7-12 Script - Geophysical Institute
... orbits to ellipses. Galileo further solidified evidence for the model when he observed the moons of Jupiter. Showing that objects orbit other planets (not just Earth) supported the idea that not everything was in orbit around us. If time allows: See JUPITER'S MOONS as you would through a telescope a ...
... orbits to ellipses. Galileo further solidified evidence for the model when he observed the moons of Jupiter. Showing that objects orbit other planets (not just Earth) supported the idea that not everything was in orbit around us. If time allows: See JUPITER'S MOONS as you would through a telescope a ...
05Sky1.ppt - NMSU Astronomy
... • For distant objects (stars), essentially all observed motion comes from reflex motion – Although stars definitely have intrinsic motion, they are so far away that we don’t see much apparent motion over the course of our lifetimes – As we will discuss later, we can measure radial motion of objects, ...
... • For distant objects (stars), essentially all observed motion comes from reflex motion – Although stars definitely have intrinsic motion, they are so far away that we don’t see much apparent motion over the course of our lifetimes – As we will discuss later, we can measure radial motion of objects, ...
Chap. 13 Gravitational Interactions
... tidal forces on the moon’s crust would be greater If the moon were too close, Earth’s tidal forces would tear the moon into a billion pieces, forming a ring around Earth similar to those around Saturn ...
... tidal forces on the moon’s crust would be greater If the moon were too close, Earth’s tidal forces would tear the moon into a billion pieces, forming a ring around Earth similar to those around Saturn ...
Gravitation
... 3. the same surface gravity 4. 1/2 as much surface gravity 5. 1/4 as much surface gravity ...
... 3. the same surface gravity 4. 1/2 as much surface gravity 5. 1/4 as much surface gravity ...
The View From Earth
... and through the zenith, which divides the visible part of the sphere into an east half and a west half is called the celestial meridian. Observation shows that all objects visible on the sphere (stars, planets, Sun, Moon, etc.) appear to pivot every 24 hours about a point elevated above the north po ...
... and through the zenith, which divides the visible part of the sphere into an east half and a west half is called the celestial meridian. Observation shows that all objects visible on the sphere (stars, planets, Sun, Moon, etc.) appear to pivot every 24 hours about a point elevated above the north po ...
taken from horizons 7th edition chapter 1 tutorial quiz
... a. They are both evolving. b. They both shine by reflected light. c. They are both about the same size. d. They both have a hot core. answer: a ...
... a. They are both evolving. b. They both shine by reflected light. c. They are both about the same size. d. They both have a hot core. answer: a ...
explaining the seasons and locating the north and south celestial
... DEC=+6.980. The above formula gives the close approximation of DEC=23.8sin(35π/365.5)=6.970 for x=17.5 days after the spring equinox. Notice that if the earth’s tilt angle were zero, then the sun’s declination would remain unchanged throughout the year and there would be no seasons. Next let us look ...
... DEC=+6.980. The above formula gives the close approximation of DEC=23.8sin(35π/365.5)=6.970 for x=17.5 days after the spring equinox. Notice that if the earth’s tilt angle were zero, then the sun’s declination would remain unchanged throughout the year and there would be no seasons. Next let us look ...
Astronomy Rough Notes
... calculator. So to build a scale model of the TC and Chicago, you could use a pin head and a tic-tac separated by the width of a calculator. To include the Moon in this scale model, start with 1 m = 10 000 mi. The Moon would be 240 000 mi/10 000 mi or 24 m away, about on Hennepin Av from the classroo ...
... calculator. So to build a scale model of the TC and Chicago, you could use a pin head and a tic-tac separated by the width of a calculator. To include the Moon in this scale model, start with 1 m = 10 000 mi. The Moon would be 240 000 mi/10 000 mi or 24 m away, about on Hennepin Av from the classroo ...
January
... against its magnitude. For nearby stars we can create a standard CM diagram of color against absolute magnitude – a measure of the stars real brightness. For clusters of stars, whose stars are at about the same distance, astronomers can compare the cluster CM diagram against the standard CM diagram ...
... against its magnitude. For nearby stars we can create a standard CM diagram of color against absolute magnitude – a measure of the stars real brightness. For clusters of stars, whose stars are at about the same distance, astronomers can compare the cluster CM diagram against the standard CM diagram ...
