Evolution of a Protostar
... A life track illustrates a star's surface temperature and luminosity at different moments in time. ...
... A life track illustrates a star's surface temperature and luminosity at different moments in time. ...
Y-band Imaging of Extragalatic Fields and High redshift
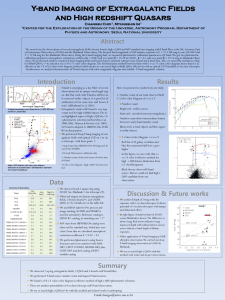
... A0V stars from HIPPARCOS catalog were observed for standard star, which have zero color. From that we calculated atmospheric ...
... A0V stars from HIPPARCOS catalog were observed for standard star, which have zero color. From that we calculated atmospheric ...
Notes_ stars and sun
... planetary nebula. • A planetary nebula looks like a beautiful colorful cloud. • Planetary nebula are usually visible for 50,000 years before it is absorbed by the atmosphere. • When a giant star dies, it causes a huge explosion known as a supernova. • According to NASA, supernova’s are the larg ...
... planetary nebula. • A planetary nebula looks like a beautiful colorful cloud. • Planetary nebula are usually visible for 50,000 years before it is absorbed by the atmosphere. • When a giant star dies, it causes a huge explosion known as a supernova. • According to NASA, supernova’s are the larg ...
Student Literacy
... You have probably wondered how far away from Earth are the celestial bodies you see in the universe, the space that consists of all matter, all light and all forms of radiation and energy. Stars are so far away that our present mode of space travel would take more than a lifetime to reach the neares ...
... You have probably wondered how far away from Earth are the celestial bodies you see in the universe, the space that consists of all matter, all light and all forms of radiation and energy. Stars are so far away that our present mode of space travel would take more than a lifetime to reach the neares ...
Define the following terms in the space provided
... Answer the following Multiple Choice Questions by circling the correct response. 1) During Spring Break you and your friends plan to travel south to Cancun, Mexico for a week of sun and fun. You arrive in Cancun on a clear night. You look up at the stars and notice that they appear different that th ...
... Answer the following Multiple Choice Questions by circling the correct response. 1) During Spring Break you and your friends plan to travel south to Cancun, Mexico for a week of sun and fun. You arrive in Cancun on a clear night. You look up at the stars and notice that they appear different that th ...
Amanda Boyle Starstuff
... and most luminous stars are born first, and there are only a few of these O and B Stars. As you go down the line, more and more of each kind exist with the most common being M. Our Sun is a G. Not as in a gangster, or bro though in a way our sun is a bro because without the sun we would be dead. Bec ...
... and most luminous stars are born first, and there are only a few of these O and B Stars. As you go down the line, more and more of each kind exist with the most common being M. Our Sun is a G. Not as in a gangster, or bro though in a way our sun is a bro because without the sun we would be dead. Bec ...
2 Measurements in Astronomy
... Measurements in Astronomy Astronomical unit: distance from Earth to the Sun (about 150,000,000 kilometers, or 93,000,000 miles). Used for measuring distances within our solar system. Light year: the distance light travels in one year (nearly 10 trillion kilometers or 6 trillion miles). Used for ...
... Measurements in Astronomy Astronomical unit: distance from Earth to the Sun (about 150,000,000 kilometers, or 93,000,000 miles). Used for measuring distances within our solar system. Light year: the distance light travels in one year (nearly 10 trillion kilometers or 6 trillion miles). Used for ...
ASTR-1020: Astronomy II Course Lecture Notes - Faculty
... on the main sequence for 57 thousand years, whereas a star like Vega (A0 V) will remain for 370 million years (Vega is relatively young), and an M0 V star will remain on the main sequence for 57 billion years! Since the Universe is about 12-14 billion years old, no M0 star has yet evolved off of the ...
... on the main sequence for 57 thousand years, whereas a star like Vega (A0 V) will remain for 370 million years (Vega is relatively young), and an M0 V star will remain on the main sequence for 57 billion years! Since the Universe is about 12-14 billion years old, no M0 star has yet evolved off of the ...
STAR TYPES
... Most stars, including the sun, are "main sequence stars," fueled by nuclear fusion converting hydrogen into helium. For these stars, the hotter they are, the brighter. These stars are in the most stable part of their existence; this stage generally lasts for about 5 billion years. As stars begin to ...
... Most stars, including the sun, are "main sequence stars," fueled by nuclear fusion converting hydrogen into helium. For these stars, the hotter they are, the brighter. These stars are in the most stable part of their existence; this stage generally lasts for about 5 billion years. As stars begin to ...
Lecture 2 - Lines in the Sky
... the sky. We will look at two methods of measuring locations in the sky. • Both methods require measuring angles. • These methods have long been used not only for timekeeping but for navigation as well. • But first we need to define some terms ...
... the sky. We will look at two methods of measuring locations in the sky. • Both methods require measuring angles. • These methods have long been used not only for timekeeping but for navigation as well. • But first we need to define some terms ...
