Earth Science: Chapter 7: Stellar Evolution: Spring 2017: Student
... Main sequence stage: The stage in which stars spend most of their “lives”. The star is fusing hydrogen into helium. The inward pull of gravity is equal to the outward force of fusion. The star is said to be in hydrostatic equilibrium. Main sequence lasts for a few million to hundreds of billion year ...
... Main sequence stage: The stage in which stars spend most of their “lives”. The star is fusing hydrogen into helium. The inward pull of gravity is equal to the outward force of fusion. The star is said to be in hydrostatic equilibrium. Main sequence lasts for a few million to hundreds of billion year ...
A-105 Homework 1
... 18. (2 pts.) If the true distance to the center of our galaxy is found to be 7 kpc (instead of 8.5 kpc) and the orbital velocity of the sun is 220 km/s, what is the minimum mass of the galaxy? (Hints: Find the orbital period of the sun at 7 kpc, and then use Kepler’s 3rd law.) ...
... 18. (2 pts.) If the true distance to the center of our galaxy is found to be 7 kpc (instead of 8.5 kpc) and the orbital velocity of the sun is 220 km/s, what is the minimum mass of the galaxy? (Hints: Find the orbital period of the sun at 7 kpc, and then use Kepler’s 3rd law.) ...
PHYSICS 1500 - ASTRONOMY TOTAL
... Why is the ecliptic not lined up with the celestial equator? (a) The ecliptic is a fixed circle in the sky, but the celestial equator is different for observers at different latitudes. (b) The Earth's orbit is not a circle, but an ellipse. (c) The Earth's axis is tilted by about 23 degrees from the ...
... Why is the ecliptic not lined up with the celestial equator? (a) The ecliptic is a fixed circle in the sky, but the celestial equator is different for observers at different latitudes. (b) The Earth's orbit is not a circle, but an ellipse. (c) The Earth's axis is tilted by about 23 degrees from the ...
Astronomy of the Northern Sky—
... The Northern Sky faces mostly away from the Milky Way center. Much of the easy-to-find nebulosity is not in this part of the sky, but there are a few we can detect with naked eye, binoculars or small telescopes, preferably the wide-field or rich-field type. All we can use in the northern sky are in ...
... The Northern Sky faces mostly away from the Milky Way center. Much of the easy-to-find nebulosity is not in this part of the sky, but there are a few we can detect with naked eye, binoculars or small telescopes, preferably the wide-field or rich-field type. All we can use in the northern sky are in ...
Stars - staff.harrisonburg.k12.va
... of a star in the sky when viewed from two different positions in earth’s revolution. – The closer a star is, the larger its parallax, or apparent movement. The farther away a star is, the smaller its parallax. ...
... of a star in the sky when viewed from two different positions in earth’s revolution. – The closer a star is, the larger its parallax, or apparent movement. The farther away a star is, the smaller its parallax. ...
here - Atomki
... On the other hand, we can estimate the free-fall timescale, tff, by ignoring the pressure term in the eqn. of motion. We then can write: d2r/dt2 ≈ R/tff2 → tff ≈ √(R/g) (≈ 1/2√(G<ρ>) = tdyn ) Examples for tff/tdyn: 30 min for the sun, 18 days for red giant (100R⊙), 4.5 s for white dwarfs (R⊙/50) << ...
... On the other hand, we can estimate the free-fall timescale, tff, by ignoring the pressure term in the eqn. of motion. We then can write: d2r/dt2 ≈ R/tff2 → tff ≈ √(R/g) (≈ 1/2√(G<ρ>) = tdyn ) Examples for tff/tdyn: 30 min for the sun, 18 days for red giant (100R⊙), 4.5 s for white dwarfs (R⊙/50) << ...
Recap: High Mass Stars
... Neutron Star • Star with a core from 1.4 to 3 times the size of the Sun becomes a neutron. • Electrons and neutrons combine into neutrons. • 10 km (6 mi) in diameter with a mass more than our Sun! • A teaspoon of neutron star would be about 10 million tons • Acts like a huge magnet with magnetic p ...
... Neutron Star • Star with a core from 1.4 to 3 times the size of the Sun becomes a neutron. • Electrons and neutrons combine into neutrons. • 10 km (6 mi) in diameter with a mass more than our Sun! • A teaspoon of neutron star would be about 10 million tons • Acts like a huge magnet with magnetic p ...
MS Word
... subcatagories. Thus you can have a B2 star, as well as a G8 star. There are A0 stars and F7 stars. Look at each of the tables and under ‘spectral type’ you will see these classifications. Remember that B0 stars are the hottest and M9 stars are the coolest. Thus the left side of an H-R diagram is for ...
... subcatagories. Thus you can have a B2 star, as well as a G8 star. There are A0 stars and F7 stars. Look at each of the tables and under ‘spectral type’ you will see these classifications. Remember that B0 stars are the hottest and M9 stars are the coolest. Thus the left side of an H-R diagram is for ...
Chapter 27 Stars and Galaxies
... Neutron Stars – small but incredibly dense ball of neutrons, formed from the collapsed core of a supernova. ...
... Neutron Stars – small but incredibly dense ball of neutrons, formed from the collapsed core of a supernova. ...
I. Determination of stellar Parameters
... – metal-rich stars are intrinsically brighter than metalpoor stars at same spectral type, so that more metalrich stars are selected in magnitude-limited samples – possibly correlation of orbital radius and metallicity ...
