Chapter 1 Periods of Western Astronomy Prehistoric Astronomy
... • In winter months of Northern hemisphere, the Sun rises south of east and sets south of west • The solstices (about June 21 and December 21) are when the Sun rises at the most extreme north and south points • The equinoxes (equal day and night and about March 21 and September 23) are when the Sun r ...
... • In winter months of Northern hemisphere, the Sun rises south of east and sets south of west • The solstices (about June 21 and December 21) are when the Sun rises at the most extreme north and south points • The equinoxes (equal day and night and about March 21 and September 23) are when the Sun r ...
view powerpoint
... agriculture • Saturn's interior composition is primarily that of simple molecules such as hydrogen and helium, which are liquids under the high pressure environments found in the interiors of the outer planets, and not solids. ...
... agriculture • Saturn's interior composition is primarily that of simple molecules such as hydrogen and helium, which are liquids under the high pressure environments found in the interiors of the outer planets, and not solids. ...
Astronomy 100—Exam 1
... D. a poppyseed on the other side of the campus. E. a creampuff at Bart’s. 9. Your friend, living on a planet 100 light-years away from the earth, has just sent to you a short message to inform you that she has just given birth to a baby. What is the age of the baby when you receive the message on th ...
... D. a poppyseed on the other side of the campus. E. a creampuff at Bart’s. 9. Your friend, living on a planet 100 light-years away from the earth, has just sent to you a short message to inform you that she has just given birth to a baby. What is the age of the baby when you receive the message on th ...
Exploring the Solar System - The Federation of Galaxy Explorers
... miles (that's 38.1 million kilometers). Venus is closer to Earth than any other large object, except for our own Moon. In 1761, and again in 1874, a rare event called a solar transit occurred when Venus moved across the disk, or face, of the Sun. By watching this transit of Venus across the disk of ...
... miles (that's 38.1 million kilometers). Venus is closer to Earth than any other large object, except for our own Moon. In 1761, and again in 1874, a rare event called a solar transit occurred when Venus moved across the disk, or face, of the Sun. By watching this transit of Venus across the disk of ...
ISP 205: Visions of the Universe Fall 2001 Professor: ER Capriotti
... B. the Earth and sky as being roughly the same size. C. the Sun as the center of the universe. D. the creation as starting with a huge explosion. E. the stars as distant suns. 2. Most Greek astronomers believed that the Earth is immobile because they did not observe A. retrograde motion of the plane ...
... B. the Earth and sky as being roughly the same size. C. the Sun as the center of the universe. D. the creation as starting with a huge explosion. E. the stars as distant suns. 2. Most Greek astronomers believed that the Earth is immobile because they did not observe A. retrograde motion of the plane ...
The Solar System Solar System Today (Not to Scale) Inner Planets
... Orbits in the Solar System • Planets all revolve (orbit) around the Sun in the same direction • Planets mostly rotate (spin) in the same ...
... Orbits in the Solar System • Planets all revolve (orbit) around the Sun in the same direction • Planets mostly rotate (spin) in the same ...
File - Mrs. Andrews` CBA classes
... The Planets sometime appear to be large, bright, and close compared to other times when they seem smaller, dimmer, and farther away. Ptolemy tried to shift each planet so that the earth was no longer the center causing an eccentric (off-center circle). Astronomers were offended by this because ...
... The Planets sometime appear to be large, bright, and close compared to other times when they seem smaller, dimmer, and farther away. Ptolemy tried to shift each planet so that the earth was no longer the center causing an eccentric (off-center circle). Astronomers were offended by this because ...
Cosmology questions (Introduction)
... travelling to the next planet aboard a futuristic spacecraft which can travel at 0.1% of the speed of light, c 2.998 108 ms-1 Ignoring relativistic effects and also differences in distances between the planets due to their various positions within their orbits, calculate how long the trip would l ...
... travelling to the next planet aboard a futuristic spacecraft which can travel at 0.1% of the speed of light, c 2.998 108 ms-1 Ignoring relativistic effects and also differences in distances between the planets due to their various positions within their orbits, calculate how long the trip would l ...
