ppt
... Therefore stars have an extremely large gravitational attraction that keeps their plasma held together. As gravity acts equally in all directions the plasma that forms the star is moulded into a sphere. But there must be some force keeping the star from collapsing in on itself. Because stars are so ...
... Therefore stars have an extremely large gravitational attraction that keeps their plasma held together. As gravity acts equally in all directions the plasma that forms the star is moulded into a sphere. But there must be some force keeping the star from collapsing in on itself. Because stars are so ...
Powerpoint for today
... Pulsars are incredibly accurate clocks! Example: period of the first discovered "millisecond pulsar" is: ...
... Pulsars are incredibly accurate clocks! Example: period of the first discovered "millisecond pulsar" is: ...
Toys Watch the Sky - The Sun is a close star
... The Sun is a huge ball of glowing gases (mostly hydrogen and helium). It is the star at the centre of our Solar System. The Sun is located in an outer spiral arm of the Milky Way Galaxy, approximately 28,000 light-years from the galaxy's centre. (One light year is about 10 million million km.) In co ...
... The Sun is a huge ball of glowing gases (mostly hydrogen and helium). It is the star at the centre of our Solar System. The Sun is located in an outer spiral arm of the Milky Way Galaxy, approximately 28,000 light-years from the galaxy's centre. (One light year is about 10 million million km.) In co ...
Document
... Sunlight is reflected off the Earth, hits the Moon and bounces back to Earth Earthshine is seen in the faint glow our world gives to dark areas of the Moon The light carries information about Earth's atmosphere and surface properties Scientists see details in the light that betray different gases, e ...
... Sunlight is reflected off the Earth, hits the Moon and bounces back to Earth Earthshine is seen in the faint glow our world gives to dark areas of the Moon The light carries information about Earth's atmosphere and surface properties Scientists see details in the light that betray different gases, e ...
Sol_157a_midterm_2016
... So, we only need to use the linearly varying temperature of the planet in the expressions above to find the curve of the apparent brightness as a function of time. The result is shown in the figure below. ...
... So, we only need to use the linearly varying temperature of the planet in the expressions above to find the curve of the apparent brightness as a function of time. The result is shown in the figure below. ...
Slide 1
... 1. A cold cloud of gas and dust starts to contract, pulled together by gravity. It breaks up into several smaller clouds and each continues to contract. 2. Within a contracting cloud, each particle attracts every other particle, so that the cloud collapses towards its centre. It forms a rotating swi ...
... 1. A cold cloud of gas and dust starts to contract, pulled together by gravity. It breaks up into several smaller clouds and each continues to contract. 2. Within a contracting cloud, each particle attracts every other particle, so that the cloud collapses towards its centre. It forms a rotating swi ...
Properties of Stars - Mr. Carter`s Earth
... The Hertzsprung-Russell diagram is actually a graph that illustrates the relationship that exists between the average surface temperature of stars and their absolute magnitude, which is how bright they would appear to be if they were all the same distance away. Rather than speak of the brightness of ...
... The Hertzsprung-Russell diagram is actually a graph that illustrates the relationship that exists between the average surface temperature of stars and their absolute magnitude, which is how bright they would appear to be if they were all the same distance away. Rather than speak of the brightness of ...
Astronomy Study Guide
... 12. The largest visible light telescopes are now all reflecting telescope. 13. What other kinds of radiation are detected by telescopes? Infrared radiation, ultraviolet radiation, Xrays, and gamma rays 14. A building that contains one or more telescopes is called a(n) observatory 15. Why can the Hu ...
... 12. The largest visible light telescopes are now all reflecting telescope. 13. What other kinds of radiation are detected by telescopes? Infrared radiation, ultraviolet radiation, Xrays, and gamma rays 14. A building that contains one or more telescopes is called a(n) observatory 15. Why can the Hu ...
Slide 1
... Stellar Magnitude (brightness) Magnitude is the degree of brightness of a star. In 1856, British astronomer Norman Pogson proposed a quantitative scale of stellar magnitudes, which was adopted by the astronomical community. Each increment in magnitude corresponds to an increase in the amount of ene ...
... Stellar Magnitude (brightness) Magnitude is the degree of brightness of a star. In 1856, British astronomer Norman Pogson proposed a quantitative scale of stellar magnitudes, which was adopted by the astronomical community. Each increment in magnitude corresponds to an increase in the amount of ene ...
H-R Diagram - SFA Physics
... Now plot all the stars from Table 7 onto Figure 3. Table 7 is a list of the 30 stars nearest the sun and the majority of these stars are considered to be the most common types of stars in the galaxy. Transfer the main sequence curve from Figure 1 to Figure 3. ...
... Now plot all the stars from Table 7 onto Figure 3. Table 7 is a list of the 30 stars nearest the sun and the majority of these stars are considered to be the most common types of stars in the galaxy. Transfer the main sequence curve from Figure 1 to Figure 3. ...
