January 2014 Astronomy Calendar by Dave Mitsky Some
... The dwarf planet Pluto is in conjunction with the Sun on January 1st. For more on the planets and how to locate them, browse http://www.nakedeyeplanets.com/ Asteroid 7 Iris shines at tenth magnitude as it travels northeastward through Pisces this month. It passes through the southern portion of the ...
... The dwarf planet Pluto is in conjunction with the Sun on January 1st. For more on the planets and how to locate them, browse http://www.nakedeyeplanets.com/ Asteroid 7 Iris shines at tenth magnitude as it travels northeastward through Pisces this month. It passes through the southern portion of the ...
Lecture 12: Evolution of the Galaxy
... heavy element mass fraction, Z, at the time of their birth. The youngest stars are therefore the most heavy-element rich, and the oldest ones (Population II stars) are the most deficient in heavy elements relative to the Sun. • Halo Population II stars have Z ~ 10-3 to 10-1 Z⊙ • Disk Population I st ...
... heavy element mass fraction, Z, at the time of their birth. The youngest stars are therefore the most heavy-element rich, and the oldest ones (Population II stars) are the most deficient in heavy elements relative to the Sun. • Halo Population II stars have Z ~ 10-3 to 10-1 Z⊙ • Disk Population I st ...
Introduction
... Disk galaxies generally resemble the Mikly Way; much of their luminosity is contained in thin, rotating disks of stars. ...
... Disk galaxies generally resemble the Mikly Way; much of their luminosity is contained in thin, rotating disks of stars. ...
Bluffer`s Guide to Sirius
... successfully bluff your way in astronomy, you will know to pause and calmly announce the answer to be “the Sun”. Apart from the Sun then? Sirius is the brightest star in the night sky. Many nonastronomers believe that the Pole star (Polaris) is the brightest star. If any of your audience suggest thi ...
... successfully bluff your way in astronomy, you will know to pause and calmly announce the answer to be “the Sun”. Apart from the Sun then? Sirius is the brightest star in the night sky. Many nonastronomers believe that the Pole star (Polaris) is the brightest star. If any of your audience suggest thi ...
2. The Anatomy of Stellar Life and Death
... the formation of diatomic hydrogen gas (H2). Consequently, the nebulae remain fairly massive even as they collapse, and they fail to fragment into smaller, denser and less massive cores. Thus the stars produced from this material tend to be particularly massive, and modeling suggests that this was a ...
... the formation of diatomic hydrogen gas (H2). Consequently, the nebulae remain fairly massive even as they collapse, and they fail to fragment into smaller, denser and less massive cores. Thus the stars produced from this material tend to be particularly massive, and modeling suggests that this was a ...
Stellar Masses
... called brown dwarfs, and are ‘star like’ in the sense that nuclear burning of deuterium occurs in their core. Below a mass of 0.015M⊙ (roughly 16 times the mass of Jupiter) not even deuterium burning can occur, and these objects are perhaps best called planets. Thus there is a natural lower limit to ...
... called brown dwarfs, and are ‘star like’ in the sense that nuclear burning of deuterium occurs in their core. Below a mass of 0.015M⊙ (roughly 16 times the mass of Jupiter) not even deuterium burning can occur, and these objects are perhaps best called planets. Thus there is a natural lower limit to ...
A Star - Cloudy Nights
... All the stars you can see without a telescope, including our Sun, are located in the same spiral arm of the Milky Way galaxy. Even though these stars are our neighbors, we can't visit them. They are too far away. Using current technology, it would take thousands of years to travel to our closest ste ...
... All the stars you can see without a telescope, including our Sun, are located in the same spiral arm of the Milky Way galaxy. Even though these stars are our neighbors, we can't visit them. They are too far away. Using current technology, it would take thousands of years to travel to our closest ste ...
Downloadable Full Text
... The UFD Reticulum II (Ret II) was recently discovered with Dark Energy Survey data12,13 and confirmed to be one of the most metal-poor galaxies known14. On 1-4 Oct 2015, we obtained high-resolution spectra of the nine brightest member stars in Ret II (see Table 1, Extended Data Figure 1). The abunda ...