Astronomy and the Universe - Department of Physics and Astronomy
... Astronomical distances are often measured in astronomical units, parsecs, or light-years • Astronomical Unit (AU) – One AU is the average distance between Earth and the Sun – 1.496 X 108 km or 92.96 million miles ...
... Astronomical distances are often measured in astronomical units, parsecs, or light-years • Astronomical Unit (AU) – One AU is the average distance between Earth and the Sun – 1.496 X 108 km or 92.96 million miles ...
ASTRONOMICAL SOC IETY OF TASMANIA BULLETIN 160
... In the Journal of the Brit. Astronomical Assn. B. Peek points out the striking consequences of the fact that the shadows of satellites III and IV cross the disk more slowly than the planet"s equatorial velocity of rotation. For either of these satellites three total eclipses normally occur in rapid ...
... In the Journal of the Brit. Astronomical Assn. B. Peek points out the striking consequences of the fact that the shadows of satellites III and IV cross the disk more slowly than the planet"s equatorial velocity of rotation. For either of these satellites three total eclipses normally occur in rapid ...
Rotation
... Earth rotates from west to east on its axis. This makes the sun, moon and stars look as though they are moving from east to west. We say that the sun, moon, and stars rise in the east and set in the west. However…it is actually the Earth’s rotation that causes this apparent movement. ...
... Earth rotates from west to east on its axis. This makes the sun, moon and stars look as though they are moving from east to west. We say that the sun, moon, and stars rise in the east and set in the west. However…it is actually the Earth’s rotation that causes this apparent movement. ...
Chapter 1
... – Our normal day is called a solar day – the Earth rotates once w.r.t. the Sun, or noon-to-noon. – The Earth moves from one sunrise to the next by about 1°, so stars appear to shift. – A sidereal day is the time for the Earth to rotate once w.r.t. the stars, and is about 4 minutes shorter. ...
... – Our normal day is called a solar day – the Earth rotates once w.r.t. the Sun, or noon-to-noon. – The Earth moves from one sunrise to the next by about 1°, so stars appear to shift. – A sidereal day is the time for the Earth to rotate once w.r.t. the stars, and is about 4 minutes shorter. ...
Earth in Space ReadingEarth in Space Reading(es)
... Most places outside the tropics have four distinct seasons: winter, spring, summer, and autumn. But there are great differences in temperature from place to place. For instance, it is warmer near the eq ...
... Most places outside the tropics have four distinct seasons: winter, spring, summer, and autumn. But there are great differences in temperature from place to place. For instance, it is warmer near the eq ...
Earth in Space Reading
... Most places outside the tropics have four distinct seasons: winter, spring, summer, and autumn. But there are great differences in temperature from place to place. For instance, it is warmer near the eq ...
... Most places outside the tropics have four distinct seasons: winter, spring, summer, and autumn. But there are great differences in temperature from place to place. For instance, it is warmer near the eq ...
The History of Astronomy
... same speed? No. A planet’s speed depends on its average distance from the Sun. The closest planet moves fastest, the most ...
... same speed? No. A planet’s speed depends on its average distance from the Sun. The closest planet moves fastest, the most ...
AST 1010 Quiz questions
... 1. Explain why the Moon goes through a series of phases. Be sure to include a description of how the relative positions of the Sun, Moon and Earth affect this process. 2. Explain why most locations on the Earth experience a cycle of seasons. Be sure to be specific as to which hemisphere you are desc ...
... 1. Explain why the Moon goes through a series of phases. Be sure to include a description of how the relative positions of the Sun, Moon and Earth affect this process. 2. Explain why most locations on the Earth experience a cycle of seasons. Be sure to be specific as to which hemisphere you are desc ...
chapter01 - California State University, Long Beach
... circle in the equatorial system that passes through the celestial poles perpendicular to the celestial equator) of the object. 9. Declination (Dec.) is an astronomical coordinate that locates objects north-south on the sky, much as latitude locates objects north-south on the Earth. Technically, decl ...
... circle in the equatorial system that passes through the celestial poles perpendicular to the celestial equator) of the object. 9. Declination (Dec.) is an astronomical coordinate that locates objects north-south on the sky, much as latitude locates objects north-south on the Earth. Technically, decl ...
a 03 Scale and Comparing Planets to Stars ppt
... • It is therefore very possible that some of the stars in Andromeda have exploded as a supernova or gone out long ago. The message of these star finishing events just has not gotten to us yet! ...
