Small images
... Procyon – 8th brighest star. About 1.4 solar masses. Another 11.5 ly main sequence star. Hotter and more luminous than the sun but not as luminous as Sirius. Type F5. May be close to finishing hydrogen burning as its luminosity is a bit high for its mass. Betelgeuse – 9th brightest star. 2nd brighte ...
... Procyon – 8th brighest star. About 1.4 solar masses. Another 11.5 ly main sequence star. Hotter and more luminous than the sun but not as luminous as Sirius. Type F5. May be close to finishing hydrogen burning as its luminosity is a bit high for its mass. Betelgeuse – 9th brightest star. 2nd brighte ...
A Faint Star Orbiting the Big Dipper’s Alcor Discovered
... technique is powerful and much faster than the usual way of confirming that objects in the sky are physically related.” The more typical method involves observing the pair of objects over much longer periods of time, even years, to show that the two are moving through space together. Alcor and its n ...
... technique is powerful and much faster than the usual way of confirming that objects in the sky are physically related.” The more typical method involves observing the pair of objects over much longer periods of time, even years, to show that the two are moving through space together. Alcor and its n ...
Sun and Other Stars Notes
... helium, this is called the proton-proton chain -Sun fuses ________________________ of material per second, very little mass is lost in the Sun, most is just converted into another element -Why is observation of Solar Neutrinos important? - Astronomers cannot witness nuclear fusion in the core of the ...
... helium, this is called the proton-proton chain -Sun fuses ________________________ of material per second, very little mass is lost in the Sun, most is just converted into another element -Why is observation of Solar Neutrinos important? - Astronomers cannot witness nuclear fusion in the core of the ...
Foundation 1 - Discovering Astronomy
... Pulsars – The discovery of rotating neutron stars • First detected in 1967 by Cambridge University graduate student Jocelyn Bell. • She found a radio source with a regular on-off-on cycle of exactly 1.3373011 seconds. • Some scientists speculated that this was evidence of an alien civilization’s co ...
... Pulsars – The discovery of rotating neutron stars • First detected in 1967 by Cambridge University graduate student Jocelyn Bell. • She found a radio source with a regular on-off-on cycle of exactly 1.3373011 seconds. • Some scientists speculated that this was evidence of an alien civilization’s co ...
Document
... There might be a signal at ~4 d, but the fact that different data sets give different answers makes me doubt this The other two „planets“ are noise → This is not a robust or confirmed planetary system because a different approach gives an entirely different answer! ...
... There might be a signal at ~4 d, but the fact that different data sets give different answers makes me doubt this The other two „planets“ are noise → This is not a robust or confirmed planetary system because a different approach gives an entirely different answer! ...
Investigation Activity 1
... can use the same relation to measure the size of the Moon. Measuring the angular size of the Moon in arcseconds, we use: (angle/206,265) = size/distance The angular size of the Moon is about 2000 arcseconds (it varies, why?) How big is the Moon? ...
... can use the same relation to measure the size of the Moon. Measuring the angular size of the Moon in arcseconds, we use: (angle/206,265) = size/distance The angular size of the Moon is about 2000 arcseconds (it varies, why?) How big is the Moon? ...
Multi-physics simulations using a hierarchical interchangeable
... combined to conduct numerical experiments. The community codes are generally written independently, so AMUSE encompasses a wide variety of computer languages and programming styles. The fundamental design feature of the framework is the abstraction of the functionality of individual community codes ...
... combined to conduct numerical experiments. The community codes are generally written independently, so AMUSE encompasses a wide variety of computer languages and programming styles. The fundamental design feature of the framework is the abstraction of the functionality of individual community codes ...
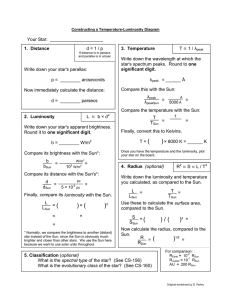
Your Star: _____________________ d = 1 / p
... intrinsic properties (temperature, luminosity, and radius.) We will then look for patterns in these properties by way of the H-R (temperature-luminosity) diagram. Your group will be in charge of a particular region of the sky (north, south, or one of four seasonal groups). Each student in the group ...
... intrinsic properties (temperature, luminosity, and radius.) We will then look for patterns in these properties by way of the H-R (temperature-luminosity) diagram. Your group will be in charge of a particular region of the sky (north, south, or one of four seasonal groups). Each student in the group ...
7_Big_bang
... use up its hydrogen. Note, Sun has been shinning for 4.6 B. years so it has about 5 B. more years to go before becoming a red giant. More massive stars, last much less then 10 B. years. Less massive stars last longer. ...
