Size Color and Temperature
... Some stars are much larger than the Sun. Giant and supergiant stars range from ten to hundreds of times larger. A supergiant called Betelgeuse (BEET-uhl-JOOZ) is more than 600 times greater in diameter than the Sun. If Betelgeuse replaced the Sun, it would fill space in our solar system well beyond ...
... Some stars are much larger than the Sun. Giant and supergiant stars range from ten to hundreds of times larger. A supergiant called Betelgeuse (BEET-uhl-JOOZ) is more than 600 times greater in diameter than the Sun. If Betelgeuse replaced the Sun, it would fill space in our solar system well beyond ...
Characteristics of stars powerpoint
... • The brightness a star would have if it was a standard distance from Earth • This requires an astronomer to determine both the apparent magnitude and distance from Earth • Ex: calculating absolute magnitude by making all stars 1 light-year away ...
... • The brightness a star would have if it was a standard distance from Earth • This requires an astronomer to determine both the apparent magnitude and distance from Earth • Ex: calculating absolute magnitude by making all stars 1 light-year away ...
Consider Average Stars
... your cursor to the time display at the top left, and advance the minutes quickly by holding down the arrow key on your keyboard. This makes the sun set rapidly – and you can watch the stars come out! ...
... your cursor to the time display at the top left, and advance the minutes quickly by holding down the arrow key on your keyboard. This makes the sun set rapidly – and you can watch the stars come out! ...
powerpoint - Physics @ IUPUI
... period of pulsation and their absolute brightness. • The longer the period, the bigger the star is, and the brighter it is (sort of like a bigger bell has a larger period of vibration). • This allows us to measure distances (especially since these are very bright stars which can be seen a LONG dista ...
... period of pulsation and their absolute brightness. • The longer the period, the bigger the star is, and the brighter it is (sort of like a bigger bell has a larger period of vibration). • This allows us to measure distances (especially since these are very bright stars which can be seen a LONG dista ...
Life cycle of the Stars - Christos N. Hadjichristidis
... repulsive force of electrons. • http://imgsrc.hubblesite.org/hu/db/2002/1 0/videos/b/formats/low_mpeg.mpg ...
... repulsive force of electrons. • http://imgsrc.hubblesite.org/hu/db/2002/1 0/videos/b/formats/low_mpeg.mpg ...
Binary Orbits
... determine parameters e.g. period and line of sight velocities – masses – done in optical and X-ray • Fact that a large fraction of stars are found in binaries indicate stars are formed in groups through gravitational collapse of ...
... determine parameters e.g. period and line of sight velocities – masses – done in optical and X-ray • Fact that a large fraction of stars are found in binaries indicate stars are formed in groups through gravitational collapse of ...
Cosmic Distance Ladder
... in one year = 9.46E17 cm=6.324E4 AU • Parsec (pc) = 3.26 ly = 3.08E18 cm • Astronomical Unit (AU) = 149.6E13 cm ...
... in one year = 9.46E17 cm=6.324E4 AU • Parsec (pc) = 3.26 ly = 3.08E18 cm • Astronomical Unit (AU) = 149.6E13 cm ...
Death of Stars
... - a sparse interstellar medium Stars form in dense clouds of this medium Gravity of denser parts of the cloud starts to attract surrounding material Increased rotation of core may lead to fragmentation that forms clusters and, later, planets Restricted movement across magnetic fields causes a disc t ...
... - a sparse interstellar medium Stars form in dense clouds of this medium Gravity of denser parts of the cloud starts to attract surrounding material Increased rotation of core may lead to fragmentation that forms clusters and, later, planets Restricted movement across magnetic fields causes a disc t ...
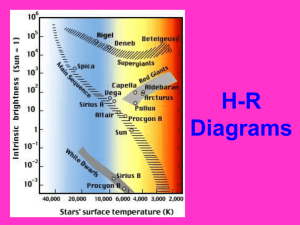
H-R Diagrams
... – It also shows color since color is related to temperature – It was made by two astronomers who plotted the data for thousands of stars and noticed some trends. ...
... – It also shows color since color is related to temperature – It was made by two astronomers who plotted the data for thousands of stars and noticed some trends. ...
Unit 12 Guide: Concepts of Earth Science Stars, Galaxies, and the
... Stars, Galaxies, and the Universe Key Concepts and Questions to Be Able to Explain and Answer: 1. What are the names and characteristics of the three types of galaxies? What type of galaxy is the Milky Way galaxy? 2. What evidence do scientists use to support the Big Bang Theory? Explain the sequenc ...