... • It is therefore very possible that some of the stars in Andromeda have exploded as a supernova or gone out long ago. The message of these star finishing events just has not gotten to us yet! ...
Document
... Astronomical distances are often measured in astronomical units, parsecs, or light-years • Astronomical Unit (AU) – One AU is the average distance between Earth and the Sun – 1.496 X 108 km or 92.96 million miles ...
... Astronomical distances are often measured in astronomical units, parsecs, or light-years • Astronomical Unit (AU) – One AU is the average distance between Earth and the Sun – 1.496 X 108 km or 92.96 million miles ...
MS-ESS1-1 Earth`s Place in the Universe
... Disciplinary Core Ideas ESS1.A: The Universe and Its Stars Patterns of the apparent motion of the sun, the moon, and stars in the sky can be observed, described, predicted, and explained with models. ESS1.B: Earth and the Solar System This model of the solar system can explain eclipses of the su ...
... Disciplinary Core Ideas ESS1.A: The Universe and Its Stars Patterns of the apparent motion of the sun, the moon, and stars in the sky can be observed, described, predicted, and explained with models. ESS1.B: Earth and the Solar System This model of the solar system can explain eclipses of the su ...
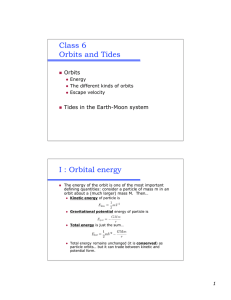
Class 6 Orbits and Tides I : Orbital energy
... This is a bound orbit A special case if that of a circular orbit… ...
... This is a bound orbit A special case if that of a circular orbit… ...
A WALK THROUGH THE SOLAR SYSTEM
... Astronomers continued to look to the skies with better optical telescopes, but it was not until about 1959 when advancements in rocketry after World War II allowed us to break free of the Earth's gravity and travel to the Moon and other planets that we entered the golden age of exploration of our So ...
... Astronomers continued to look to the skies with better optical telescopes, but it was not until about 1959 when advancements in rocketry after World War II allowed us to break free of the Earth's gravity and travel to the Moon and other planets that we entered the golden age of exploration of our So ...
Motion of the Moon Phases of the Moon
... • Lunar eclipses do not occur every month because the Moon’s orbital plane is tilted by 5 degrees with respect to the ecliptic – a total lunar eclipse occurs when the Moon crosses the ecliptic at full Moon – since the Earth’s shadow is much bigger than the Moon, total lunar eclipses occur more often ...
... • Lunar eclipses do not occur every month because the Moon’s orbital plane is tilted by 5 degrees with respect to the ecliptic – a total lunar eclipse occurs when the Moon crosses the ecliptic at full Moon – since the Earth’s shadow is much bigger than the Moon, total lunar eclipses occur more often ...
Boonesborough Days - Tri
... revolution time. But with the last three planets, we have known their orbital periods shortly after their discovery. Here is where that guy Johannes Kepler can help us understand the planets once again with his Third Law. Law Three: The squares of the period of revolution of any two planets are prop ...
... revolution time. But with the last three planets, we have known their orbital periods shortly after their discovery. Here is where that guy Johannes Kepler can help us understand the planets once again with his Third Law. Law Three: The squares of the period of revolution of any two planets are prop ...
Extraterrestrial skies

In astronomy, the term extraterrestrial sky refers to a view of outer space from the surface of a world other than Earth.The sky of the Moon has been directly observed or photographed by astronauts, while those of Titan, Mars, and Venus have been observed indirectly by space probes designed to land on the surface and transmit images back to Earth.Characteristics of extraterrestrial skies appear to vary substantially due to a number of factors. An extraterrestrial atmosphere, if present, has a large bearing on visible characteristics. The atmosphere's density and chemical composition can contribute to differences in colour, opacity (including haze) and the presence of clouds. Astronomical objects may also be visible and can include natural satellites, rings, star systems and nebulas and other planetary system bodies.For skies that have not been directly or indirectly observed, their appearance can be simulated based on known parameters such as the position of astronomical objects relative to the surface and atmospheric composition.