printer-friendly sample test questions
... Students know the Sun is a medium-sized star located in the Milky Way Galaxy, part of which can be seen as a glowing band of light spanning the clear night sky. W/S Answers to Sample Test Questions 2. C, DOK level 1 3. B, DOK level 1 4. C, DOK level 1 5. D, DOK level 1 6. A, DOK level 2 7. B, DOK le ...
... Students know the Sun is a medium-sized star located in the Milky Way Galaxy, part of which can be seen as a glowing band of light spanning the clear night sky. W/S Answers to Sample Test Questions 2. C, DOK level 1 3. B, DOK level 1 4. C, DOK level 1 5. D, DOK level 1 6. A, DOK level 2 7. B, DOK le ...
The Evolution of Low Mass Stars
... consume that fuel at a much higher rate than less massive stars. As a result, more massive stars exhaust their fuel much faster and have shorter main sequence lifetimes. The lifetimes for the most massive stars are only a few million years while the least massive stars fuse hydrogen for trillions of ...
... consume that fuel at a much higher rate than less massive stars. As a result, more massive stars exhaust their fuel much faster and have shorter main sequence lifetimes. The lifetimes for the most massive stars are only a few million years while the least massive stars fuse hydrogen for trillions of ...
PHYS 175 Fall 2014 Final Recitation Ch. 16 The Sun
... A white dwarf is the carbon core lefty over from a low mass star at the end of its H- and Heburning life. These objects are supported by electron degeneracy pressure, are very hot and not very luminous due to their small size. A neutron star is smaller than a white dwarf and is made up entirely of n ...
... A white dwarf is the carbon core lefty over from a low mass star at the end of its H- and Heburning life. These objects are supported by electron degeneracy pressure, are very hot and not very luminous due to their small size. A neutron star is smaller than a white dwarf and is made up entirely of n ...
TYPES OF STARS
... When astronomers look through their telescopes, they see billions of stars. How do they make sense of all these stars? The goal of this problem set is for you to understand that astronomers classify stars on the basis of two different criteria: (1) the intensity of one of the H absorption lines (cal ...
... When astronomers look through their telescopes, they see billions of stars. How do they make sense of all these stars? The goal of this problem set is for you to understand that astronomers classify stars on the basis of two different criteria: (1) the intensity of one of the H absorption lines (cal ...
25drake6s
... A planet of moderate mass in the habitable zone Organic compounds reacting to form simple life Life evolving over billions of years with no ...
... A planet of moderate mass in the habitable zone Organic compounds reacting to form simple life Life evolving over billions of years with no ...
Name Physics 130 Astronomy Exam 2 August 2, 2004 Multiple Choice
... 34. _____ During helium burning in a star’s later life, the chemical element produced by the combination of helium nuclei is a.) beryllium, 8Be b.) carbon, 12C c.) the light isotope of helium, 3He d.) Heavy hydrogen, 2H 35. _____ Cepheid stars are a.) members of binary systems, in which one star pe ...
... 34. _____ During helium burning in a star’s later life, the chemical element produced by the combination of helium nuclei is a.) beryllium, 8Be b.) carbon, 12C c.) the light isotope of helium, 3He d.) Heavy hydrogen, 2H 35. _____ Cepheid stars are a.) members of binary systems, in which one star pe ...
Stars, Stellar classification, H
... These two stars have about the same luminosity -which one appears brighter? A. Alpha Centauri B. The Sun ...
... These two stars have about the same luminosity -which one appears brighter? A. Alpha Centauri B. The Sun ...
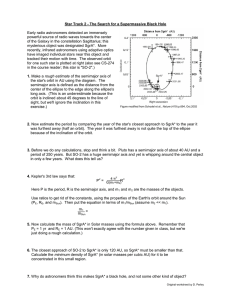
Star Track 2 - The Search for a Supermassive Black... Early radio astronomers detected an immensely
... Star Track 2 - The Search for a Supermassive Black Hole Early radio astronomers detected an immensely powerful source of radio waves towards the center of the Galaxy in the constellation Sagittarius; this mysterious object was designated SgrA*. More recently, infrared astronomers using adaptive opti ...
... Star Track 2 - The Search for a Supermassive Black Hole Early radio astronomers detected an immensely powerful source of radio waves towards the center of the Galaxy in the constellation Sagittarius; this mysterious object was designated SgrA*. More recently, infrared astronomers using adaptive opti ...
Volume 20 Number 10 September 2012
... transiting planets in 20 star systems, increasing the “The second one I saw was the brightest one I ever saw. number of Kepler's confirmed planets to 116 in 67 It was so bright that it cast shadows and left an ionized tail systems, over half of which contain more than one planet. for about 20 to thi ...
... transiting planets in 20 star systems, increasing the “The second one I saw was the brightest one I ever saw. number of Kepler's confirmed planets to 116 in 67 It was so bright that it cast shadows and left an ionized tail systems, over half of which contain more than one planet. for about 20 to thi ...
five minute episode script
... DISTINCTIVE BELT OF THREE STARS. IF YOU LOOK A LITTLE CLOSER YOU'LL SEE STARS OF DIFFERENT BRIGHTNESS AND COLOR. DEAN: STAR COLOR IS AN INDICATION OF ITS TEMPERATURE - BLUE STARS BEING THE HOTTEST AND RED STARS BEING THE COLDEST. YOU CAN REALLY SEE THE COLORS OF THE BRIGHTEST STARS LIKE THOSE IN ORI ...