... – metal-rich stars are intrinsically brighter than metalpoor stars at same spectral type, so that more metalrich stars are selected in magnitude-limited samples – possibly correlation of orbital radius and metallicity ...
Powerpoint - Astronomy at Swarthmore College
... simulations. Below are color contour plots of temperature, material density, speed, and a representation of the magnetic field, all of which are data that are included in the output files of the simulations. In all of these images, the small white circle is the star itself, while the remainder of th ...
... simulations. Below are color contour plots of temperature, material density, speed, and a representation of the magnetic field, all of which are data that are included in the output files of the simulations. In all of these images, the small white circle is the star itself, while the remainder of th ...
Sirius Astronomer - Orange County Astronomers
... used infrared from the Spitzer Space Telescope as well as ground-based observations to probe far deeper into the nebula than seen before. Huge numbers of newly-formed stars were found. ...
... used infrared from the Spitzer Space Telescope as well as ground-based observations to probe far deeper into the nebula than seen before. Huge numbers of newly-formed stars were found. ...
The Hertzsprung-Russell Diagram
... 9. Label the following steps on your H-R diagram to show the series of changes that our sun has undergone since its formation 4.6 billion years ago. a. Originally, a big cloud of gas and dust called a nebula condensed to form a young, cool star called a red dwarf. In this first stage of life, our s ...
... 9. Label the following steps on your H-R diagram to show the series of changes that our sun has undergone since its formation 4.6 billion years ago. a. Originally, a big cloud of gas and dust called a nebula condensed to form a young, cool star called a red dwarf. In this first stage of life, our s ...
Ch. 22 Honors Study Guide Name 1. How did Eratosthenes
... 7. Even though Copernicus was right about the Heliocentric model, the planets did not line up where he thought they should. What was wrong with Copernicus’ model? 8. Why were Tycho Brahe’s observations so important in Astronomy? 9. Why didn’t Tycho Brahe believe the Sun was the center of the Solar S ...
... 7. Even though Copernicus was right about the Heliocentric model, the planets did not line up where he thought they should. What was wrong with Copernicus’ model? 8. Why were Tycho Brahe’s observations so important in Astronomy? 9. Why didn’t Tycho Brahe believe the Sun was the center of the Solar S ...
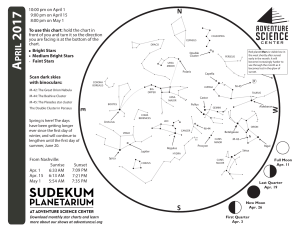
1704 chart front - Adventure Science Center
... Look to the west after sunset for the last glimpses of winter constellations. Orion the Hunter stands out early in the month, but will be lost in the glow of sunset by May. Follow Orion’s belt to the left to find the brightest star in the night sky, Sirius, in Canis Major the Big Dog. Follow the belt ...
... Look to the west after sunset for the last glimpses of winter constellations. Orion the Hunter stands out early in the month, but will be lost in the glow of sunset by May. Follow Orion’s belt to the left to find the brightest star in the night sky, Sirius, in Canis Major the Big Dog. Follow the belt ...
Comets, Meteors, and Meteoroids
... It is always exciting to see a falling star. It is gone almost as soon as you see it. You point to where it was and stare at the dark sky. You hope that you will see another falling star. What is a falling star? A falling star is not a star at all. It is not even part of a star. Stars do not fall. O ...
... It is always exciting to see a falling star. It is gone almost as soon as you see it. You point to where it was and stare at the dark sky. You hope that you will see another falling star. What is a falling star? A falling star is not a star at all. It is not even part of a star. Stars do not fall. O ...
Stars: from Adolescence to Old Age
... in a quick burst called the helium flash After this, the star becomes stable, its surface temperature increases, and its luminosity and size decreases At this stage, carbon nuclei sometimes fuse with helium nuclei to form oxygen nuclei ...
... in a quick burst called the helium flash After this, the star becomes stable, its surface temperature increases, and its luminosity and size decreases At this stage, carbon nuclei sometimes fuse with helium nuclei to form oxygen nuclei ...
Planets and Stars Key Vocabulary: Comparing and Contrasting
... There are more stars in the sky than a person can count one-at-a-time during an entire lifetime. There is just one star in our solar system - the sun. The sun is a medium-sized star, but it appears larger than other stars because it is so close to Earth. ...
... There are more stars in the sky than a person can count one-at-a-time during an entire lifetime. There is just one star in our solar system - the sun. The sun is a medium-sized star, but it appears larger than other stars because it is so close to Earth. ...
Hipparcos

Hipparcos was a scientific satellite of the European Space Agency (ESA), launched in 1989 and operated until 1993. It was the first space experiment devoted to precision astrometry, the accurate measurement of the positions of celestial objects on the sky. This permitted the accurate determination of proper motions and parallaxes of stars, allowing a determination of their distance and tangential velocity. When combined with radial-velocity measurements from spectroscopy, this pinpointed all six quantities needed to determine the motion of stars. The resulting Hipparcos Catalogue, a high-precision catalogue of more than 118,200 stars, was published in 1997. The lower-precision Tycho Catalogue of more than a million stars was published at the same time, while the enhanced Tycho-2 Catalogue of 2.5 million stars was published in 2000. Hipparcos ' follow-up mission, Gaia, was launched in 2013.The word ""Hipparcos"" is an acronym for High precision parallax collecting satellite and also a reference to the ancient Greek astronomer Hipparchus of Nicaea, who is noted for applications of trigonometry to astronomy and his discovery of the precession of the equinoxes.