... Stars, Galaxies, and the Universe Key Concepts and Questions to Be Able to Explain and Answer: 1. What are the names and characteristics of the three types of galaxies? What type of galaxy is the Milky Way galaxy? 2. What evidence do scientists use to support the Big Bang Theory? Explain the sequenc ...
changing constellations
... winter, but during summer. positions So, what is going on? The ause each day bec r yea the ing change dur n 2.5 million the Earth moves more tha the Sun (or und aro kilometres as it orbits stars The it). orb full a about 1/365th of dually gra ht nig mid at ds hea above our g a full cycle in change e ...
... winter, but during summer. positions So, what is going on? The ause each day bec r yea the ing change dur n 2.5 million the Earth moves more tha the Sun (or und aro kilometres as it orbits stars The it). orb full a about 1/365th of dually gra ht nig mid at ds hea above our g a full cycle in change e ...
doc - IAC
... Massive stars are much heavier than the Sun. They can be up to 10 or 100 times more massive. They stand out because of their high luminosity. These stars can become a million times brighter than the Sun. Their masses can be measured dynamically, in the same way as planetary masses are measured. The ...
... Massive stars are much heavier than the Sun. They can be up to 10 or 100 times more massive. They stand out because of their high luminosity. These stars can become a million times brighter than the Sun. Their masses can be measured dynamically, in the same way as planetary masses are measured. The ...
File
... 8-25 X larger than our Sun Consume their fuel very fast – die more quickly and more violently Star expands into a Supergiant which causes the core to collapse and the outer portion to explode creating a Supernova then a Neutron Star ...
... 8-25 X larger than our Sun Consume their fuel very fast – die more quickly and more violently Star expands into a Supergiant which causes the core to collapse and the outer portion to explode creating a Supernova then a Neutron Star ...
The Family of Stars
... With ground-based telescopes, we can measure parallaxes p ≥ 0.02 arc sec => d ≤ 50 pc ...
... With ground-based telescopes, we can measure parallaxes p ≥ 0.02 arc sec => d ≤ 50 pc ...
the california planet survey. i. four new giant exoplanets
... * The host star, HD 13931, is also similar to the Sun in mass (M= 1.02 M⊙) and metallicity. HD 13931 b is one of only four known RV-detected planets with orbital periods longer than 10 yr. The other such planets are all in multi-planet systems. GJ 179 b * Is a Jovian-mass (M sin i = 0.82 MJup ) plan ...
... * The host star, HD 13931, is also similar to the Sun in mass (M= 1.02 M⊙) and metallicity. HD 13931 b is one of only four known RV-detected planets with orbital periods longer than 10 yr. The other such planets are all in multi-planet systems. GJ 179 b * Is a Jovian-mass (M sin i = 0.82 MJup ) plan ...
Life Cycle of Stars
... • Luminosity – brightness, or energy output of a star per second • Temperature- in stars, the temperature determines the luminosity and the rate of nuclear reactions (fusion) ...
... • Luminosity – brightness, or energy output of a star per second • Temperature- in stars, the temperature determines the luminosity and the rate of nuclear reactions (fusion) ...
Slide 1
... The mass loss rates for OB (and WR) stars are currently in question at the order-of-magnitude level ( see Fig 1 ) with profound implications for stellar evolution, mass loss processes across the HR diagram and the injection of enriched gas into the ISM. The recognition of clumped and/or porous radia ...
... The mass loss rates for OB (and WR) stars are currently in question at the order-of-magnitude level ( see Fig 1 ) with profound implications for stellar evolution, mass loss processes across the HR diagram and the injection of enriched gas into the ISM. The recognition of clumped and/or porous radia ...
Hipparcos

Hipparcos was a scientific satellite of the European Space Agency (ESA), launched in 1989 and operated until 1993. It was the first space experiment devoted to precision astrometry, the accurate measurement of the positions of celestial objects on the sky. This permitted the accurate determination of proper motions and parallaxes of stars, allowing a determination of their distance and tangential velocity. When combined with radial-velocity measurements from spectroscopy, this pinpointed all six quantities needed to determine the motion of stars. The resulting Hipparcos Catalogue, a high-precision catalogue of more than 118,200 stars, was published in 1997. The lower-precision Tycho Catalogue of more than a million stars was published at the same time, while the enhanced Tycho-2 Catalogue of 2.5 million stars was published in 2000. Hipparcos ' follow-up mission, Gaia, was launched in 2013.The word ""Hipparcos"" is an acronym for High precision parallax collecting satellite and also a reference to the ancient Greek astronomer Hipparchus of Nicaea, who is noted for applications of trigonometry to astronomy and his discovery of the precession of the equinoxes.