... The UFD Reticulum II (Ret II) was recently discovered with Dark Energy Survey data12,13 and confirmed to be one of the most metal-poor galaxies known14. On 1-4 Oct 2015, we obtained high-resolution spectra of the nine brightest member stars in Ret II (see Table 1, Extended Data Figure 1). The abunda ...
CW9_MOST_GSphot_RK_v1
... • exposure time is usually 1.5 sec (range from 0.3 to 1.5 applied) • no images are recovered, the image data is processed on board: a mean background value is removed and the signal is the sum of high signal pixels (exceeding the background and a 20 ADU threshold) • for the brightest guide stars noi ...
... • exposure time is usually 1.5 sec (range from 0.3 to 1.5 applied) • no images are recovered, the image data is processed on board: a mean background value is removed and the signal is the sum of high signal pixels (exceeding the background and a 20 ADU threshold) • for the brightest guide stars noi ...
Planetary Nebulae: Observational Properties, Mimics, and Diagnostics
... A classical planetary nebula (PN) is a shell of ionized gas, ejected from a low- to intermediate-mass star (∼1 to 8 M⊙ ) towards the end of its life. A PN is produced at the end of the asymptotic giant branch (AGB) phase, as the red giant ejects its outer envelope in a final stage of copious mass lo ...
... A classical planetary nebula (PN) is a shell of ionized gas, ejected from a low- to intermediate-mass star (∼1 to 8 M⊙ ) towards the end of its life. A PN is produced at the end of the asymptotic giant branch (AGB) phase, as the red giant ejects its outer envelope in a final stage of copious mass lo ...
15.1 Introduction
... and UV spectra are dominated by strong, broad emission lines instead of the narrow absorption lines that are typical of ‘normal’ stars (Figure 15.3). The emission lines are so strong that they were first noticed as early as 1867 by... Charles Wolf and Georges Rayet (!) using the 40 cm Foucault teles ...
... and UV spectra are dominated by strong, broad emission lines instead of the narrow absorption lines that are typical of ‘normal’ stars (Figure 15.3). The emission lines are so strong that they were first noticed as early as 1867 by... Charles Wolf and Georges Rayet (!) using the 40 cm Foucault teles ...
Exploring the Universe
... – Hottest stars are blue, coolest are red – Hertzspurg-Russel diagram classifies stars • 90° of stars are called the main sequence • Other stars include red giants, supergiants, and dwarfs ...
... – Hottest stars are blue, coolest are red – Hertzspurg-Russel diagram classifies stars • 90° of stars are called the main sequence • Other stars include red giants, supergiants, and dwarfs ...
Open clusters in the Third Galactic Quadrant III. Alleged binary
... metal content used to compute color excesses and distance moduli. Despite the special care put in fitting all the potential cluster members, some sequences are not satisfactorily reproduced by one single isochrone, as said above, and a range of them has been indicated in each cluster of Table 4. Kno ...
... metal content used to compute color excesses and distance moduli. Despite the special care put in fitting all the potential cluster members, some sequences are not satisfactorily reproduced by one single isochrone, as said above, and a range of them has been indicated in each cluster of Table 4. Kno ...
A search for a new class of pulsating DA white dwarf stars in the DB
... cooling sequence in the HR diagram have effective temperatures of nearly 200 000 K, ranging down to about 80 000 K. Some of these hottest white dwarf stars are central stars of planetary nebulae, some are not; some pulsate, some do not. ...
... cooling sequence in the HR diagram have effective temperatures of nearly 200 000 K, ranging down to about 80 000 K. Some of these hottest white dwarf stars are central stars of planetary nebulae, some are not; some pulsate, some do not. ...
No Slide Title - Laboratory for Atmospheric and Space Physics
... • Cranmer, van Ballegooijen, & Edgar (2007) computed solutions for the waves & background one-fluid plasma state along various flux tubes... going from the photosphere to the heliosphere. ...
... • Cranmer, van Ballegooijen, & Edgar (2007) computed solutions for the waves & background one-fluid plasma state along various flux tubes... going from the photosphere to the heliosphere. ...
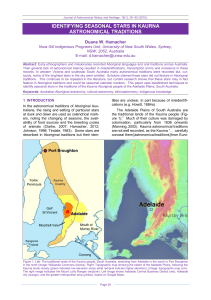
identifying seasonal stars in kaurna astronomical traditions
... emu on the celestial plain, while the Mangkamangkaranna (the Pleiades star cluster) represents a group of girls digging roots. The red star Madletaltarni, probably Betelgeuse (Alpha Orionis) or Aldebaran (Alpha Taurii), is the mother of the Tinniinyaranna, and Parnakkoyerli is the father, described ...
