Refusing to Go Quietly: GRBs and Their Progenitors
... Advanced LIGO will be able to detect gravitational waves that stretch the length of the arms by a fraction of the size of a proton ...
... Advanced LIGO will be able to detect gravitational waves that stretch the length of the arms by a fraction of the size of a proton ...
11-Massive Stars
... mechanism as those from low-mass stars? For example, the magnetocentrifugal wind scenarios predicts outflows which are morphologically similar to low-mass outflows and which show a high degree of collimation due to the star-disk interaction (§10.6). On the contrary, colliding protostars are expected ...
... mechanism as those from low-mass stars? For example, the magnetocentrifugal wind scenarios predicts outflows which are morphologically similar to low-mass outflows and which show a high degree of collimation due to the star-disk interaction (§10.6). On the contrary, colliding protostars are expected ...
- Cosmotography
... Our observations of NGC 4449 and its surroundings consist of two main components. The first is imaging from a small robotic telescope, to confirm the presence of a low-surface-brightness substructure and provide its basic characteristics (similar techniques were used with larger galaxies in Martı́ne ...
... Our observations of NGC 4449 and its surroundings consist of two main components. The first is imaging from a small robotic telescope, to confirm the presence of a low-surface-brightness substructure and provide its basic characteristics (similar techniques were used with larger galaxies in Martı́ne ...
Ground-Based Astrometry 2010-2020
... space density is rudimentary at best. High accuracy astrometry at infrared wavelengths in particular is a nascent field, and breakthroughs in brown dwarf research are imminent as large sky surveys come online and push to fainter magnitudes. By 2020, we will know the relative populations of stars an ...
... space density is rudimentary at best. High accuracy astrometry at infrared wavelengths in particular is a nascent field, and breakthroughs in brown dwarf research are imminent as large sky surveys come online and push to fainter magnitudes. By 2020, we will know the relative populations of stars an ...
Observing Stellar Evolution
... Stellar evolution – refers to the stages in the lifetime of one star. When biologists talk about evolution they mean intergenerational evolution. While stars change from one generation to the next, the focus of this program is stellar lifetimes. Burning – The materials that comprise stars do not 'bu ...
... Stellar evolution – refers to the stages in the lifetime of one star. When biologists talk about evolution they mean intergenerational evolution. While stars change from one generation to the next, the focus of this program is stellar lifetimes. Burning – The materials that comprise stars do not 'bu ...
16_Testbank
... Note that this is much larger than the balance mass in the cooler clouds that we see today. The early universe clouds that did not have any other molecules to cool them down, required very large masses to collapse. Consequently, they probably produced very massive stars. 6) Why does a cloud collapse ...
... Note that this is much larger than the balance mass in the cooler clouds that we see today. The early universe clouds that did not have any other molecules to cool them down, required very large masses to collapse. Consequently, they probably produced very massive stars. 6) Why does a cloud collapse ...
Examining the M67 Classification as an Open Cluster
... purple color indicates the positions of the main sequence stars. The red color indicates the positions of the horizontal branch stars. The yellow color indicates the positions of the giant stars. The positions of blue stragglers are indicated in the diagram by the blue color. As is seen, the color-m ...
... purple color indicates the positions of the main sequence stars. The red color indicates the positions of the horizontal branch stars. The yellow color indicates the positions of the giant stars. The positions of blue stragglers are indicated in the diagram by the blue color. As is seen, the color-m ...
Astrophysics Pristine CNO abundances from Magellanic Cloud B stars
... Large Magellanic Cloud (LMC). Apart from H ii regions, unevolved OB-type stars are currently the only accessible source of present-day CNO abundances for the MCs not altered by stellar evolution. Using UVES on the VLT, we obtained spectra of sufficient resolution (R = 20 000) and signal-to-noise (S/ ...