... DISTINCTIVE BELT OF THREE STARS. IF YOU LOOK A LITTLE CLOSER YOU'LL SEE STARS OF DIFFERENT BRIGHTNESS AND COLOR. DEAN: STAR COLOR IS AN INDICATION OF ITS TEMPERATURE - BLUE STARS BEING THE HOTTEST AND RED STARS BEING THE COLDEST. YOU CAN REALLY SEE THE COLORS OF THE BRIGHTEST STARS LIKE THOSE IN ORI ...
IOSR Journal of Applied Physics (IOSR-JAP)
... For the experiment I took a big plastic ball (a very light weight plastic ball) and tie the north pole of the ball with a thin yarn. Then tie the yarn with board and rotate the ball in the highest possible speed with my hand. The ball started to rotate in an angle and the ball was slightly angled wi ...
... For the experiment I took a big plastic ball (a very light weight plastic ball) and tie the north pole of the ball with a thin yarn. Then tie the yarn with board and rotate the ball in the highest possible speed with my hand. The ball started to rotate in an angle and the ball was slightly angled wi ...
Prospecting for Planets – Radial Velocity Searches
... Elodie – an instrument at the Haute Provence Observatory in France, where the first planet discovered by the RV method was found. ...
... Elodie – an instrument at the Haute Provence Observatory in France, where the first planet discovered by the RV method was found. ...
Main Sequence Stars
... is that there is only one way to make a star with a given mass and chemical composition – if we start with a just formed protostar of a given mass and chemical composition, we can calculate how that star will evolve over its entire life. • This is extremely useful because it greatly simplifies the s ...
... is that there is only one way to make a star with a given mass and chemical composition – if we start with a just formed protostar of a given mass and chemical composition, we can calculate how that star will evolve over its entire life. • This is extremely useful because it greatly simplifies the s ...
Study Guide for 3RD Astronomy Exam
... Write or identify the definition of the stellar motion term “Proper Motion” Describe or identify types of binary stars. State or identify what additional information can be obtained from and eclipsing binaries besides the combined mass of the stars. Properly label the axes of an HR diagram and ident ...
... Write or identify the definition of the stellar motion term “Proper Motion” Describe or identify types of binary stars. State or identify what additional information can be obtained from and eclipsing binaries besides the combined mass of the stars. Properly label the axes of an HR diagram and ident ...
Our Sun, Sol - Hobbs High School
... pattern, becoming a red giant two or more times, each time having its core temperature heating until it starts fusing in turn carbon, neon, oxygen, and then silicon. It becomes a VARIABLE STAR, moving back and forth between the red giant area of the H-R diagram and the main sequence. ...
... pattern, becoming a red giant two or more times, each time having its core temperature heating until it starts fusing in turn carbon, neon, oxygen, and then silicon. It becomes a VARIABLE STAR, moving back and forth between the red giant area of the H-R diagram and the main sequence. ...
Star and Galaxies
... • Stars with masses similar to the sun evolve in essentially the same way as low-mass stars. • During their collapse from red giants to white dwarfs, medium-mass stars are thought to cast off their bloated outer layer, creating an expanding round cloud of gas called planetary nebula. ...
... • Stars with masses similar to the sun evolve in essentially the same way as low-mass stars. • During their collapse from red giants to white dwarfs, medium-mass stars are thought to cast off their bloated outer layer, creating an expanding round cloud of gas called planetary nebula. ...
Volcanoes and Igneous Activity Earth
... • Stars with masses similar to the sun evolve in essentially the same way as low-mass stars. • During their collapse from red giants to white dwarfs, medium-mass stars are thought to cast off their bloated outer layer, creating an expanding round cloud of gas called planetary nebula. ...
... • Stars with masses similar to the sun evolve in essentially the same way as low-mass stars. • During their collapse from red giants to white dwarfs, medium-mass stars are thought to cast off their bloated outer layer, creating an expanding round cloud of gas called planetary nebula. ...
Exploring the Universe
... microwaves that are emitted all over the sky i. Scientists believe that these microwaves are the remains of the radiation produced during the Big ...
... microwaves that are emitted all over the sky i. Scientists believe that these microwaves are the remains of the radiation produced during the Big ...
Lyra

Lyra (/ˈlaɪərə/; Latin for lyre, from Greek λύρα) is a small constellation. It is one of 48 listed by the 2nd century astronomer Ptolemy, and is one of the 88 constellations recognized by the International Astronomical Union. Lyra was often represented on star maps as a vulture or an eagle carrying a lyre, and hence sometimes referred to as Aquila Cadens or Vultur Cadens. Beginning at the north, Lyra is bordered by Draco, Hercules, Vulpecula, and Cygnus. Lyra is visible from the northern hemisphere from spring through autumn, and nearly overhead, in temperate latitudes, during the summer months. From the southern hemisphere, it is visible low in the northern sky during the winter months.The lucida or brightest star—and one of the brightest stars in the sky—is the white main sequence star Vega, a corner of the Summer Triangle. Beta Lyrae is the prototype of a class of stars known as Beta Lyrae variables, binary stars so close to each other that they become egg-shaped and material flows from one to the other. Epsilon Lyrae, known informally as the Double Double, is a complex multiple star system. Lyra also hosts the Ring Nebula, the second-discovered and best-known planetary nebula.