Chapter 3: the Sun
... radial velocity. • Otherwise (if the orbit is inclined at an angle i relative to the plane of the sky) the radial velocities are a sinusoidal function of time. The minimum and maximum velocities (about the centre of mass velocity) are given by ...
... radial velocity. • Otherwise (if the orbit is inclined at an angle i relative to the plane of the sky) the radial velocities are a sinusoidal function of time. The minimum and maximum velocities (about the centre of mass velocity) are given by ...
Comet Pan-Starrs 12 March 2013
... Crab. July 4, 1054. Seen in Asia and America Tycho’s supernova. 1572 Kepler’s supernova. 1604 S Andromedae (in M31). 1885 SN 1987A (in LMC). 1987 ...
... Crab. July 4, 1054. Seen in Asia and America Tycho’s supernova. 1572 Kepler’s supernova. 1604 S Andromedae (in M31). 1885 SN 1987A (in LMC). 1987 ...
4. How can we select stars whose planets are likely homes for life?
... Travel between stars is nearly impossible because the distances are too great and nature has imposed a very real speed limit that we can not exceed. Nothing can travel faster than the speed of light, and human travel can not be expected to exceed even a small fraction of the speed of light. Therefor ...
... Travel between stars is nearly impossible because the distances are too great and nature has imposed a very real speed limit that we can not exceed. Nothing can travel faster than the speed of light, and human travel can not be expected to exceed even a small fraction of the speed of light. Therefor ...
ASTR100 Class 01 - University of Maryland Department of
... What would happen to a protostar that formed without any rotation at all? A. Its jets would go in multiple directions. B. It would not have planets. C. It would be very bright in the infrared. D. It would not be round. ...
... What would happen to a protostar that formed without any rotation at all? A. Its jets would go in multiple directions. B. It would not have planets. C. It would be very bright in the infrared. D. It would not be round. ...
File
... During the late 1800s and early 1900s, many scientists were using telescopes to catalog and classify all of the stars and other objects visible from Earth. Scientists noticed that there was great variation in the brightness and color of stars. Spectroscopes, which split white light into its componen ...
... During the late 1800s and early 1900s, many scientists were using telescopes to catalog and classify all of the stars and other objects visible from Earth. Scientists noticed that there was great variation in the brightness and color of stars. Spectroscopes, which split white light into its componen ...
Seasons and the Changing Sky
... • Rising and setting of Sun, Moon, stars as viewed from Earth → Rotating celestial sphere • Celestial poles: the points around which the stars appear to rotate • Celestial equator: an extension of the Earth’s equator onto the celestial sphere ...
... • Rising and setting of Sun, Moon, stars as viewed from Earth → Rotating celestial sphere • Celestial poles: the points around which the stars appear to rotate • Celestial equator: an extension of the Earth’s equator onto the celestial sphere ...
First young loose association in the northern hemisphere?
... presence of nearby gas can help to disentangle them from older ones. Nevertheless, in the RasTyc sample, we discovered 4 lithium-rich field stars displaying the same space motion, which are located within a few degrees from each other on the celestial sphere near the Cepheus-Cassiopeia complex and a ...
... presence of nearby gas can help to disentangle them from older ones. Nevertheless, in the RasTyc sample, we discovered 4 lithium-rich field stars displaying the same space motion, which are located within a few degrees from each other on the celestial sphere near the Cepheus-Cassiopeia complex and a ...
Wavelength
... • Eventually, the outer parts grow larger and drift out into space creating a planetary nebula. ...
... • Eventually, the outer parts grow larger and drift out into space creating a planetary nebula. ...
Reach for the Stars B
... 4. What will eventually cause the dust and gas in this DSO to dissipate? 5. Which DSO, a very bright radio source, is depicted in Image [3]? 6. Why might this DSO not have been visible in the past? 7. Which DSO, a massive star-forming region, is depicted in Image [4]? 8. [T10] What is the common nic ...
... 4. What will eventually cause the dust and gas in this DSO to dissipate? 5. Which DSO, a very bright radio source, is depicted in Image [3]? 6. Why might this DSO not have been visible in the past? 7. Which DSO, a massive star-forming region, is depicted in Image [4]? 8. [T10] What is the common nic ...
Hipparcos

Hipparcos was a scientific satellite of the European Space Agency (ESA), launched in 1989 and operated until 1993. It was the first space experiment devoted to precision astrometry, the accurate measurement of the positions of celestial objects on the sky. This permitted the accurate determination of proper motions and parallaxes of stars, allowing a determination of their distance and tangential velocity. When combined with radial-velocity measurements from spectroscopy, this pinpointed all six quantities needed to determine the motion of stars. The resulting Hipparcos Catalogue, a high-precision catalogue of more than 118,200 stars, was published in 1997. The lower-precision Tycho Catalogue of more than a million stars was published at the same time, while the enhanced Tycho-2 Catalogue of 2.5 million stars was published in 2000. Hipparcos ' follow-up mission, Gaia, was launched in 2013.The word ""Hipparcos"" is an acronym for High precision parallax collecting satellite and also a reference to the ancient Greek astronomer Hipparchus of Nicaea, who is noted for applications of trigonometry to astronomy and his discovery of the precession of the equinoxes.