HomeWork #2
... Why do we see different phases of the Moon? j 1. Because the Moon's distance from the Earth changes as it moves in its elliptical orbit, thereby k l m n changing its apparent brightness. 2. Because the illuminated half of the Moon becomes more or less visible from Earth as the Moon orbits the Earth. ...
... Why do we see different phases of the Moon? j 1. Because the Moon's distance from the Earth changes as it moves in its elliptical orbit, thereby k l m n changing its apparent brightness. 2. Because the illuminated half of the Moon becomes more or less visible from Earth as the Moon orbits the Earth. ...
Cosmic Distance Ladder Terrence Tao (UCLA)
... • Aristarchus knew that lunar eclipses were caused by the shadow of the Earth, which would be roughly two Earth radii in diameter. (This assumes the sun is very far away from the Earth; more on this in the “third rung” section.) • From many observations it was known that lunar eclipses last a maxim ...
... • Aristarchus knew that lunar eclipses were caused by the shadow of the Earth, which would be roughly two Earth radii in diameter. (This assumes the sun is very far away from the Earth; more on this in the “third rung” section.) • From many observations it was known that lunar eclipses last a maxim ...
Science - Mansfield ISD
... 4a.html What is the planet order sunlight 4F – Graphic in relation to the sun? Inner planets Organizers, 2.A student observed Visual/Videos, and Manipulatives (soil) Teacher Notes: the apparent shape of Review the following 3H- Accountable the moon every night TEKS conversation stems for a period of ...
... 4a.html What is the planet order sunlight 4F – Graphic in relation to the sun? Inner planets Organizers, 2.A student observed Visual/Videos, and Manipulatives (soil) Teacher Notes: the apparent shape of Review the following 3H- Accountable the moon every night TEKS conversation stems for a period of ...
Earth is an
... 3 effects: length of day/night, changing seasons, changing climates with latitude (know this) ...
... 3 effects: length of day/night, changing seasons, changing climates with latitude (know this) ...
The magnitude scale
... object in the sky using the magnitude scale. The scale is somewhat strange because brighter objects have smaller magnitudes, while fainter objects have larger magnitudes - the opposite of what you might expect. ...
... object in the sky using the magnitude scale. The scale is somewhat strange because brighter objects have smaller magnitudes, while fainter objects have larger magnitudes - the opposite of what you might expect. ...
a ComparativePlanetology 27
... • On Earth, the C is absorbed into the oceans, where it is used by living organisms and becomes deposited as limestone (aka, the carbon cycle). • On Venus, the oceans evaporated away, so the carbon cycle won’t start. Instead C finds the O in the atmosphere, makes still more CO2, and traps more hea ...
... • On Earth, the C is absorbed into the oceans, where it is used by living organisms and becomes deposited as limestone (aka, the carbon cycle). • On Venus, the oceans evaporated away, so the carbon cycle won’t start. Instead C finds the O in the atmosphere, makes still more CO2, and traps more hea ...
apparent retrograde motion - Indiana University Astronomy
... seeking natural explanations for these patterns ...
... seeking natural explanations for these patterns ...
Lecture 1
... • I sit in the middle of the room and measure the angular separation of two dots on the screen. Someone rotates the walls of the building by 90 degrees. What happens to my measurement of the angular separation? ...
... • I sit in the middle of the room and measure the angular separation of two dots on the screen. Someone rotates the walls of the building by 90 degrees. What happens to my measurement of the angular separation? ...
Teachers Notes - Edinburgh International Science Festival
... Due to the vast distances between Earth and our neighbouring planets, stars and galaxies, the main way that scientists explore our universe is by observing and detecting light with telescopes. Light is emitted and reflected off many objects in space. This light contains information about the object ...
... Due to the vast distances between Earth and our neighbouring planets, stars and galaxies, the main way that scientists explore our universe is by observing and detecting light with telescopes. Light is emitted and reflected off many objects in space. This light contains information about the object ...
PHS 111 Test 3 Review Chapters 26-28
... region. There is a minor component of phosphorescent minerals distributed fairly evenly on the lunar surface. The Moon's thin atmosphere acts as a mirror, reflecting light being cast from neighboring stars. Background microwave radiation becomes excited during the lunar eclipse, and shifts towards v ...
... region. There is a minor component of phosphorescent minerals distributed fairly evenly on the lunar surface. The Moon's thin atmosphere acts as a mirror, reflecting light being cast from neighboring stars. Background microwave radiation becomes excited during the lunar eclipse, and shifts towards v ...
1” “Sky-Notes” of the Open University Astronomy Club. June 2005. A
... the Moon too bright use a filter to reduce the glare. At times features along different parts of the limb are better presented due the effect of libration – an apparent wobbling of the Moon about its axis – that allows us to see about 59% of its surface. The BAA Handbook and some monthly magazines ( ...
... the Moon too bright use a filter to reduce the glare. At times features along different parts of the limb are better presented due the effect of libration – an apparent wobbling of the Moon about its axis – that allows us to see about 59% of its surface. The BAA Handbook and some monthly magazines ( ...
PHS 111 Test 3 Review Chapters 26-28
... minor component of phosphorescent minerals distributed fairly evenly on the lunar surface. The Moon's thin atmosphere acts as a mirror, reflecting light being cast from neighboring stars. Background microwave radiation becomes excited during the lunar eclipse, and shifts towards visual light, which ...
... minor component of phosphorescent minerals distributed fairly evenly on the lunar surface. The Moon's thin atmosphere acts as a mirror, reflecting light being cast from neighboring stars. Background microwave radiation becomes excited during the lunar eclipse, and shifts towards visual light, which ...