... use up its hydrogen. Note, Sun has been shinning for 4.6 B. years so it has about 5 B. more years to go before becoming a red giant. More massive stars, last much less then 10 B. years. Less massive stars last longer. ...
slides - Walter Burke Institute for Theoretical Physics
... to fully interpret the data – Novel analytics and mechanisms (Cantiello et al. 2014; Fuller et al. 2014) to transport J – Suggestions of new ways to look at the data to reveal rare physical states (e.g. core flash) ...
... to fully interpret the data – Novel analytics and mechanisms (Cantiello et al. 2014; Fuller et al. 2014) to transport J – Suggestions of new ways to look at the data to reveal rare physical states (e.g. core flash) ...
X-Ray Astronomy and Accretion Phenomena
... produce some X-rays in their outer atmosphere. The gas in this regions, known as the Chromosphere, is very hot and tenuous. Flares and prominences on the surface of the Sun also produce X-rays as a result of reconnection of magnetic fields. Although in the history of X-ray astronomy" it was stated t ...
... produce some X-rays in their outer atmosphere. The gas in this regions, known as the Chromosphere, is very hot and tenuous. Flares and prominences on the surface of the Sun also produce X-rays as a result of reconnection of magnetic fields. Although in the history of X-ray astronomy" it was stated t ...
Sirius Astronomer - Orange County Astronomers
... leading theory of how they formed is that water underground was released by large areas of crust collapsing in a catastrophic flood. A new study says that the observations support slow and continued frequent releases of ground water through fractures in the crust to form the lakes and seas. Such fra ...
... leading theory of how they formed is that water underground was released by large areas of crust collapsing in a catastrophic flood. A new study says that the observations support slow and continued frequent releases of ground water through fractures in the crust to form the lakes and seas. Such fra ...
Stellar population models in the Near-Infrared Meneses
... with models constructed according to a slightly different prescription than the classical stellar population synthesis. In this approach we only partially populate the points on each stellar isochrone, leaving out the points corresponding to the AGB phase. During the spectral fiting, we instead allo ...
... with models constructed according to a slightly different prescription than the classical stellar population synthesis. In this approach we only partially populate the points on each stellar isochrone, leaving out the points corresponding to the AGB phase. During the spectral fiting, we instead allo ...
ON THE FORMATION OF MASSIVE STELLAR CLUSTERS
... form in the unstable shell (at R = Rk ) and then, due to their negligible cross-section, freely fall towards the centre of the configuration as they evolve into stars. The larger number of sources continuously enhances the forming cluster mechanical luminosity and with it the amount of mass returned ...
... form in the unstable shell (at R = Rk ) and then, due to their negligible cross-section, freely fall towards the centre of the configuration as they evolve into stars. The larger number of sources continuously enhances the forming cluster mechanical luminosity and with it the amount of mass returned ...
Formation and Evolution of Infalling Disks Around Protostars
... Summary part2: Star Formation Triggered by First Supernovae Supernovae of first stars ...
... Summary part2: Star Formation Triggered by First Supernovae Supernovae of first stars ...
Stellar Populations of Galaxies- 2 Lectures H
... "hot" opaque bodies emits a continuous spectra. "hot" low density gas emits a sequence of emission lines. - a neon sign. "cold" low density gas, placed in front of a hot opaque body, produces a continuous spectrum with dark lines on top ( absorption lines). light from the sun. Every element (Hydroge ...
... "hot" opaque bodies emits a continuous spectra. "hot" low density gas emits a sequence of emission lines. - a neon sign. "cold" low density gas, placed in front of a hot opaque body, produces a continuous spectrum with dark lines on top ( absorption lines). light from the sun. Every element (Hydroge ...
Hipparcos

Hipparcos was a scientific satellite of the European Space Agency (ESA), launched in 1989 and operated until 1993. It was the first space experiment devoted to precision astrometry, the accurate measurement of the positions of celestial objects on the sky. This permitted the accurate determination of proper motions and parallaxes of stars, allowing a determination of their distance and tangential velocity. When combined with radial-velocity measurements from spectroscopy, this pinpointed all six quantities needed to determine the motion of stars. The resulting Hipparcos Catalogue, a high-precision catalogue of more than 118,200 stars, was published in 1997. The lower-precision Tycho Catalogue of more than a million stars was published at the same time, while the enhanced Tycho-2 Catalogue of 2.5 million stars was published in 2000. Hipparcos ' follow-up mission, Gaia, was launched in 2013.The word ""Hipparcos"" is an acronym for High precision parallax collecting satellite and also a reference to the ancient Greek astronomer Hipparchus of Nicaea, who is noted for applications of trigonometry to astronomy and his discovery of the precession of the equinoxes.