Methods Of Discovering Extra solar Planets.
... • This method is rarely used, by that the planet and the star must be aligned in the direction astronomers are looking at. • That is the only time astronomers used this method, but it is vital and can be used if ...
... • This method is rarely used, by that the planet and the star must be aligned in the direction astronomers are looking at. • That is the only time astronomers used this method, but it is vital and can be used if ...
ch16 b - Manasquan Public Schools
... give Earth perfect conditions to support life as we know it. ...
... give Earth perfect conditions to support life as we know it. ...
How are stars formed
... Stars of roughly sun’s mass ( < 8 solar masses) do not have necessary gravitational pull to create heat and pressure necessary to begin fusing carbon ...
... Stars of roughly sun’s mass ( < 8 solar masses) do not have necessary gravitational pull to create heat and pressure necessary to begin fusing carbon ...
Beyond the Solar System Homework for Geology 8
... B. Red giant E. White dwarf 23. The final stage in the evolution of only the most massive stars is a: A. Black hole C. Black dwarf D. Main-sequence star B. Red giant E. White dwarf 24. A star that spins rapidly and emits pulsating radio waves is called a: A. Black hole C. Black dwarf D. Red giant B. ...
... B. Red giant E. White dwarf 23. The final stage in the evolution of only the most massive stars is a: A. Black hole C. Black dwarf D. Main-sequence star B. Red giant E. White dwarf 24. A star that spins rapidly and emits pulsating radio waves is called a: A. Black hole C. Black dwarf D. Red giant B. ...
Phobos
... the middle of the night and is highest in the south at dawn. Mercury reaches greatest elongation in the morning sky this month, but is better viewed from the southern hemisphere. Dates & Time: Thursday 1st March is the 60th day of the year and it is also number 2454160 in the Julian Calendar. The Su ...
... the middle of the night and is highest in the south at dawn. Mercury reaches greatest elongation in the morning sky this month, but is better viewed from the southern hemisphere. Dates & Time: Thursday 1st March is the 60th day of the year and it is also number 2454160 in the Julian Calendar. The Su ...
Rogava_Course_-_First_lecture
... its Roche lobe and the other does not. Gas from the surface of the Roche lobe filling component (donor) is transferred to the other, accreting star. The mass transfer dominates the evolution of the system; the inflowing gas may form accretion disc around the accreting star. Examples: X-ray binaries ...
... its Roche lobe and the other does not. Gas from the surface of the Roche lobe filling component (donor) is transferred to the other, accreting star. The mass transfer dominates the evolution of the system; the inflowing gas may form accretion disc around the accreting star. Examples: X-ray binaries ...
No Slide Title
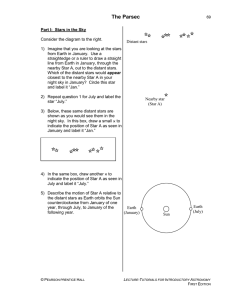
... observer. Remember looking at your finger through the left and then right eye? One parsec is the distance an object must be in order to have a parallax of one arc second. One parsec = 3.3 light years Alpha Centauri is the closest star. Most stars are too distant to measure a parallax. ...
... observer. Remember looking at your finger through the left and then right eye? One parsec is the distance an object must be in order to have a parallax of one arc second. One parsec = 3.3 light years Alpha Centauri is the closest star. Most stars are too distant to measure a parallax. ...
Double Stars in Scorpio`s Claws
... but you should be able to see two dim red stars that form a line with brighter ρ Scorpii between them. ...
... but you should be able to see two dim red stars that form a line with brighter ρ Scorpii between them. ...
Laboratory Title
... 1. The students with the red “stars”(balloons) put a small Styrofoam ball inside, those with a white “star” are to put a marble or bead inside, and those with a blue “star” are to put a tablespoon of powder or confetti inside. 2. The student with the yellow balloon will go first, the student without ...
... 1. The students with the red “stars”(balloons) put a small Styrofoam ball inside, those with a white “star” are to put a marble or bead inside, and those with a blue “star” are to put a tablespoon of powder or confetti inside. 2. The student with the yellow balloon will go first, the student without ...
Document
... a. Always has the same luminosity. b. Has some means of knowing its luminosity without first needing to know its distance. c. Can vary in brightness (as long as it always has the same average luminosity). d. Has a known absolute magnitude. e. Always gives off the same amount of energy, regardless of ...
... a. Always has the same luminosity. b. Has some means of knowing its luminosity without first needing to know its distance. c. Can vary in brightness (as long as it always has the same average luminosity). d. Has a known absolute magnitude. e. Always gives off the same amount of energy, regardless of ...
reach for the stars
... 9. What is Alpha Orionis better known as? (1 pt) Betelgeuse 10. What famous asterism is formed by the three stars Altair, Deneb, and Vega? (1 pt) ...
... 9. What is Alpha Orionis better known as? (1 pt) Betelgeuse 10. What famous asterism is formed by the three stars Altair, Deneb, and Vega? (1 pt) ...
The most important questions to study for the exam
... 6. A star appears to move back and forth with a period of exactly 1 year with respect to a distant galaxy that appears close to it in our sky. What is the most likely cause of this observed motion? • The observed motion is simply the motion of the star around the center of the galaxy. ...