... Large Magellanic Cloud (LMC). Apart from H ii regions, unevolved OB-type stars are currently the only accessible source of present-day CNO abundances for the MCs not altered by stellar evolution. Using UVES on the VLT, we obtained spectra of sufficient resolution (R = 20 000) and signal-to-noise (S/ ...
instructor notes stellar evolution, star clusters
... The effect shows up in the H-R diagrams for young clusters as a lower main-sequence turn-on point. Many, but not all, pre-main-sequence stars are still associated with the material from which they formed. Often such stars are found to be losing mass and to have emission lines in their spectra origi ...
... The effect shows up in the H-R diagrams for young clusters as a lower main-sequence turn-on point. Many, but not all, pre-main-sequence stars are still associated with the material from which they formed. Often such stars are found to be losing mass and to have emission lines in their spectra origi ...
instructor notes stellar evolution, star clusters
... The effect shows up in the H-R diagrams for young clusters as a lower main-sequence turn-on point. Many, but not all, pre-main-sequence stars are still associated with the material from which they formed. Often such stars are found to be losing mass and to have emission lines in their spectra origi ...
... The effect shows up in the H-R diagrams for young clusters as a lower main-sequence turn-on point. Many, but not all, pre-main-sequence stars are still associated with the material from which they formed. Often such stars are found to be losing mass and to have emission lines in their spectra origi ...
October 2016 BRAS Newsletter - The Baton Rouge Astronomical
... on telescopes both on the ground and in space. Exultant astronomers worldwide captured data at visible, X-ray, gamma-ray, and radio wavelengths from telescopes both on the ground and in space. Three independent RAPTOR (Rapid Telescopes for Optical Response) full-sky monitoring telescopes—two in New ...
... on telescopes both on the ground and in space. Exultant astronomers worldwide captured data at visible, X-ray, gamma-ray, and radio wavelengths from telescopes both on the ground and in space. Three independent RAPTOR (Rapid Telescopes for Optical Response) full-sky monitoring telescopes—two in New ...
Archaeoastronomical Study of the Main Pyramids of Giza
... lowest one in the maps. Obviously this choice is opposite to that adopted by the cartographers of the XVII century who decided to put North on the top of their maps, a convention that we too continue to make today. In any case there is no objective reason to put necessarily North at the top of the g ...
... lowest one in the maps. Obviously this choice is opposite to that adopted by the cartographers of the XVII century who decided to put North on the top of their maps, a convention that we too continue to make today. In any case there is no objective reason to put necessarily North at the top of the g ...
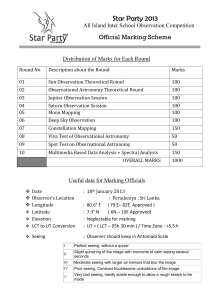
Marking Scheme of Observational Sessions
... mark every report and SELECT 8 REPORTS THAT HAVE HIGEST MARKS to enter to the marks list. If the observer will be drawn deep sky objects such as ( Nebulas, Galaxies, Messier objects in the constellation mapping area, Give MINUS MARKS for that. ( drawing those objects inside constellation mapping are ...
... mark every report and SELECT 8 REPORTS THAT HAVE HIGEST MARKS to enter to the marks list. If the observer will be drawn deep sky objects such as ( Nebulas, Galaxies, Messier objects in the constellation mapping area, Give MINUS MARKS for that. ( drawing those objects inside constellation mapping are ...
The 2006 RBSE Journal - National Optical Astronomy Observatory
... Significant variation was detected; and there were a couple of microvariability events in the graph. The time scale if the change is such that something exceptionally small must have interfered with the flux to cause it. With changes happening over the course of just a few minutes could be caused by ...
... Significant variation was detected; and there were a couple of microvariability events in the graph. The time scale if the change is such that something exceptionally small must have interfered with the flux to cause it. With changes happening over the course of just a few minutes could be caused by ...
ppt - SLAC
... Wolf-Rayet stars are hot (25-50,000+ degrees K), massive stars (20+ solar mass) with a high rate of mass loss. (This is WR124, at 19h11 +16 ) A few other spectral types don't fit the sequence but instead parallel it. Type W or Wolf-Rayet stars are as hot and blue as the hottest O stars but show stro ...
