Neutron Stars PowerPoint
... ~ 1,837 times the mass of an electron Proton mass + Electron mass = Neutron mass ...
... ~ 1,837 times the mass of an electron Proton mass + Electron mass = Neutron mass ...
PH607lec12
... Downsizing. A comprehensive survey of more than 4,000 elliptical and lenticular galaxies in 93 nearby galaxy clusters has found a curious case of galactic "downsizing." Contrary to expectations, the largest, brightest galaxies in the census consist almost exclusively of very old stars, with much of ...
... Downsizing. A comprehensive survey of more than 4,000 elliptical and lenticular galaxies in 93 nearby galaxy clusters has found a curious case of galactic "downsizing." Contrary to expectations, the largest, brightest galaxies in the census consist almost exclusively of very old stars, with much of ...
Results from the search for tidal disruption flares in the GALEX Deep
... emission requires excitation by a persistent Seyfert nucleus. ...
... emission requires excitation by a persistent Seyfert nucleus. ...
Colloquial Jakartan Indonesian
... has corresponding terms—rua poto and rua maoro. Maori has the one term, mārua roa ‘long pit’ for both solstices, and applies the term also to the month or season during which the sun is at its furthermost points (Makemson 1941:85). The only Micronesian terms I have located have been recorded in a Gi ...
... has corresponding terms—rua poto and rua maoro. Maori has the one term, mārua roa ‘long pit’ for both solstices, and applies the term also to the month or season during which the sun is at its furthermost points (Makemson 1941:85). The only Micronesian terms I have located have been recorded in a Gi ...
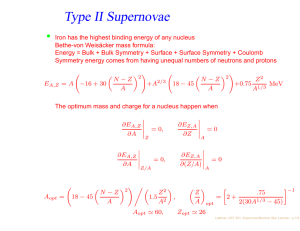
Type II Supernovae
... An observer in the orbital plane has θ = π/2 and h× = 0. The observed frequency of gravitational waves is ν = Ω/π. The intensity of gravitational waves decreases as 1/r. Consider two 1.4 M⊙ neutron stars in a binary with separation of R⊙ observed from a distance of 1 kpc: P ≃ 7000 s, ν ≃ 2.9 · 10−4 ...
... An observer in the orbital plane has θ = π/2 and h× = 0. The observed frequency of gravitational waves is ν = Ω/π. The intensity of gravitational waves decreases as 1/r. Consider two 1.4 M⊙ neutron stars in a binary with separation of R⊙ observed from a distance of 1 kpc: P ≃ 7000 s, ν ≃ 2.9 · 10−4 ...
Ground-Based Astrometry 2010-2020
... • How many white dwarfs are there in the Galaxy? White dwarfs are important chronometers for age-dating Galactic components, but their number densities in the disk and halo are poorly known. Even within 25 pc the number of known white dwarfs has climbed 25% since 2000 (e.g., Subasavage et al. 2009). ...
... • How many white dwarfs are there in the Galaxy? White dwarfs are important chronometers for age-dating Galactic components, but their number densities in the disk and halo are poorly known. Even within 25 pc the number of known white dwarfs has climbed 25% since 2000 (e.g., Subasavage et al. 2009). ...
Bayesian mass and age estimates for transiting exoplanet host stars⋆
... the age to within 25% based on the density, effective temperature and metallicity predicted by a range of different stellar models. The masses of stars in eclipsing binaries are recovered to within the calculated uncertainties (typically 5%) in about 90% of cases. There is a tendency for the masses to ...
... the age to within 25% based on the density, effective temperature and metallicity predicted by a range of different stellar models. The masses of stars in eclipsing binaries are recovered to within the calculated uncertainties (typically 5%) in about 90% of cases. There is a tendency for the masses to ...
3D Tour of the Universe Template
... regions, resulting in the formation of new young stars. As is common in these kinds of encounters, spiral structure was induced in the more massive galaxy. M51 is an easily found astronomical showpiece if the sky is dark, where suggestions of its spiral arms may be visible. As is also common with th ...
... regions, resulting in the formation of new young stars. As is common in these kinds of encounters, spiral structure was induced in the more massive galaxy. M51 is an easily found astronomical showpiece if the sky is dark, where suggestions of its spiral arms may be visible. As is also common with th ...
exemplars and commentary
... Barnard's Star is a very low-mass red dwarf star about six light-years away from Earth in the constellation of Ophiuchus. Barnard's Star is the fourth-closest known individual star to the Sun, after the three components of the Alpha Centauri system. Despite its proximity, Barnard's Star, at a dim ap ...
... Barnard's Star is a very low-mass red dwarf star about six light-years away from Earth in the constellation of Ophiuchus. Barnard's Star is the fourth-closest known individual star to the Sun, after the three components of the Alpha Centauri system. Despite its proximity, Barnard's Star, at a dim ap ...
Planetary Nebula
... It’s the dim star, not the bright one, near the center of NGC 3132 that created this odd but beautiful planetary nebula. The pool of light seen surrounding this binary system is energized by the hot surface of the faint star. Blue represents the hottest gas, which is confined to the inner region of ...
... It’s the dim star, not the bright one, near the center of NGC 3132 that created this odd but beautiful planetary nebula. The pool of light seen surrounding this binary system is energized by the hot surface of the faint star. Blue represents the hottest gas, which is confined to the inner region of ...
AAVSO: Epsilon Aurigae
... Most recent interpretations of the observations seem to confirm the model set forth in 1991. It is now likely that there is an early-type binary system with components having spectral class B5 or earlier at the center of the disk, based upon the ultraviolet spectrum obtained with FUSE (Bennett et al ...
