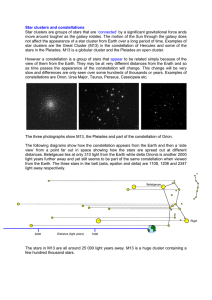
Stars
... star really looks from Earth. The farther away from us, the dimmer the star looks. • Absolute Magnitude – How bright the star really is. If all stars were the same distance from us, how bright would it look compared to the other stars? ...
... star really looks from Earth. The farther away from us, the dimmer the star looks. • Absolute Magnitude – How bright the star really is. If all stars were the same distance from us, how bright would it look compared to the other stars? ...
Stars - White Plains Public Schools
... Compared to other stars it is not too bright and not too hot. It’s just perfect! ...
... Compared to other stars it is not too bright and not too hot. It’s just perfect! ...
Stars…Giants, Supergiants, Dwarfs….
... luminous than others of the same color (=temperature). • There is a wide range in luminosity (and size) for stars of the same temperature. • Leads to the classification of dwarfs, giants, and supergiants ...
... luminous than others of the same color (=temperature). • There is a wide range in luminosity (and size) for stars of the same temperature. • Leads to the classification of dwarfs, giants, and supergiants ...
Properties of Stars
... Measuring Distance to Stars • Parallax is determined by taking a picture of a star at one time, and another picture six months later; using the angle between its apparent shift, astronomers can determine how far away it is • The nearest stars have large parallax angles, while those of distant stars ...
... Measuring Distance to Stars • Parallax is determined by taking a picture of a star at one time, and another picture six months later; using the angle between its apparent shift, astronomers can determine how far away it is • The nearest stars have large parallax angles, while those of distant stars ...
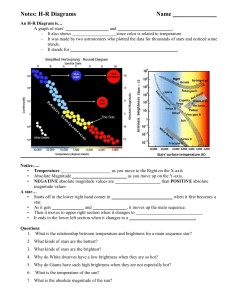
H-R Diagram Notes
... • Temperature ______________________ as you move to the Right on the X-axis • Absolute Magnitude ________________________ as you move up on the Y-axis. • NEGATIVE absolute magnitude values are ____________________ than POSITIVE absolute magnitude values A star… • Starts off in the lower right hand c ...
... • Temperature ______________________ as you move to the Right on the X-axis • Absolute Magnitude ________________________ as you move up on the Y-axis. • NEGATIVE absolute magnitude values are ____________________ than POSITIVE absolute magnitude values A star… • Starts off in the lower right hand c ...
A Brief History of Planetary Science
... Photometry We want to get an accurate quantitative measure of brightness Our system is composed of two things: ...
... Photometry We want to get an accurate quantitative measure of brightness Our system is composed of two things: ...
Astronomy word grid
... 40. The largest planet 42. The line in the sky along which the Sun and the planets move Down 1. An object with an escape velocity greater than the speed of light 2. A huge cloud of low density gas sometimes shining 3. A huge collection of some hundred thousand million stars 5. A ball of ice and rock ...
... 40. The largest planet 42. The line in the sky along which the Sun and the planets move Down 1. An object with an escape velocity greater than the speed of light 2. A huge cloud of low density gas sometimes shining 3. A huge collection of some hundred thousand million stars 5. A ball of ice and rock ...
Astrophysics
... star -- so if it looks dim it must be a very long way away A red star is not as bright, so if it looks bright it must be relatively close. For example: Sirius and Alpha Centauri are similar in apparent brightness but Sirius is bluish while A.Cent. is yellowish ...
... star -- so if it looks dim it must be a very long way away A red star is not as bright, so if it looks bright it must be relatively close. For example: Sirius and Alpha Centauri are similar in apparent brightness but Sirius is bluish while A.Cent. is yellowish ...
Exploring Space
... Traditional telescopes (optical) detect visible light (small part of the spectrum) Radio telescopes detect non-visible wavelengths ...
... Traditional telescopes (optical) detect visible light (small part of the spectrum) Radio telescopes detect non-visible wavelengths ...
Answer titese questions on a piece of loose leaf paper.
... I I . The Hcrczspiung-Russcll diagram shows the relationship between wliai two charaeteiistios of stars? 12- More than 90% of all stars arc cotisiderx;d stars and can be found in a diagonal path aaoss the center of the H-R diagram. 13. Within the main sequence, surface temperatures increase as absol ...
... I I . The Hcrczspiung-Russcll diagram shows the relationship between wliai two charaeteiistios of stars? 12- More than 90% of all stars arc cotisiderx;d stars and can be found in a diagonal path aaoss the center of the H-R diagram. 13. Within the main sequence, surface temperatures increase as absol ...
WHAT IS A STAR? - cloudfront.net
... NEBULA: A large cloud of gas (helium and hydrogen) and dust which forms into a star. Dust and gas particles exert a gravitational force on each other ...
... NEBULA: A large cloud of gas (helium and hydrogen) and dust which forms into a star. Dust and gas particles exert a gravitational force on each other ...
here - ESA Science
... Information from Hipparcos has enabled astronomers to trace the Sun’s passage through the Galaxy back in time. This has shown that over the last 500 million years the Sun has passed through four of the Milky Way’s spiral arms. The times that these traverses occurred appear to coincide with extended ...
... Information from Hipparcos has enabled astronomers to trace the Sun’s passage through the Galaxy back in time. This has shown that over the last 500 million years the Sun has passed through four of the Milky Way’s spiral arms. The times that these traverses occurred appear to coincide with extended ...