... Wolf-Rayet stars are hot (25-50,000+ degrees K), massive stars (20+ solar mass) with a high rate of mass loss. (This is WR124, at 19h11 +16 ) A few other spectral types don't fit the sequence but instead parallel it. Type W or Wolf-Rayet stars are as hot and blue as the hottest O stars but show stro ...
Main-Sequence Stars and the Sun
... so are never technically considered stars. Objects just below the cutoff often emit energy produced by gravitational collapse, and are called brown dwarfs. These objects are brightest in the infrared. The most massive stars known (for example, Eta Carinae) are as large as 150 MSun . In general, more ...
... so are never technically considered stars. Objects just below the cutoff often emit energy produced by gravitational collapse, and are called brown dwarfs. These objects are brightest in the infrared. The most massive stars known (for example, Eta Carinae) are as large as 150 MSun . In general, more ...
IAU-Perraut-2013 - Putting A Stars into Context
... IAU Conference « Putting A Stars into Context” Moscow, 2013 June 3rd ...
... IAU Conference « Putting A Stars into Context” Moscow, 2013 June 3rd ...
Have You Seen Canopus Tonight?
... Alpha Centauri system. Betelgeuse and Rigel help outline winter’s Orion while Vega, Deneb and Altair form the summer triangle. Regulus, heart of Leo the Lion, heralds spring, and Aldebaran follows the seven Pleiades sisters into autumn. Many know reddish Antares rivals Mars during warm summer nights ...
... Alpha Centauri system. Betelgeuse and Rigel help outline winter’s Orion while Vega, Deneb and Altair form the summer triangle. Regulus, heart of Leo the Lion, heralds spring, and Aldebaran follows the seven Pleiades sisters into autumn. Many know reddish Antares rivals Mars during warm summer nights ...
Night Sky Observations
... Constellation: A pattern of stars connected with imaginary lines to form a figure in the sky. Constellation boundary: The whole sky is divided into 88 official “patches” and these patches are the areas that the constellations take up in the sky. Each constellation’s area has an official boundary. Ma ...
... Constellation: A pattern of stars connected with imaginary lines to form a figure in the sky. Constellation boundary: The whole sky is divided into 88 official “patches” and these patches are the areas that the constellations take up in the sky. Each constellation’s area has an official boundary. Ma ...
The High Resolution Camera CXC Newsletter
... search for time variability of the sources, we included 23 observations from November 1999 to February 2005 (adding about 250 ks exposure time). We detected 318 X-ray sources and created long term light curves for all of them. We classified sources as highly variable or outbursting (with subclasses ...
... search for time variability of the sources, we included 23 observations from November 1999 to February 2005 (adding about 250 ks exposure time). We detected 318 X-ray sources and created long term light curves for all of them. We classified sources as highly variable or outbursting (with subclasses ...
Corona Australis

Corona Australis /kɵˈroʊnə ɒˈstreɪlɨs/ or Corona Austrina /kɵˈroʊnə ɒˈstraɪnə/ is a constellation in the Southern Celestial Hemisphere. Its Latin name means ""southern crown"", and it is the southern counterpart of Corona Borealis, the northern crown. One of the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd-century astronomer Ptolemy, it remains one of the 88 modern constellations. The Ancient Greeks saw Corona Australis as a wreath rather than a crown and associated it with Sagittarius or Centaurus. Other cultures have likened the pattern to a turtle, ostrich nest, a tent, or even a hut belonging to a rock hyrax.Although fainter than its namesake, the oval- or horseshoe-shaped pattern of its brighter stars renders it distinctive. Alpha and Beta Coronae Australis are the two brightest stars with an apparent magnitude of around 4.1. Epsilon Coronae Australis is the brightest example of a W Ursae Majoris variable in the southern sky. Lying alongside the Milky Way, Corona Australis contains one of the closest star-forming regions to our Solar System—a dusty dark nebula known as the Corona Australis Molecular Cloud, lying about 430 light years away. Within it are stars at the earliest stages of their lifespan. The variable stars R and TY Coronae Australis light up parts of the nebula, which varies in brightness accordingly.