Heliacal Rising of Canopus in Indian Astronomy
... body’s entry into the Sun’s range of effulgence is called ‘heliacal setting’ [Heliacal: related to the Sun]. Similarly the body’s coming out of the Sun’s range of brightness is called heliacal rising. Since the concerned star is close to the Sun in this interval of its heliacal setting and heliacal ...
... body’s entry into the Sun’s range of effulgence is called ‘heliacal setting’ [Heliacal: related to the Sun]. Similarly the body’s coming out of the Sun’s range of brightness is called heliacal rising. Since the concerned star is close to the Sun in this interval of its heliacal setting and heliacal ...
Chapter 17--Star Stuff
... only a million years or less. A star like our Sun takes about 50 million years to go from the beginning of the protostellar stage to the main sequence. A very low-mass star of spectral type M may spend more than a hundred million years as a protostar. Thus, the most massive stars in a young star clu ...
... only a million years or less. A star like our Sun takes about 50 million years to go from the beginning of the protostellar stage to the main sequence. A very low-mass star of spectral type M may spend more than a hundred million years as a protostar. Thus, the most massive stars in a young star clu ...
Document
... We can only see them visually when they block out light from behind Dark nebula absorb in the visible and UV Dark nebula radiate in the infrared In the Milky Way there are dark nebula throughout the plane of the galaxy ...
... We can only see them visually when they block out light from behind Dark nebula absorb in the visible and UV Dark nebula radiate in the infrared In the Milky Way there are dark nebula throughout the plane of the galaxy ...
Sec 30.1 - Highland High School
... Population I stars tend to follow circular orbits with low (flat) eccentricity, and their orbits lie close to the plane of the disk. Population I stars also have normal compositions, meaning that approximately 2 percent of their mass is made up of elements heavier than helium. ...
... Population I stars tend to follow circular orbits with low (flat) eccentricity, and their orbits lie close to the plane of the disk. Population I stars also have normal compositions, meaning that approximately 2 percent of their mass is made up of elements heavier than helium. ...
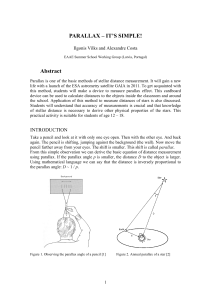
PARALLAX – IT`S SIMPLE! Abstract
... measure. Even for the nearest star, Alpha Centauri the annual parallax is less than 1 arcsecond (less than 1/3600 of one arc degree). Until recent time the annual parallaxes of only a few hundreds of stars were known. The accuracy of parallax measurements was vastly improved when the European Space ...
... measure. Even for the nearest star, Alpha Centauri the annual parallax is less than 1 arcsecond (less than 1/3600 of one arc degree). Until recent time the annual parallaxes of only a few hundreds of stars were known. The accuracy of parallax measurements was vastly improved when the European Space ...
Enhanced lithium depletion in Sun-like stars with orbiting planets.
... targets. It is known19 that chromospheric activity correlates with stellar rotation (vsini). If the planet hosts were older than the comparison sample, their rotational velocities would be smaller than in the comparison sample. This is not observed either (Fig 2b), adding support to our previous con ...
... targets. It is known19 that chromospheric activity correlates with stellar rotation (vsini). If the planet hosts were older than the comparison sample, their rotational velocities would be smaller than in the comparison sample. This is not observed either (Fig 2b), adding support to our previous con ...
The Stars - Springer
... Y stars are sub-brown dwarfs. As of the time of writing, no Y objects have yet been discovered! The star types R, N and S actually overlap class M, and so R and N have been reclassified as C-type stars, the C standing for carbon stars. Complicated, isn’t it! ...
... Y stars are sub-brown dwarfs. As of the time of writing, no Y objects have yet been discovered! The star types R, N and S actually overlap class M, and so R and N have been reclassified as C-type stars, the C standing for carbon stars. Complicated, isn’t it! ...
