in the colour-magnitude ...
... Figure 6.1: The globular cluster ω Centauri (at a distance of 5 kpc in the Galactic halo, with a mass of 107 M ) is unique among Galactic globular clusters in showing two distinct populations of stars, a bluer population and a redder one, with quite distinct main sequences in the colour-magnitude ...
Lyra

Lyra (/ˈlaɪərə/; Latin for lyre, from Greek λύρα) is a small constellation. It is one of 48 listed by the 2nd century astronomer Ptolemy, and is one of the 88 constellations recognized by the International Astronomical Union. Lyra was often represented on star maps as a vulture or an eagle carrying a lyre, and hence sometimes referred to as Aquila Cadens or Vultur Cadens. Beginning at the north, Lyra is bordered by Draco, Hercules, Vulpecula, and Cygnus. Lyra is visible from the northern hemisphere from spring through autumn, and nearly overhead, in temperate latitudes, during the summer months. From the southern hemisphere, it is visible low in the northern sky during the winter months.The lucida or brightest star—and one of the brightest stars in the sky—is the white main sequence star Vega, a corner of the Summer Triangle. Beta Lyrae is the prototype of a class of stars known as Beta Lyrae variables, binary stars so close to each other that they become egg-shaped and material flows from one to the other. Epsilon Lyrae, known informally as the Double Double, is a complex multiple star system. Lyra also hosts the Ring Nebula, the second-discovered and best-known planetary nebula.