... emu on the celestial plain, while the Mangkamangkaranna (the Pleiades star cluster) represents a group of girls digging roots. The red star Madletaltarni, probably Betelgeuse (Alpha Orionis) or Aldebaran (Alpha Taurii), is the mother of the Tinniinyaranna, and Parnakkoyerli is the father, described ...
The STIS CCD Spectroscopic Line Spread Functions
... light into the instrument for LAMP calibrations. To minimize the movement of the shutter, an alternate light path feeds light from the calibration optical train through a permanently mounted mirror and a hole in the second relay mirror (the relay mirrors correct for optical aberrations of HST ), and ...
... light into the instrument for LAMP calibrations. To minimize the movement of the shutter, an alternate light path feeds light from the calibration optical train through a permanently mounted mirror and a hole in the second relay mirror (the relay mirrors correct for optical aberrations of HST ), and ...
hr diagrams of star clusters
... your cluster HR diagram. Once you have matched the zero-age main-sequence, you can then call up the isochrone-fitting tool. On the menu bar of the ColorMagnitude diagram window, call up Tools > Isochrones, and you will see an isochrone plotted on your HR diagram near the plot of your cluster stars. ...
... your cluster HR diagram. Once you have matched the zero-age main-sequence, you can then call up the isochrone-fitting tool. On the menu bar of the ColorMagnitude diagram window, call up Tools > Isochrones, and you will see an isochrone plotted on your HR diagram near the plot of your cluster stars. ...
HR DIAGRAMS OF STAR CLUSTERS
... your cluster HR diagram. Once you have matched the zero-age main-sequence, you can then call up the isochrone-fitting tool. On the menu bar of the ColorMagnitude diagram window, call up Tools > Isochrones, and you will see an isochrone plotted on your HR diagram near the plot of your cluster stars. ...
... your cluster HR diagram. Once you have matched the zero-age main-sequence, you can then call up the isochrone-fitting tool. On the menu bar of the ColorMagnitude diagram window, call up Tools > Isochrones, and you will see an isochrone plotted on your HR diagram near the plot of your cluster stars. ...
THE PERIOD OF ROTATION OF THE SUN
... your cluster HR diagram. Once you have matched the zero-age main-sequence, you can then call up the isochrone-fitting tool. On the menu bar of the ColorMagnitude diagram window, call up Tools > Isochrones, and you will see an isochrone plotted on your HR diagram near the plot of your cluster stars. ...
... your cluster HR diagram. Once you have matched the zero-age main-sequence, you can then call up the isochrone-fitting tool. On the menu bar of the ColorMagnitude diagram window, call up Tools > Isochrones, and you will see an isochrone plotted on your HR diagram near the plot of your cluster stars. ...
Corona Australis

Corona Australis /kɵˈroʊnə ɒˈstreɪlɨs/ or Corona Austrina /kɵˈroʊnə ɒˈstraɪnə/ is a constellation in the Southern Celestial Hemisphere. Its Latin name means ""southern crown"", and it is the southern counterpart of Corona Borealis, the northern crown. One of the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd-century astronomer Ptolemy, it remains one of the 88 modern constellations. The Ancient Greeks saw Corona Australis as a wreath rather than a crown and associated it with Sagittarius or Centaurus. Other cultures have likened the pattern to a turtle, ostrich nest, a tent, or even a hut belonging to a rock hyrax.Although fainter than its namesake, the oval- or horseshoe-shaped pattern of its brighter stars renders it distinctive. Alpha and Beta Coronae Australis are the two brightest stars with an apparent magnitude of around 4.1. Epsilon Coronae Australis is the brightest example of a W Ursae Majoris variable in the southern sky. Lying alongside the Milky Way, Corona Australis contains one of the closest star-forming regions to our Solar System—a dusty dark nebula known as the Corona Australis Molecular Cloud, lying about 430 light years away. Within it are stars at the earliest stages of their lifespan. The variable stars R and TY Coronae Australis light up parts of the nebula, which varies in brightness accordingly.