Distance determination for RAVE stars using stellar models
... The power spectrum is used to measure the power of density perturbations on a certain scale. The current cosmological model predicts a HarrisonZel’dovich spectrum (P (k) ∝ k, where k is the wavenumber). This power spectrum predicts more power on small scale, so there should be more dwarf galaxies th ...
... The power spectrum is used to measure the power of density perturbations on a certain scale. The current cosmological model predicts a HarrisonZel’dovich spectrum (P (k) ∝ k, where k is the wavenumber). This power spectrum predicts more power on small scale, so there should be more dwarf galaxies th ...
A star`s life is a struggle between ______ wanting to crush it, and
... b) Nuclear fusion would be impossible so stars would slowly cool and dim after their initial formation. c) Nuclear fission would be impossible and elements heavier than iron would not exist. d) Stars would continue burning heavier and heavier elements and the universe would have far more lead and ...
... b) Nuclear fusion would be impossible so stars would slowly cool and dim after their initial formation. c) Nuclear fission would be impossible and elements heavier than iron would not exist. d) Stars would continue burning heavier and heavier elements and the universe would have far more lead and ...
Solaria Binaria - The Grazian Archive
... double or triple star system. Inasmuch as we cannot judge the organization of distant star systems, this statistic may or may not characterize the starry Universe. Even within our sample of sixty nearby stars, the star density and the binary frequency drop with increasing distance (van de Kamp 1971, ...
... double or triple star system. Inasmuch as we cannot judge the organization of distant star systems, this statistic may or may not characterize the starry Universe. Even within our sample of sixty nearby stars, the star density and the binary frequency drop with increasing distance (van de Kamp 1971, ...
Video Lesson Information Astronomy: Observations & Theories Astronomy 1
... constellations, and brought the aspects of the sky into their buildings and structures, such as those of Chaco Canyon in the southwestern United States. Lesson 3 - Celestial Cycles This video lesson explains the motion of Earth around the sun and its yearly cycle. Astronomers explain the unique orbi ...
... constellations, and brought the aspects of the sky into their buildings and structures, such as those of Chaco Canyon in the southwestern United States. Lesson 3 - Celestial Cycles This video lesson explains the motion of Earth around the sun and its yearly cycle. Astronomers explain the unique orbi ...
Observations of binary systems with pulsating components
... • Spectroscopic binaries: stars which exhibit periodic displacement of their spectral lines owing to Doppler effect caused by orbital motion. • Depending on components’ relative brightness, the observed spectrum will show the displacement of lines of one or both components (if a star is too faint, i ...
... • Spectroscopic binaries: stars which exhibit periodic displacement of their spectral lines owing to Doppler effect caused by orbital motion. • Depending on components’ relative brightness, the observed spectrum will show the displacement of lines of one or both components (if a star is too faint, i ...
April 2015 Astronomy Calendar by Dave Mitsky
... Brilliant Venus is positioned high in the west at sunset. It sets about three hours after the Sun in early April and three-and-one-half hours after sunset by month’s end. Venus is at perihelion on April 18th. During the second week of April, the planet passes between the Hyades (Melotte 25) and Plei ...
... Brilliant Venus is positioned high in the west at sunset. It sets about three hours after the Sun in early April and three-and-one-half hours after sunset by month’s end. Venus is at perihelion on April 18th. During the second week of April, the planet passes between the Hyades (Melotte 25) and Plei ...
Blocking Starlight Much Closer to Home 2: This Year`s
... For Charon, with no atmosphere (and our occultation method is very sensitive), the starlight disappears abruptly. If the star is brighter than the occulting object, the occultation is quite noticeable; if the star is fainter, then just a percentage is subtracted from the total. For Pluto (and, earli ...
... For Charon, with no atmosphere (and our occultation method is very sensitive), the starlight disappears abruptly. If the star is brighter than the occulting object, the occultation is quite noticeable; if the star is fainter, then just a percentage is subtracted from the total. For Pluto (and, earli ...
Stars & Galaxies - newmanlib.ibri.org
... • The ancients called the brightest stars 'first magnitude,' the next brightest 'second magnitude,' and so on thru 6th. • Modern astronomy has regularized this, using zero and negative numbers for the very brightest objects, and higher numbers for objects invisible w/o optical help. • For instance, ...