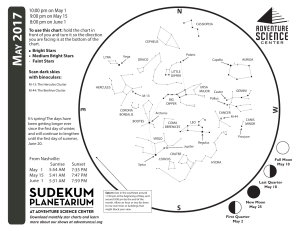
1705 chart front
... stars that make up the Summer Triangle. Low in the southeast you may find the bright red star Antares in Scorpius the Scorpion, and just to its left the even brighter planet Saturn. A backyard telescope will easily reveal the rings of Saturn, but binoculars will only show the planet as looking sligh ...
... stars that make up the Summer Triangle. Low in the southeast you may find the bright red star Antares in Scorpius the Scorpion, and just to its left the even brighter planet Saturn. A backyard telescope will easily reveal the rings of Saturn, but binoculars will only show the planet as looking sligh ...
Study Guide Beginning Astronomy
... amount of money, you can get a more powerful telescope for your budget by investing in a reflector, as opposed to a refractor. Also, since the refraction of light is a function of wavelength, it is not possible to make a refractor totally free of chromatic aberration. For optical viewing any telesco ...
... amount of money, you can get a more powerful telescope for your budget by investing in a reflector, as opposed to a refractor. Also, since the refraction of light is a function of wavelength, it is not possible to make a refractor totally free of chromatic aberration. For optical viewing any telesco ...
Planetary Systems Unit Part 3: The Solar System
... 1. If you were a bird flying over Talley Middle School, what would it look like when you looked down? Draw what you would see… (2 points) ...
... 1. If you were a bird flying over Talley Middle School, what would it look like when you looked down? Draw what you would see… (2 points) ...
Chapter 1 Daily Note Sheets Completed Power Point
... • -In the Universe • In the Solar System • 3rd planet from the Sun ...
... • -In the Universe • In the Solar System • 3rd planet from the Sun ...
Test 1 - History of Astronomy and Planetary Motion - ppt
... Sun’s apparent path for four different observers on June 21st. Notice how the path and position of the noontime sun change for each location. Latitude: The closer you are to the poles, the lower the noon time sun and the greater the difference between the winter and summer length of daylight. At th ...
... Sun’s apparent path for four different observers on June 21st. Notice how the path and position of the noontime sun change for each location. Latitude: The closer you are to the poles, the lower the noon time sun and the greater the difference between the winter and summer length of daylight. At th ...
Ch.2: Celestial Mechanics
... Sidereal and Synodic periods A satellite is placed in a circular orbit around the Sun, orbiting the Sun once every 10 months. How often does the satellite pass between the Earth and the Sun? ...
... Sidereal and Synodic periods A satellite is placed in a circular orbit around the Sun, orbiting the Sun once every 10 months. How often does the satellite pass between the Earth and the Sun? ...
Volume 20 Number 10 September 2012
... Northeast. This shower is not the same as the spectacular Perseids shower which peaks in mid-August and is one of the year's highlights. They both appear to radiate from the same constellation but are not related - they were formed by different comets. September has five minor showers with three or ...
... Northeast. This shower is not the same as the spectacular Perseids shower which peaks in mid-August and is one of the year's highlights. They both appear to radiate from the same constellation but are not related - they were formed by different comets. September has five minor showers with three or ...
Solar System
... • A space station is a satellite that people can live in for long periods of time. ...
... • A space station is a satellite that people can live in for long periods of time. ...
ASTR 101 Final Study Guide I received study guides for Chapters 1
... Spring tides: highest high tides, lowest low tides; during new and full moon Neap tides: a lower than normal difference between high and low tides; during ¼ and ¾ moon tides change every six hours, so from one tide to that same tide again it takes 12 hours Tidal breaking: gravitational pull from the ...
... Spring tides: highest high tides, lowest low tides; during new and full moon Neap tides: a lower than normal difference between high and low tides; during ¼ and ¾ moon tides change every six hours, so from one tide to that same tide again it takes 12 hours Tidal breaking: gravitational pull from the ...
PHYS 2410 General Astronomy Homework 1
... If we say that an object is 1,000 light-years away we see it ...
... If we say that an object is 1,000 light-years away we see it ...
Planets - uni
... (originally, before the Copernican resolution, it was seen the other way around), and one "month" is roughly the time our Moon needs to orbit the Earth. The currently most widely used calender system, the Christian calender in use in Europe, Northern and Southern Americas and many other parts of t ...
... (originally, before the Copernican resolution, it was seen the other way around), and one "month" is roughly the time our Moon needs to orbit the Earth. The currently most widely used calender system, the Christian calender in use in Europe, Northern and Southern Americas and many other parts of t ...
Extraterrestrial skies

In astronomy, the term extraterrestrial sky refers to a view of outer space from the surface of a world other than Earth.The sky of the Moon has been directly observed or photographed by astronauts, while those of Titan, Mars, and Venus have been observed indirectly by space probes designed to land on the surface and transmit images back to Earth.Characteristics of extraterrestrial skies appear to vary substantially due to a number of factors. An extraterrestrial atmosphere, if present, has a large bearing on visible characteristics. The atmosphere's density and chemical composition can contribute to differences in colour, opacity (including haze) and the presence of clouds. Astronomical objects may also be visible and can include natural satellites, rings, star systems and nebulas and other planetary system bodies.For skies that have not been directly or indirectly observed, their appearance can be simulated based on known parameters such as the position of astronomical objects relative to the surface and atmospheric composition.