Slide 1
... even thought of before the structure of the Solar System and Earth’s position in it was found out in the 16th century. ...
... even thought of before the structure of the Solar System and Earth’s position in it was found out in the 16th century. ...
Section 25.1 Properties of Stars
... Binary Stars and Stellar Mass A binary star is one of two stars revolving around a common center of mass under their mutual gravitational attraction. Binary stars are used to determine the star property most difficult to calculate—its mass. Common Center of Mass ...
... Binary Stars and Stellar Mass A binary star is one of two stars revolving around a common center of mass under their mutual gravitational attraction. Binary stars are used to determine the star property most difficult to calculate—its mass. Common Center of Mass ...
The Science behind the Stars ctY Astrophysics by Spencer McClung
... of images of light from a star and had to determine the mass of its binary companion. For an hour we used two sticks to monitor small changes in the star’s light and then used a very long series of calculations with very big numbers. In the end, we were off by a couple orders of magnitude, but this ...
... of images of light from a star and had to determine the mass of its binary companion. For an hour we used two sticks to monitor small changes in the star’s light and then used a very long series of calculations with very big numbers. In the end, we were off by a couple orders of magnitude, but this ...
Astronomy – Interpreting Main Sequence Star Data The
... Astronomy – Interpreting Main Sequence Star Data The classification of stars by surface temperature and spectral pattern is a painstaking process requiring the efforts of many scientists from hundreds of observatories around the world. To make it easier to refer to the different types of main sequen ...
... Astronomy – Interpreting Main Sequence Star Data The classification of stars by surface temperature and spectral pattern is a painstaking process requiring the efforts of many scientists from hundreds of observatories around the world. To make it easier to refer to the different types of main sequen ...
stars - Legacy High School
... 16. The less massive stars end their lifecycle as a _____________ ___________________. 17. The most massive stars will end up as a ___________________ _______________. 18. When nuclear fusion is occurring in a star, the element_____________ fuses to form______________. 19. When objects are moving aw ...
... 16. The less massive stars end their lifecycle as a _____________ ___________________. 17. The most massive stars will end up as a ___________________ _______________. 18. When nuclear fusion is occurring in a star, the element_____________ fuses to form______________. 19. When objects are moving aw ...
Lecture 10 February 13
... Astrometric Binary proper motion wiggles to show orbit Spectrum Binary spectra of two stars of different type Spectroscopic Binary Doppler shift shows orbital motion Eclipsing Binary light varies Half of all stars are in binaries…. Binary stars are formed at birth. Both components will have same age ...
... Astrometric Binary proper motion wiggles to show orbit Spectrum Binary spectra of two stars of different type Spectroscopic Binary Doppler shift shows orbital motion Eclipsing Binary light varies Half of all stars are in binaries…. Binary stars are formed at birth. Both components will have same age ...
KMS Universe Test Study Guide
... 6) Why does the sun have such a great apparent magnitude, when it has only an average absolute magnitude? The Sun is very close to us, so it appears to be brighter than it is compared to other stars in the Universe. 7) Why are red giant stars so bright, when they are among the coolest of stars? Beca ...
... 6) Why does the sun have such a great apparent magnitude, when it has only an average absolute magnitude? The Sun is very close to us, so it appears to be brighter than it is compared to other stars in the Universe. 7) Why are red giant stars so bright, when they are among the coolest of stars? Beca ...
Astronomy Objectives
... Red-shift → going away from us; blue-shift → coming toward us The Hubble Law; state it and describe the evidence that supports it Big Bang Theory: be able to explain how the universe was formed according to this theory; know the particles formed at each step, but not specific times or temperatures ...
... Red-shift → going away from us; blue-shift → coming toward us The Hubble Law; state it and describe the evidence that supports it Big Bang Theory: be able to explain how the universe was formed according to this theory; know the particles formed at each step, but not specific times or temperatures ...
IV International Astronomy Olympiad
... military ships: to construct very small black holes from their material (patent yzarc048UA7). Estimate the diameter of a black hole constructed using this patent from a ship with the mass of 5000 tn (1 tn = 1000 kg). What physical object has a size of the same order of magnitude? Describe propagatio ...
... military ships: to construct very small black holes from their material (patent yzarc048UA7). Estimate the diameter of a black hole constructed using this patent from a ship with the mass of 5000 tn (1 tn = 1000 kg). What physical object has a size of the same order of magnitude? Describe propagatio ...
Hipparcos

Hipparcos was a scientific satellite of the European Space Agency (ESA), launched in 1989 and operated until 1993. It was the first space experiment devoted to precision astrometry, the accurate measurement of the positions of celestial objects on the sky. This permitted the accurate determination of proper motions and parallaxes of stars, allowing a determination of their distance and tangential velocity. When combined with radial-velocity measurements from spectroscopy, this pinpointed all six quantities needed to determine the motion of stars. The resulting Hipparcos Catalogue, a high-precision catalogue of more than 118,200 stars, was published in 1997. The lower-precision Tycho Catalogue of more than a million stars was published at the same time, while the enhanced Tycho-2 Catalogue of 2.5 million stars was published in 2000. Hipparcos ' follow-up mission, Gaia, was launched in 2013.The word ""Hipparcos"" is an acronym for High precision parallax collecting satellite and also a reference to the ancient Greek astronomer Hipparchus of Nicaea, who is noted for applications of trigonometry to astronomy and his discovery of the precession of the equinoxes.