... • The ancients called the brightest stars 'first magnitude,' the next brightest 'second magnitude,' and so on thru 6th. • Modern astronomy has regularized this, using zero and negative numbers for the very brightest objects, and higher numbers for objects invisible w/o optical help. • For instance, ...
CENTRAL TEXAS COLLEGE
... An Administrative Withdrawal: An administrative withdrawal may be initiated when the student fails to meet College attendance requirements. The instructor will assign the appropriate grade on the Administrative Withdrawal Form for submission to the registrar. The following specific rules apply to ab ...
... An Administrative Withdrawal: An administrative withdrawal may be initiated when the student fails to meet College attendance requirements. The instructor will assign the appropriate grade on the Administrative Withdrawal Form for submission to the registrar. The following specific rules apply to ab ...
Constraining the star formation histories of spiral bulges
... R. N. Proctor, A. E. Sansom and I. N. Reid Table 2. Error table for NGC 3623. Top: index values for the central 3 arcsec and the associated Poisson noise are given. Sky errors are derived as detailed in Section 2.4. Calculations of both velocity dispersion and recession velocity errors (s and v resp ...
... R. N. Proctor, A. E. Sansom and I. N. Reid Table 2. Error table for NGC 3623. Top: index values for the central 3 arcsec and the associated Poisson noise are given. Sky errors are derived as detailed in Section 2.4. Calculations of both velocity dispersion and recession velocity errors (s and v resp ...
Export To Word
... Response Template may help students organize their thoughts and make grading faster, but if you wish to focus on student writing skills, spelling, and grammar, then you may wish to have them respond in an essay without using the template. (51-90 min.) Once the students understand the instructions fo ...
... Response Template may help students organize their thoughts and make grading faster, but if you wish to focus on student writing skills, spelling, and grammar, then you may wish to have them respond in an essay without using the template. (51-90 min.) Once the students understand the instructions fo ...
KS1 Education Guide - Immersive Theatres
... (From the Merriam-Webster Dictionary) Average – (adjective) being about midway between extremes, not out of the ordinary: Common Planet – any of the large bodies that revolve around the sun in the solar system Star – a: a natural luminous body visible in the sky especially at night b: a self-luminou ...
... (From the Merriam-Webster Dictionary) Average – (adjective) being about midway between extremes, not out of the ordinary: Common Planet – any of the large bodies that revolve around the sun in the solar system Star – a: a natural luminous body visible in the sky especially at night b: a self-luminou ...
Perseus (constellation)

Perseus, named after the Greek mythological hero Perseus, is a constellation in the northern sky. It was one of 48 listed by the 2nd-century astronomer Ptolemy and among the 88 modern constellations defined by the International Astronomical Union (IAU). It is located in the northern celestial hemisphere near several other constellations named after legends surrounding Perseus, including Andromeda to the west and Cassiopeia to the north. Perseus is also bordered by Aries and Taurus to the south, Auriga to the east, Camelopardalis to the north, and Triangulum to the west.The galactic plane of the Milky Way passes through Perseus but is mostly obscured by molecular clouds. The constellation's brightest star is the yellow-white supergiant Alpha Persei (also called Mirfak), which shines at magnitude 1.79. It and many of the surrounding stars are members of an open cluster known as the Alpha Persei Cluster. The best-known star, however, is Algol (Beta Persei), linked with ominous legends because of its variability, which is noticeable to the naked eye. Rather than being an intrinsically variable star, it is an eclipsing binary. Other notable star systems in Perseus include X Persei, a binary system containing a neutron star, and GK Persei, a nova that peaked at magnitude 0.2 in 1901. The Double Cluster, comprising two open clusters quite near each other in the sky, was known to the ancient Chinese. The constellation gives its name to the Perseus Cluster (Abell 426), a massive galaxy cluster located 250 million light-years from Earth. It hosts the radiant of the annual Perseids meteor shower—one of the most prominent meteor showers in the sky.