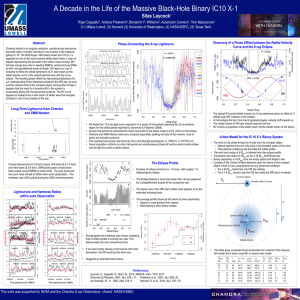
A Decade in the Life of the Massive Black-Hole Binary... Silas Laycock !
... galaxy IC 10. The Wolf Rayet + BH binary known as IC10 X-1 is regarded as one of the most massive stellar black holes; a class of objects representing the pinnacle of the stellar mass function. BH binaries occupy key roles in seeding SMBHs, producing long GRBs at birth, and gravitational waves at de ...
... galaxy IC 10. The Wolf Rayet + BH binary known as IC10 X-1 is regarded as one of the most massive stellar black holes; a class of objects representing the pinnacle of the stellar mass function. BH binaries occupy key roles in seeding SMBHs, producing long GRBs at birth, and gravitational waves at de ...
Deep Space Mystery Note Form 2
... companion star to raise its core temperature enough to ignite carbon fusion. The violent explosion of a massive star makes the expanding gases to glow briefly and brightly. During this short interval, a supernova can radiate as much energy as our Sun could emit over its life span. The explosion expe ...
... companion star to raise its core temperature enough to ignite carbon fusion. The violent explosion of a massive star makes the expanding gases to glow briefly and brightly. During this short interval, a supernova can radiate as much energy as our Sun could emit over its life span. The explosion expe ...
Chap 11 Characterizing Stars v2
... Determining stellar distances from Earth is the first step to understanding the nature of the stars. Distances to the nearer stars can be determined by stellar parallax, which is the apparent shift of a star’s location against the background stars while Earth moves along its orbit around the Sun. Th ...
... Determining stellar distances from Earth is the first step to understanding the nature of the stars. Distances to the nearer stars can be determined by stellar parallax, which is the apparent shift of a star’s location against the background stars while Earth moves along its orbit around the Sun. Th ...
Slide 1
... The diameter of a typical neutron star is only about 20 km. The outer crust of a neutron star is largely electrons and ...
... The diameter of a typical neutron star is only about 20 km. The outer crust of a neutron star is largely electrons and ...
REGIONAL exam 2013
... 5. Each question is worth one point. Tiebreaker questions are indicated with a (T#) in which the number indicates the order of consultation in the event of a tie. Tiebreaker questions count toward the overall raw score, and are only used as tiebreakers when there is a tie. In such cases, (T1) will b ...
... 5. Each question is worth one point. Tiebreaker questions are indicated with a (T#) in which the number indicates the order of consultation in the event of a tie. Tiebreaker questions count toward the overall raw score, and are only used as tiebreakers when there is a tie. In such cases, (T1) will b ...
Today`s Powerpoint
... If initial star mass < 8 MSun or so. (and remember: Maximum WD mass is 1.4 MSun , radius is about that of the Earth) 2. Neutron Star If initial mass > 8 MSun and < 25 MSun . ...
... If initial star mass < 8 MSun or so. (and remember: Maximum WD mass is 1.4 MSun , radius is about that of the Earth) 2. Neutron Star If initial mass > 8 MSun and < 25 MSun . ...
MIDTERM #1 AST209 - The Cosmos Feb 10, 2012 50 minutes
... C) They will not speed up at all, but move at a constant speed because they are in space and the rocket has nothing against which to push. D) It is impossible to say with only the information provided E) The one with the higher mass. 29. Why is it summer in the Northern Hemisphere when it is winter ...
... C) They will not speed up at all, but move at a constant speed because they are in space and the rocket has nothing against which to push. D) It is impossible to say with only the information provided E) The one with the higher mass. 29. Why is it summer in the Northern Hemisphere when it is winter ...
Lyra

Lyra (/ˈlaɪərə/; Latin for lyre, from Greek λύρα) is a small constellation. It is one of 48 listed by the 2nd century astronomer Ptolemy, and is one of the 88 constellations recognized by the International Astronomical Union. Lyra was often represented on star maps as a vulture or an eagle carrying a lyre, and hence sometimes referred to as Aquila Cadens or Vultur Cadens. Beginning at the north, Lyra is bordered by Draco, Hercules, Vulpecula, and Cygnus. Lyra is visible from the northern hemisphere from spring through autumn, and nearly overhead, in temperate latitudes, during the summer months. From the southern hemisphere, it is visible low in the northern sky during the winter months.The lucida or brightest star—and one of the brightest stars in the sky—is the white main sequence star Vega, a corner of the Summer Triangle. Beta Lyrae is the prototype of a class of stars known as Beta Lyrae variables, binary stars so close to each other that they become egg-shaped and material flows from one to the other. Epsilon Lyrae, known informally as the Double Double, is a complex multiple star system. Lyra also hosts the Ring Nebula, the second-discovered and best-known planetary nebula.