SRMP Stars Curriculum - American Museum of Natural History
... For this activity, the brighter the light, the better. Hand out one diffraction grating per student. Explain that these act like prisms and break up light into its constituent parts. Turn the dimmable light on low, and turn off the classroom lights. Ask students to view the light through the diffrac ...
... For this activity, the brighter the light, the better. Hand out one diffraction grating per student. Explain that these act like prisms and break up light into its constituent parts. Turn the dimmable light on low, and turn off the classroom lights. Ask students to view the light through the diffrac ...
IYA 2009 - AAVSO Beginner/Intermediate Amateur Astronomer
... At HPO using a DSI Pro II and 2,400 lines/mm grating, the window is only about 90 Å wide. The ...
... At HPO using a DSI Pro II and 2,400 lines/mm grating, the window is only about 90 Å wide. The ...
star formation and galactic evolution
... star formation efficiency becomes only about 2 percent, similar to what is observed. Thus, the feedback effects of massive star formation can plausibly prolong the timescale for gas depletion from a gravitational timescale to a time much closer to the Hubble time, as is required to account for the o ...
... star formation efficiency becomes only about 2 percent, similar to what is observed. Thus, the feedback effects of massive star formation can plausibly prolong the timescale for gas depletion from a gravitational timescale to a time much closer to the Hubble time, as is required to account for the o ...
Why Spectroscopy?
... At HPO using a DSI Pro II and 2,400 lines/mm grating, the window is only about 90 Å wide. The ...
... At HPO using a DSI Pro II and 2,400 lines/mm grating, the window is only about 90 Å wide. The ...
The HIRES science case
... solve some of the issues, others remain puzzling and may hint to more fundamental problems in our understanding. For example, the migration timescale appears to be quite short, so why have not all the planets "fallen" into their star? Why is it that Jupiter appears not to have migrated significantl ...
... solve some of the issues, others remain puzzling and may hint to more fundamental problems in our understanding. For example, the migration timescale appears to be quite short, so why have not all the planets "fallen" into their star? Why is it that Jupiter appears not to have migrated significantl ...
instructor notes stellar evolution, star clusters
... lines in their spectra originating from circumstellar gas; most are light variable. Pre-main-sequence variable stars are referred to as Orion Population variables. B and Atype pre-main-sequence stars are often found to be Herbig Ae and Be stars. F, G, and K-type pre-mainsequence stars are usually T ...
... lines in their spectra originating from circumstellar gas; most are light variable. Pre-main-sequence variable stars are referred to as Orion Population variables. B and Atype pre-main-sequence stars are often found to be Herbig Ae and Be stars. F, G, and K-type pre-mainsequence stars are usually T ...
instructor notes stellar evolution, star clusters
... lines in their spectra originating from circumstellar gas; most are light variable. Pre-main-sequence variable stars are referred to as Orion Population variables. B and Atype pre-main-sequence stars are often found to be Herbig Ae and Be stars. F, G, and K-type pre-mainsequence stars are usually T ...
... lines in their spectra originating from circumstellar gas; most are light variable. Pre-main-sequence variable stars are referred to as Orion Population variables. B and Atype pre-main-sequence stars are often found to be Herbig Ae and Be stars. F, G, and K-type pre-mainsequence stars are usually T ...
The empirical mass distribution of hot B subdwarfs
... in 2001 [13], and since a decade our group has published detailed analyses of 15 pulsating B subdwarfs, including estimates of the masses of these pulsators. Several mass estimates are also available in the literature for sdBs residing in binary systems, from binary light curve modeling combined wit ...
... in 2001 [13], and since a decade our group has published detailed analyses of 15 pulsating B subdwarfs, including estimates of the masses of these pulsators. Several mass estimates are also available in the literature for sdBs residing in binary systems, from binary light curve modeling combined wit ...