Planetary Cycles
... cycle in the sky with reference to the Sun is called its synodical period, a motion which takes a little over 29 days to complete. With reference to the Earth or a fixed star, the Moon finishes the cycle in about 28 days. This is its sidereal period. An interesting cycle to study is the Lunar or Met ...
... cycle in the sky with reference to the Sun is called its synodical period, a motion which takes a little over 29 days to complete. With reference to the Earth or a fixed star, the Moon finishes the cycle in about 28 days. This is its sidereal period. An interesting cycle to study is the Lunar or Met ...
Jupiter is 90000 miles in diameter. It is 10 times the size of the earth
... Jupiter has the most moons of any of the planets in our solar System. 63 moons have been discovered around the gas giant. Four satellites are comparable to the Earth's moons in size; the rest are smaller. ...
... Jupiter has the most moons of any of the planets in our solar System. 63 moons have been discovered around the gas giant. Four satellites are comparable to the Earth's moons in size; the rest are smaller. ...
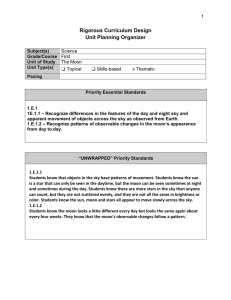
Rigorous Curriculum Design
... apparent movement of objects across the sky as observed from Earth. 1.E.1.2 – Recognize patterns of observable changes in the moon’s appearance from day to day. ...
... apparent movement of objects across the sky as observed from Earth. 1.E.1.2 – Recognize patterns of observable changes in the moon’s appearance from day to day. ...
planet
... How many planets are known to exist outside the solar system? • There have been more than three hundred planets (373 as of yesterday) discovered orbiting other stars to date. ...
... How many planets are known to exist outside the solar system? • There have been more than three hundred planets (373 as of yesterday) discovered orbiting other stars to date. ...
Studying Space Section 2
... confusion about the point on Earth’s surface where the date changes. • This imaginary line runs from north to south through the Pacific Ocean. • The line is drawn so that it does not cut through islands or continents. Thus, everyone living within one country has the same date. ...
... confusion about the point on Earth’s surface where the date changes. • This imaginary line runs from north to south through the Pacific Ocean. • The line is drawn so that it does not cut through islands or continents. Thus, everyone living within one country has the same date. ...
Sun - UNT Physics
... 6. The apparent visual magnitude of star A is 2 and the apparent visual magnitude of star B is 1. Based on this information which statement below must be true? a. Star A emits more light than star B. b. Star B emits more light than star A. c. Star A is closer than star B. d. Star B is closer than st ...
... 6. The apparent visual magnitude of star A is 2 and the apparent visual magnitude of star B is 1. Based on this information which statement below must be true? a. Star A emits more light than star B. b. Star B emits more light than star A. c. Star A is closer than star B. d. Star B is closer than st ...
Cosmic Distance Ladder Terrence Tao (UCLA)
... the ancient Babylonians, who knew that the apparent motion of Mars (say) repeated itself every 780 days (the synodic period of Mars). ...
... the ancient Babylonians, who knew that the apparent motion of Mars (say) repeated itself every 780 days (the synodic period of Mars). ...
STAAR Science Tutorial 35 TEK 8.8B: The Sun
... Sun) is Proxima Centauri, which is about 4.2 light years away from Earth. This is 263,000 times further away from Earth than our Sun. (Our Sun is 0.000016 lightyears away from Earth.) While there are 11 stars within 10 light-years of Earth, most of the other stars visible in the night sky are many t ...
... Sun) is Proxima Centauri, which is about 4.2 light years away from Earth. This is 263,000 times further away from Earth than our Sun. (Our Sun is 0.000016 lightyears away from Earth.) While there are 11 stars within 10 light-years of Earth, most of the other stars visible in the night sky are many t ...
4-eclipses-and-tides
... 26. Base your answer to the following question on the passage below. A Newly Discovered Planet Scientists studying a Sun-like star named Ogle-Tr-3 discovered a planet that is, on the average, 3.5 million kilometers away from the star’s surface. The planet was discovered as a result of observing a c ...
... 26. Base your answer to the following question on the passage below. A Newly Discovered Planet Scientists studying a Sun-like star named Ogle-Tr-3 discovered a planet that is, on the average, 3.5 million kilometers away from the star’s surface. The planet was discovered as a result of observing a c ...
