Properties of Stars
... outside: the light-year (ly) equals the distance travelled by light in one year speed of light = 300 000 km/s ...
... outside: the light-year (ly) equals the distance travelled by light in one year speed of light = 300 000 km/s ...
Chapter 19 Star Formation
... in the globular cluster is due to its extreme age—those stars have already used up their fuel and have moved off the main sequence. ...
... in the globular cluster is due to its extreme age—those stars have already used up their fuel and have moved off the main sequence. ...
Sections F and G
... dwarfs lead to optical emission (novae), while those around neutron stars (or black holes) result in X-ray emission (X-ray binaries). Novae A nova (short for stella nova, or new star) is a star which undergoes a large increase in brightness (by factors up to 107) on a short time scale. In many cases ...
... dwarfs lead to optical emission (novae), while those around neutron stars (or black holes) result in X-ray emission (X-ray binaries). Novae A nova (short for stella nova, or new star) is a star which undergoes a large increase in brightness (by factors up to 107) on a short time scale. In many cases ...
Stellar Classification and Evolution What is a star? A cloud of gas
... from helium fusion _____________ much of their mass The ejected material expands and cools, becoming a planetary ________________ (which actually has nothing to do with planets, but we didn’t know that in the 18th century when Herschel coined the term) The core _____________________ to form a Wh ...
... from helium fusion _____________ much of their mass The ejected material expands and cools, becoming a planetary ________________ (which actually has nothing to do with planets, but we didn’t know that in the 18th century when Herschel coined the term) The core _____________________ to form a Wh ...
The Milky Way
... • How do astronomers refer to stars and compare their brightness? • How does the sky appear to move as Earth rotates? • What causes the seasons? • How can astronomical cycles affect Earth’s climate? As you study the sky and its motions, you will be learning to think of Earth as a planet rotating on ...
... • How do astronomers refer to stars and compare their brightness? • How does the sky appear to move as Earth rotates? • What causes the seasons? • How can astronomical cycles affect Earth’s climate? As you study the sky and its motions, you will be learning to think of Earth as a planet rotating on ...
Spring 2014 Astronomy Exam Study Guide (Co-Taught)
... 15. Which region of the electromagnetic spectrum has the longest wavelength? 16. Which region of the electromagnetic spectrum will travel with the fastest speed? 17. Which color of the visible light spectrum has the greatest frequency? 18. Which color of the visible light spectrum has the greatest w ...
... 15. Which region of the electromagnetic spectrum has the longest wavelength? 16. Which region of the electromagnetic spectrum will travel with the fastest speed? 17. Which color of the visible light spectrum has the greatest frequency? 18. Which color of the visible light spectrum has the greatest w ...
final fate of a massive star
... A tremendous creation and destruction of particles will take place in its vicinity. One could imagine it as the `cosmic dance' of basic forces of nature, which may come together in a unified manner. This is because the energies and all physical quantities reach their extreme values in the vicinity ...
... A tremendous creation and destruction of particles will take place in its vicinity. One could imagine it as the `cosmic dance' of basic forces of nature, which may come together in a unified manner. This is because the energies and all physical quantities reach their extreme values in the vicinity ...
Find true north without a compass Which way is north?
... 2. Point the hour hand at the sun. You can use a stick to cast a shadow to aid in your alignment if you wish, but it is not necessary. 3. Bisect (find the centre point of) the angle between the hour hand and the twelve o'clock mark (the number 12 on the watch). The centre of the angle between the ho ...
... 2. Point the hour hand at the sun. You can use a stick to cast a shadow to aid in your alignment if you wish, but it is not necessary. 3. Bisect (find the centre point of) the angle between the hour hand and the twelve o'clock mark (the number 12 on the watch). The centre of the angle between the ho ...
MAUI STARGAZING MAY OBSERVING LIST DEEP SPACE
... and dark matter The word galaxy is derived from the Greek galaxias (γαλαξίας), literally "milky," a reference to The Milky Way. Galaxies range in size from dwarfs with just a few thousand stars to giants with one hundred trillion stars, each orbiting their galaxy's own center of mass. NEBULAE A nebu ...
... and dark matter The word galaxy is derived from the Greek galaxias (γαλαξίας), literally "milky," a reference to The Milky Way. Galaxies range in size from dwarfs with just a few thousand stars to giants with one hundred trillion stars, each orbiting their galaxy's own center of mass. NEBULAE A nebu ...
Exercise 4 (Stars and the universe) Suggested answers
... Exercise 4 (Stars and the universe) Suggested answers 1. (a) The star is nearly a blackbody, the spectrum of a star can be approximated as a blackbody radiation curve. On the curve, there is a peak which shifts to shorter wavelength when the temperature of the blackbody increases. From the position ...
... Exercise 4 (Stars and the universe) Suggested answers 1. (a) The star is nearly a blackbody, the spectrum of a star can be approximated as a blackbody radiation curve. On the curve, there is a peak which shifts to shorter wavelength when the temperature of the blackbody increases. From the position ...
doc - EU-HOU
... In this exercise, we explain how an invisible companion orbiting its parent star can be detected using precise measurement of the star’s velocity. The radial-velocity method uses the fact that a star with a companion will be in orbit around the center of mass of the system. The goal is thus to measu ...
... In this exercise, we explain how an invisible companion orbiting its parent star can be detected using precise measurement of the star’s velocity. The radial-velocity method uses the fact that a star with a companion will be in orbit around the center of mass of the system. The goal is thus to measu ...
kepler` s laws
... seventeen century, observations were made with the naked eye. Nonetheless, with great patience and ingenuity, astronomers were able to chart the motion of many stars and planets across the sky. Tycho Brahe, a Danish astronomer (1546-1601), was credited to have made very careful observations of the m ...