12 The Milky Way - Journigan-wiki
... range from a few hundred thousand stars to several million per cluster. Their radii usually range form 40 to 160 light-years. Because they are more massive, they pull their stars into a tighter ball. Astronomers estimate that between 150 to 200 globular clusters exist within the Milky Way. ...
... range from a few hundred thousand stars to several million per cluster. Their radii usually range form 40 to 160 light-years. Because they are more massive, they pull their stars into a tighter ball. Astronomers estimate that between 150 to 200 globular clusters exist within the Milky Way. ...
arXiv:1705.00964v1 [astro-ph.GA] 2 May 2017
... of three hot stars with z < 60 pc is, in itself, slightly surprising. The cylindrical regions shown in Figure 1 encompass a volume 9× greater than the volume of interest, and together they contain 8 hot stars (blue points, in the figure). We would therefore expect to see 0.9 hot stars within ρ < 2 p ...
... of three hot stars with z < 60 pc is, in itself, slightly surprising. The cylindrical regions shown in Figure 1 encompass a volume 9× greater than the volume of interest, and together they contain 8 hot stars (blue points, in the figure). We would therefore expect to see 0.9 hot stars within ρ < 2 p ...
Luminosity, Flux and Magnitudes Outline
... Make a sphere of radius, r, around an object (such as the Sun or a light bulb) which is radiating power. All energy radiated from the object must pass through this sphere The size of the sphere does not matter! ...
... Make a sphere of radius, r, around an object (such as the Sun or a light bulb) which is radiating power. All energy radiated from the object must pass through this sphere The size of the sphere does not matter! ...
A search for a new class of pulsating DA white dwarf stars in the DB
... Most importantly in the context of this discussion: gravitational settling stratifies the structure of white dwarf stars, and in the presence of such strong gravitational fields it does so quickly. In the absence of any mixing – particularly in the absence of convection – we would expect all white d ...
... Most importantly in the context of this discussion: gravitational settling stratifies the structure of white dwarf stars, and in the presence of such strong gravitational fields it does so quickly. In the absence of any mixing – particularly in the absence of convection – we would expect all white d ...
The Milky Way`s Restless Swarms of Stars
... Majewski’s group sees tidal streams from Sagittarius wrapping clear around the Milky Way. However, several of the dwarf’s globular clusters will outlast this dissolution for billions of years.The Milky Way’s largest globular cluster, Omega Centauri, might be the core of a dwarf galaxy whose outer pa ...
... Majewski’s group sees tidal streams from Sagittarius wrapping clear around the Milky Way. However, several of the dwarf’s globular clusters will outlast this dissolution for billions of years.The Milky Way’s largest globular cluster, Omega Centauri, might be the core of a dwarf galaxy whose outer pa ...
Starfarer
... the eastern horizon at its own special point and makes an arc across the sky. It does not rise straight up the horizon but at an angle, thus if a star rises at north-east, it will change its bearing while moving across the sky and set at its precise westerly bearing—the north west. Thus a horizon st ...
... the eastern horizon at its own special point and makes an arc across the sky. It does not rise straight up the horizon but at an angle, thus if a star rises at north-east, it will change its bearing while moving across the sky and set at its precise westerly bearing—the north west. Thus a horizon st ...
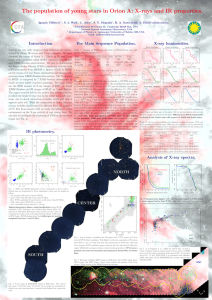
The population of young stars in Orion A: X-rays and... Ignazio Pillitteri , S. J. Wolk , L. Allen
... and XMM-Newton observatories. We aim to characterize the Young Stellar Objects (YSOs) population with the help of IR photometry from 2MASS + Spitzer (IRAC & MIPS) and by means of X-rays fluxes, luminosities and plasma temperatures from XMM-Newton observations. The X-ray part of SOXS is composed by 7 ...