4-eclipses-and-tides
... 26. Base your answer to the following question on the passage below. A Newly Discovered Planet Scientists studying a Sun-like star named Ogle-Tr-3 discovered a planet that is, on the average, 3.5 million kilometers away from the star’s surface. The planet was discovered as a result of observing a c ...
... 26. Base your answer to the following question on the passage below. A Newly Discovered Planet Scientists studying a Sun-like star named Ogle-Tr-3 discovered a planet that is, on the average, 3.5 million kilometers away from the star’s surface. The planet was discovered as a result of observing a c ...
1-4 The Moon`s Phases 1. The rotation and
... 5. A lunar eclipse does not occur at each full Moon because the Moon’s plane of revolution is tilted 5° compared to the Earth’s plane of revolution around the Sun. Only during the two eclipse seasons that occur each year are the Earth and Moon positioned so that the Moon will enter the Earth’s shado ...
... 5. A lunar eclipse does not occur at each full Moon because the Moon’s plane of revolution is tilted 5° compared to the Earth’s plane of revolution around the Sun. Only during the two eclipse seasons that occur each year are the Earth and Moon positioned so that the Moon will enter the Earth’s shado ...
Introduction: - TrevorMander.com
... A planet is a larger body orbiting a star. Pluto is not considered to be a planet now because 1) it is so small and 2) its orbit is crazy and 3) there’s a bunch more rocks out there that are even bigger. The solar system rotates around a common centre of mass located just beneath the surface of the ...
... A planet is a larger body orbiting a star. Pluto is not considered to be a planet now because 1) it is so small and 2) its orbit is crazy and 3) there’s a bunch more rocks out there that are even bigger. The solar system rotates around a common centre of mass located just beneath the surface of the ...
Chapter 10 - Macmillan Learning
... 65. •Astronomy The International Space Station (ISS) orbits Earth in a nearly circular orbit that is 345 km above Earth’s surface. (a) How many hours does it take for the ISS to make each orbit? (b) Some of the experiments performed by astronauts in the ISS involve the effects of “weightlessness” ...
... 65. •Astronomy The International Space Station (ISS) orbits Earth in a nearly circular orbit that is 345 km above Earth’s surface. (a) How many hours does it take for the ISS to make each orbit? (b) Some of the experiments performed by astronauts in the ISS involve the effects of “weightlessness” ...
Day 1: How to Describe the Sky The Motions of the Stars
... • One evening at midnight, you observe Leo high in the Southern sky. Virgo is to the East of Leo and Cancer is to the West. One month earlier, which of these constellations was high in the Southern sky at midnight? • A: Leo • B: Virgo • C: Cancer ...
... • One evening at midnight, you observe Leo high in the Southern sky. Virgo is to the East of Leo and Cancer is to the West. One month earlier, which of these constellations was high in the Southern sky at midnight? • A: Leo • B: Virgo • C: Cancer ...
Here
... If we do some careful observations, we find: 1) The length of the daylight hours at a given spot varies throughout the year: the Sun is out a longer time when it is warmer (i.e. summer), and out a shorter time when it is colder. 2) On a given day, the length of the daylight hours depends on where yo ...
... If we do some careful observations, we find: 1) The length of the daylight hours at a given spot varies throughout the year: the Sun is out a longer time when it is warmer (i.e. summer), and out a shorter time when it is colder. 2) On a given day, the length of the daylight hours depends on where yo ...
Extraterrestrial skies

In astronomy, the term extraterrestrial sky refers to a view of outer space from the surface of a world other than Earth.The sky of the Moon has been directly observed or photographed by astronauts, while those of Titan, Mars, and Venus have been observed indirectly by space probes designed to land on the surface and transmit images back to Earth.Characteristics of extraterrestrial skies appear to vary substantially due to a number of factors. An extraterrestrial atmosphere, if present, has a large bearing on visible characteristics. The atmosphere's density and chemical composition can contribute to differences in colour, opacity (including haze) and the presence of clouds. Astronomical objects may also be visible and can include natural satellites, rings, star systems and nebulas and other planetary system bodies.For skies that have not been directly or indirectly observed, their appearance can be simulated based on known parameters such as the position of astronomical objects relative to the surface and atmospheric composition.