... seventeen century, observations were made with the naked eye. Nonetheless, with great patience and ingenuity, astronomers were able to chart the motion of many stars and planets across the sky. Tycho Brahe, a Danish astronomer (1546-1601), was credited to have made very careful observations of the m ...
Foundation 1 - Discovering Astronomy
... graduate student Jocelyn Bell. • She found a radio source with a regular on-off-on cycle of exactly 1.3373011 seconds. • Some scientists speculated that this was evidence of an alien civilization’s communication system and dubbed the source LGM (Little Green Men!!!) • Today, we know pulsars are rapi ...
... graduate student Jocelyn Bell. • She found a radio source with a regular on-off-on cycle of exactly 1.3373011 seconds. • Some scientists speculated that this was evidence of an alien civilization’s communication system and dubbed the source LGM (Little Green Men!!!) • Today, we know pulsars are rapi ...
Lecture 6
... If the distance between Earth and the Sun were cut in half, how much brighter would the sun appear in our sky? a. 2x brighter b. 4x brighter c. 8x brighter d. 16x brighter Brightness is a function of the inverse square of distance, so if distance was cut by half it would get brighter by 4x=1/(.5)2 ...
... If the distance between Earth and the Sun were cut in half, how much brighter would the sun appear in our sky? a. 2x brighter b. 4x brighter c. 8x brighter d. 16x brighter Brightness is a function of the inverse square of distance, so if distance was cut by half it would get brighter by 4x=1/(.5)2 ...
Powerpoint of lecture 1
... Gravitationally bound groups of stars, moving together Globular clusters: • compact, roughly spherical, 105-106 stars; • in spherical halo around centre of Galaxy Galactic (or open) clusters: • open, irregular, 102-103 stars; ...
... Gravitationally bound groups of stars, moving together Globular clusters: • compact, roughly spherical, 105-106 stars; • in spherical halo around centre of Galaxy Galactic (or open) clusters: • open, irregular, 102-103 stars; ...
Final Review Sheet - Astronomy Part 2
... Physics of the Earth CP Study Guide – Astronomy Part II Final Exam Date:________ 1. Describe the life cycle of a medium size star. (Our sun) ...
... Physics of the Earth CP Study Guide – Astronomy Part II Final Exam Date:________ 1. Describe the life cycle of a medium size star. (Our sun) ...
Document
... • Low-mass stars create carbon and oxygen in their cores at the end of their life, thanks to the high temperature and pressure present in a red giant star. • High-mass stars produce heavier elements like silicon, magnesium, etc. up through iron, by nuclear fusion in their ...
... • Low-mass stars create carbon and oxygen in their cores at the end of their life, thanks to the high temperature and pressure present in a red giant star. • High-mass stars produce heavier elements like silicon, magnesium, etc. up through iron, by nuclear fusion in their ...
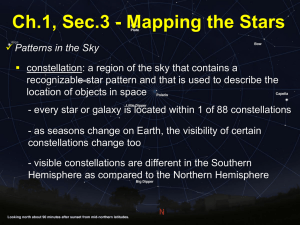
Ch.1, Sec.3 - Mapping the Stars
... constellation: a region of the sky that contains a recognizable star pattern and that is used to describe the location of objects in space - every star or galaxy is located within 1 of 88 constellations - as seasons change on Earth, the visibility of certain ...
... constellation: a region of the sky that contains a recognizable star pattern and that is used to describe the location of objects in space - every star or galaxy is located within 1 of 88 constellations - as seasons change on Earth, the visibility of certain ...
Universe and Star Formation - White Plains Public Schools
... • Stars with masses similar to the sun evolve in essentially the same way as low-mass stars. • During their collapse from red giants to white dwarfs, medium-mass stars are thought to cast off their bloated outer layer, creating an expanding round cloud of gas called planetary nebula. ...
... • Stars with masses similar to the sun evolve in essentially the same way as low-mass stars. • During their collapse from red giants to white dwarfs, medium-mass stars are thought to cast off their bloated outer layer, creating an expanding round cloud of gas called planetary nebula. ...
Phobos
... Algol (beta Persei): Ane of the most famous stars stars in the sky with an intriguing name. The name has been translated as the Demon Star associated with the eye of the Gorgon, Medusa, within the mythology tales of the hero Perseus. It is likely that Montanari first recorded the star's variability ...
... Algol (beta Persei): Ane of the most famous stars stars in the sky with an intriguing name. The name has been translated as the Demon Star associated with the eye of the Gorgon, Medusa, within the mythology tales of the hero Perseus. It is likely that Montanari first recorded the star's variability ...
Lyra

Lyra (/ˈlaɪərə/; Latin for lyre, from Greek λύρα) is a small constellation. It is one of 48 listed by the 2nd century astronomer Ptolemy, and is one of the 88 constellations recognized by the International Astronomical Union. Lyra was often represented on star maps as a vulture or an eagle carrying a lyre, and hence sometimes referred to as Aquila Cadens or Vultur Cadens. Beginning at the north, Lyra is bordered by Draco, Hercules, Vulpecula, and Cygnus. Lyra is visible from the northern hemisphere from spring through autumn, and nearly overhead, in temperate latitudes, during the summer months. From the southern hemisphere, it is visible low in the northern sky during the winter months.The lucida or brightest star—and one of the brightest stars in the sky—is the white main sequence star Vega, a corner of the Summer Triangle. Beta Lyrae is the prototype of a class of stars known as Beta Lyrae variables, binary stars so close to each other that they become egg-shaped and material flows from one to the other. Epsilon Lyrae, known informally as the Double Double, is a complex multiple star system. Lyra also hosts the Ring Nebula, the second-discovered and best-known planetary nebula.