... 6. A star appears to move back and forth with a period of exactly 1 year with respect to a distant galaxy that appears close to it in our sky. What is the most likely cause of this observed motion? • The observed motion is simply the motion of the star around the center of the galaxy. ...
AY 20 Fall 2010
... 2. The net force acting on a particle is proportional to the object’s mass and and its resultant acceleration the rate of change of momentum of a particle is equal to the net force applied Fnet = ni=1Fi = dp/dt = mdv/dt =ma ...
... 2. The net force acting on a particle is proportional to the object’s mass and and its resultant acceleration the rate of change of momentum of a particle is equal to the net force applied Fnet = ni=1Fi = dp/dt = mdv/dt =ma ...
Chapter 13: The Death of Stars
... In a binary system, each star controls a finite region of space, bounded by the Roche Lobes (or Roche surfaces). ...
... In a binary system, each star controls a finite region of space, bounded by the Roche Lobes (or Roche surfaces). ...
The magnitude scale
... The faintest object visible to the naked eye from a dark site has magnitude six. Sirius, the brightest star, has magnitude -1.4. The planets, Mercury, Venus, Mars, Jupiter and Saturn vary in brightness, but are generally quite bright - the brightest being Venus which can reach a magnitude of -4.4. ...
... The faintest object visible to the naked eye from a dark site has magnitude six. Sirius, the brightest star, has magnitude -1.4. The planets, Mercury, Venus, Mars, Jupiter and Saturn vary in brightness, but are generally quite bright - the brightest being Venus which can reach a magnitude of -4.4. ...
8hrdiagram1s
... If you know the luminosity and you measure the flux you can find the distance (F = L/4pd2) Called spectroscopic parallax ...
... If you know the luminosity and you measure the flux you can find the distance (F = L/4pd2) Called spectroscopic parallax ...
The Warrumbungle Observer The Warrumbungle Observer
... constellation Capricorn which looks like the letter ‘D’ in the eastern evening sky. Careful observations of Jupiter’s position each night will show Jupiter moving compared to the other stars in Capricorn and appearing to be moving up the left side of ‘the letter D’ Four of Jupiter’s moons are easily ...
... constellation Capricorn which looks like the letter ‘D’ in the eastern evening sky. Careful observations of Jupiter’s position each night will show Jupiter moving compared to the other stars in Capricorn and appearing to be moving up the left side of ‘the letter D’ Four of Jupiter’s moons are easily ...
The Life Cycle of Stars Webquest
... 3. Understand the forces involved in stars that maintain this nuclear reaction and how these forces change as the star ages. 4. Explore the stages stars progress through from birth to death and how the death of a star depends on its ...
... 3. Understand the forces involved in stars that maintain this nuclear reaction and how these forces change as the star ages. 4. Explore the stages stars progress through from birth to death and how the death of a star depends on its ...
IB_Op_F_04 - Effectsmeister
... Most of the stars seem to be along a line from the upper left corner to the lower right corner of the HR Diagram. Stars which fall into this category of stars are called main sequence stars . Does our Sun fit into this category? White dwarfs are hot dim stars while red giants are bright cool stars. ...
... Most of the stars seem to be along a line from the upper left corner to the lower right corner of the HR Diagram. Stars which fall into this category of stars are called main sequence stars . Does our Sun fit into this category? White dwarfs are hot dim stars while red giants are bright cool stars. ...
Supernovae - Michigan State University
... Little Ghost Nebula distance 2-5 kLy blue: OIII green: HII red: NII ...
... Little Ghost Nebula distance 2-5 kLy blue: OIII green: HII red: NII ...
Stars_Galaxies_Introduction - Etiwanda E
... question to each group Project may still include typical science assignments/routines Incorporates technology at many different levels Students are able to differentiate within the project by choice of assignment ...
... question to each group Project may still include typical science assignments/routines Incorporates technology at many different levels Students are able to differentiate within the project by choice of assignment ...
Lyra

Lyra (/ˈlaɪərə/; Latin for lyre, from Greek λύρα) is a small constellation. It is one of 48 listed by the 2nd century astronomer Ptolemy, and is one of the 88 constellations recognized by the International Astronomical Union. Lyra was often represented on star maps as a vulture or an eagle carrying a lyre, and hence sometimes referred to as Aquila Cadens or Vultur Cadens. Beginning at the north, Lyra is bordered by Draco, Hercules, Vulpecula, and Cygnus. Lyra is visible from the northern hemisphere from spring through autumn, and nearly overhead, in temperate latitudes, during the summer months. From the southern hemisphere, it is visible low in the northern sky during the winter months.The lucida or brightest star—and one of the brightest stars in the sky—is the white main sequence star Vega, a corner of the Summer Triangle. Beta Lyrae is the prototype of a class of stars known as Beta Lyrae variables, binary stars so close to each other that they become egg-shaped and material flows from one to the other. Epsilon Lyrae, known informally as the Double Double, is a complex multiple star system. Lyra also hosts the Ring Nebula, the second-discovered and best-known planetary nebula.