... Most recent interpretations of the observations seem to confirm the model set forth in 1991. It is now likely that there is an early-type binary system with components having spectral class B5 or earlier at the center of the disk, based upon the ultraviolet spectrum obtained with FUSE (Bennett et al ...
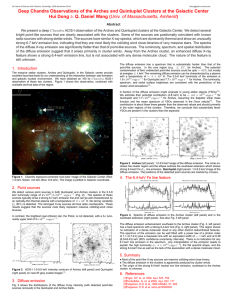
Deep Chandra Observations of the Arches and Quintuplet Clusters at... Hui Dong Q. Daniel Wang ( &
... The diffuse emission has a spectrum that is substantially harder than that of the point-like sources. In the core region (e.g. ≤ 15”, for Arches). The potential contamination of faint undetected point-like sources could be upto ∼ 65%, but mostly at energies ≤ 4 keV. The remaining diffuse emission ca ...
... The diffuse emission has a spectrum that is substantially harder than that of the point-like sources. In the core region (e.g. ≤ 15”, for Arches). The potential contamination of faint undetected point-like sources could be upto ∼ 65%, but mostly at energies ≤ 4 keV. The remaining diffuse emission ca ...
Homework #3, AST 1002
... Which of the following is (are) correct? (a) Energy is transported from the Sun's core to its surface primarily by a process called convection. (b) It takes about five minutes for energy from the Sun's core to reach its surface. (c) The proton cycle describes the process of energy production in the ...
... Which of the following is (are) correct? (a) Energy is transported from the Sun's core to its surface primarily by a process called convection. (b) It takes about five minutes for energy from the Sun's core to reach its surface. (c) The proton cycle describes the process of energy production in the ...
Project Icarus: Astronomical Considerations Relating to the Choice
... Within 15 light-years of the Sun there are approximately 56 stars, in 38 separate stellar systems. The number is approximate for several reasons. Firstly, at the outer boundary the errors on the distances can amount to a few tenths of a light-year, which could mean that some stars notionally just be ...
... Within 15 light-years of the Sun there are approximately 56 stars, in 38 separate stellar systems. The number is approximate for several reasons. Firstly, at the outer boundary the errors on the distances can amount to a few tenths of a light-year, which could mean that some stars notionally just be ...
28.2 Calculating Luminosity
... describes how much light is coming from the star each second. Luminosity can be measured in watts (W). Measuring the luminosity of something as far away as a star is difficult to do. However, we can measure its brightness. Brightness describes the amount of the star’s light that reaches a square met ...
... describes how much light is coming from the star each second. Luminosity can be measured in watts (W). Measuring the luminosity of something as far away as a star is difficult to do. However, we can measure its brightness. Brightness describes the amount of the star’s light that reaches a square met ...
EQUINOCTIAL vLOBE ·
... Fig. 1. Let P be the pole of the ecliptic CV" $ � vY. N the pole of the equator CV" �, cutting the ecliptic in
... Fig. 1. Let P be the pole of the ecliptic CV" $ � vY. N the pole of the equator CV" �, cutting the ecliptic in
Stellar Explosions
... Material keeps being transferred to the white dwarf, and the process repeats, as illustrated here ...
... Material keeps being transferred to the white dwarf, and the process repeats, as illustrated here ...
The new Basel high-latitude field star survey of the Galaxy
... Abstract. We discuss star count and three-color data for the two inner-Galaxy fields SA 107 and NGC 6171 observed in the new Basel RGU high-latitude field star survey. Our analysis is based on the structural models of the Galactic population components that were derived from the previous studies of ...
... Abstract. We discuss star count and three-color data for the two inner-Galaxy fields SA 107 and NGC 6171 observed in the new Basel RGU high-latitude field star survey. Our analysis is based on the structural models of the Galactic population components that were derived from the previous studies of ...
Galaxies - University of Iowa Astrophysics
... A) They all have the same distance. B) Their luminosity can be determined from their pulsation period. C) They all have the same luminosity. D) They all have the same radius. ...
... A) They all have the same distance. B) Their luminosity can be determined from their pulsation period. C) They all have the same luminosity. D) They all have the same radius. ...
Perseus (constellation)

Perseus, named after the Greek mythological hero Perseus, is a constellation in the northern sky. It was one of 48 listed by the 2nd-century astronomer Ptolemy and among the 88 modern constellations defined by the International Astronomical Union (IAU). It is located in the northern celestial hemisphere near several other constellations named after legends surrounding Perseus, including Andromeda to the west and Cassiopeia to the north. Perseus is also bordered by Aries and Taurus to the south, Auriga to the east, Camelopardalis to the north, and Triangulum to the west.The galactic plane of the Milky Way passes through Perseus but is mostly obscured by molecular clouds. The constellation's brightest star is the yellow-white supergiant Alpha Persei (also called Mirfak), which shines at magnitude 1.79. It and many of the surrounding stars are members of an open cluster known as the Alpha Persei Cluster. The best-known star, however, is Algol (Beta Persei), linked with ominous legends because of its variability, which is noticeable to the naked eye. Rather than being an intrinsically variable star, it is an eclipsing binary. Other notable star systems in Perseus include X Persei, a binary system containing a neutron star, and GK Persei, a nova that peaked at magnitude 0.2 in 1901. The Double Cluster, comprising two open clusters quite near each other in the sky, was known to the ancient Chinese. The constellation gives its name to the Perseus Cluster (Abell 426), a massive galaxy cluster located 250 million light-years from Earth. It hosts the radiant of the annual Perseids meteor shower—one of the most prominent meteor showers in the sky.