... and XMM-Newton observatories. We aim to characterize the Young Stellar Objects (YSOs) population with the help of IR photometry from 2MASS + Spitzer (IRAC & MIPS) and by means of X-rays fluxes, luminosities and plasma temperatures from XMM-Newton observations. The X-ray part of SOXS is composed by 7 ...
Andromeda Galaxy www.AssignmentPoint.com The Andromeda
... concerning the nature of the Milky Way, spiral nebulae, and the dimensions of the universe. To support his claim of the Great Andromeda Nebula being, in fact, an external galaxy, Curtis also noted the appearance of dark lanes resembling the dust clouds in our own galaxy within Andromeda- the Milky W ...
... concerning the nature of the Milky Way, spiral nebulae, and the dimensions of the universe. To support his claim of the Great Andromeda Nebula being, in fact, an external galaxy, Curtis also noted the appearance of dark lanes resembling the dust clouds in our own galaxy within Andromeda- the Milky W ...
A Bayesian method for the detection of planetary transits
... into account the limb darkening effect and light curves were modelized on the assumption that the signal of the stars is processed by an instrument similar to that developed for the COROT space mission, adding appropriate white noises to account for the instrumental noises and extrapolating the vari ...
... into account the limb darkening effect and light curves were modelized on the assumption that the signal of the stars is processed by an instrument similar to that developed for the COROT space mission, adding appropriate white noises to account for the instrumental noises and extrapolating the vari ...
Formation and Detectability of Terrestrial Planets around
... is presented by the triple planet system orbiting HD 69830. This system has been shown to contain three Neptune-mass planets, including one on a 197-day orbit, all revealed after only 74 radial velocity observations with residual noise of 0.6 m s−1 (Lovis et al. 2006). The detection of the HD 69830 ...
... is presented by the triple planet system orbiting HD 69830. This system has been shown to contain three Neptune-mass planets, including one on a 197-day orbit, all revealed after only 74 radial velocity observations with residual noise of 0.6 m s−1 (Lovis et al. 2006). The detection of the HD 69830 ...
PPT presentation
... • Two point sources bright in the on-band and fainter but visible in the offband. Could be high-z quasars or star forming regions or even a PN within a globular cluster in NGC 4697, as reported recently in the case of NGC 5128 by Minniti and Rejkuba. Again no confusion is possible since the continuu ...
... • Two point sources bright in the on-band and fainter but visible in the offband. Could be high-z quasars or star forming regions or even a PN within a globular cluster in NGC 4697, as reported recently in the case of NGC 5128 by Minniti and Rejkuba. Again no confusion is possible since the continuu ...
Lyra

Lyra (/ˈlaɪərə/; Latin for lyre, from Greek λύρα) is a small constellation. It is one of 48 listed by the 2nd century astronomer Ptolemy, and is one of the 88 constellations recognized by the International Astronomical Union. Lyra was often represented on star maps as a vulture or an eagle carrying a lyre, and hence sometimes referred to as Aquila Cadens or Vultur Cadens. Beginning at the north, Lyra is bordered by Draco, Hercules, Vulpecula, and Cygnus. Lyra is visible from the northern hemisphere from spring through autumn, and nearly overhead, in temperate latitudes, during the summer months. From the southern hemisphere, it is visible low in the northern sky during the winter months.The lucida or brightest star—and one of the brightest stars in the sky—is the white main sequence star Vega, a corner of the Summer Triangle. Beta Lyrae is the prototype of a class of stars known as Beta Lyrae variables, binary stars so close to each other that they become egg-shaped and material flows from one to the other. Epsilon Lyrae, known informally as the Double Double, is a complex multiple star system. Lyra also hosts the Ring Nebula, the second-discovered and best-known planetary nebula.








![arXiv:1705.00964v1 [astro-ph.GA] 2 May 2017](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/013011793_1-8f89fb3e8b5cd5cf78613aebb3c8e2a5-300x300.png)