POSTERS SESSION I: Atmospheres of Massive Stars
... be directly measured from the Doppler broadening of their photospheric lines. In Wolf-Rayet (WR) stars, however, such measurements are impossible, since their continuum emission is formed in the dense wind that hides the hydrostatic, stellar surface. Here, we present a technique to derive the rotati ...
... be directly measured from the Doppler broadening of their photospheric lines. In Wolf-Rayet (WR) stars, however, such measurements are impossible, since their continuum emission is formed in the dense wind that hides the hydrostatic, stellar surface. Here, we present a technique to derive the rotati ...
CH12.AST1001.F16.EDS
... • Stellar properties depend on both mass and age: those that have finished fusing H to He in their cores are no longer on the main sequence. • All stars become larger and redder after exhausting their core hydrogen: giants and supergiants. • Most stars end up small and white after fusion has ceased: ...
... • Stellar properties depend on both mass and age: those that have finished fusing H to He in their cores are no longer on the main sequence. • All stars become larger and redder after exhausting their core hydrogen: giants and supergiants. • Most stars end up small and white after fusion has ceased: ...
Chapter 12: Surveying the Stars 12.1 Properties of Stars How do we
... Thought Question How would the apparent brightness of Alpha Centauri change if it were three times farther away? A. It would be only 1/3 as bright. B. It would be only 1/6 as bright. C. It would be only 1/9 as bright. D. It would be three times as bright. So how far away are these stars? © 2015 ...
... Thought Question How would the apparent brightness of Alpha Centauri change if it were three times farther away? A. It would be only 1/3 as bright. B. It would be only 1/6 as bright. C. It would be only 1/9 as bright. D. It would be three times as bright. So how far away are these stars? © 2015 ...
Open clusters and associations in the Gaia era
... the object luminosity and therefore the mass estimate. Indeed fast rotators may have a larger radius which would result in a larger luminosity and an overestimated mass. At the opposite, strong magnetic activity could create large cool spots which would reduce the effective temperature and underesti ...
... the object luminosity and therefore the mass estimate. Indeed fast rotators may have a larger radius which would result in a larger luminosity and an overestimated mass. At the opposite, strong magnetic activity could create large cool spots which would reduce the effective temperature and underesti ...
PDF format
... – An H-R diagram plots stellar luminosity of stars versus surface temperature (or color or spectral type). • What is the significance of the main sequence? – Normal stars that fuse H to He in their cores fall on the main sequence of an H-R diagram. – A star's mass determines its position along t ...
... – An H-R diagram plots stellar luminosity of stars versus surface temperature (or color or spectral type). • What is the significance of the main sequence? – Normal stars that fuse H to He in their cores fall on the main sequence of an H-R diagram. – A star's mass determines its position along t ...
VY Canis Majoris: The Astrophysical Basis of Its Luminosity
... VY CMa is not alone. In previous papers (Humphreys et al 1997, Smith et al 2001) I have pointed out that about 10 known M-type supergiants in the Milky Way and Local Group galaxies have Mbol brighter than -9 mag. About half of these stars, in the Milky Way and in the LMC, are known OH/IR stars with ...
... VY CMa is not alone. In previous papers (Humphreys et al 1997, Smith et al 2001) I have pointed out that about 10 known M-type supergiants in the Milky Way and Local Group galaxies have Mbol brighter than -9 mag. About half of these stars, in the Milky Way and in the LMC, are known OH/IR stars with ...
NAME: SECTION: Mon Tue Wed Thu ASTRONOMY LAB Stellarium
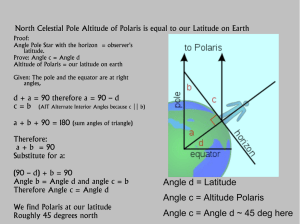
... 2. There are also a set of grid lines that radiate outward from the North Celestial Pole. These lines are analogous to the longitude lines on Earth. Notice that these lines are also labeled. The labels are not in degrees, but “hours” (e.g., “21h”). If you look carefully the labels run from 0h to 24 ...
... 2. There are also a set of grid lines that radiate outward from the North Celestial Pole. These lines are analogous to the longitude lines on Earth. Notice that these lines are also labeled. The labels are not in degrees, but “hours” (e.g., “21h”). If you look carefully the labels run from 0h to 24 ...
The HIRES science case
... predictions of disc migration. Recent results have shown that hot Jupiter planets on non-coplanar orbits are common, including some planets on retrograde orbits (Triaud et al. 2010). Those measurements have been interpreted as showing that dynamical events are probably not uncommon and that not all ...
... predictions of disc migration. Recent results have shown that hot Jupiter planets on non-coplanar orbits are common, including some planets on retrograde orbits (Triaud et al. 2010). Those measurements have been interpreted as showing that dynamical events are probably not uncommon and that not all ...
Age-Dating of Young Stars and Stellar Systems
... core-helium or helium-shell flashes at masses below ∼8 M . I will later return to the importance of RSGs when emphasizing dust obscuration effects in young stellar systems. Here I highlight the different Teff scales of cool stars adopted in spectral classification and in evolution models. Note that ...
... core-helium or helium-shell flashes at masses below ∼8 M . I will later return to the importance of RSGs when emphasizing dust obscuration effects in young stellar systems. Here I highlight the different Teff scales of cool stars adopted in spectral classification and in evolution models. Note that ...
Epsilon Aurigae: a rare stellar eclipse - Project VS
... observed the mysterious dark companion in a binary star system of epsilon Aurigae. Using an instrument developed at the University of Michigan, scientists have taken close-up pictures of Epsilon Aurigae during its eclipse. A series of images obtained at the Center for High Angular Resolution interfe ...
... observed the mysterious dark companion in a binary star system of epsilon Aurigae. Using an instrument developed at the University of Michigan, scientists have taken close-up pictures of Epsilon Aurigae during its eclipse. A series of images obtained at the Center for High Angular Resolution interfe ...
NASA FUSE Satellite Solves the Case of the Missing Deuterium
... deuterium has been destroyed, FUSE has found, suggesting that less than the amount expected has cycled through stars. "The peak galactic detection levels are likely close to the real total deuterium abundance in the Milky Way, with the rest of it in hiding, not destroyed," said Warren Moos of Johns ...
... deuterium has been destroyed, FUSE has found, suggesting that less than the amount expected has cycled through stars. "The peak galactic detection levels are likely close to the real total deuterium abundance in the Milky Way, with the rest of it in hiding, not destroyed," said Warren Moos of Johns ...
Seeing Earth`s Orbit in the Stars: Parallax and Aberration
... and certain aspects of planetary motions in the Copernican system. But if Earth has a yearly orbit around the Sun, then the stars should also display a parallactic wobble with a period of one ...
... and certain aspects of planetary motions in the Copernican system. But if Earth has a yearly orbit around the Sun, then the stars should also display a parallactic wobble with a period of one ...
An introduction to photometry and photometric measurements Henry
... • Other work provides an absolute flux calibration linked to Vega. • Practical difficulties: (1) not everyone can (or should) observe Vega -- it’s much too bright -- so a network of secondary standards of fainter sources have been established. • The Landolt system, based on A0 stars has become the sta ...
... • Other work provides an absolute flux calibration linked to Vega. • Practical difficulties: (1) not everyone can (or should) observe Vega -- it’s much too bright -- so a network of secondary standards of fainter sources have been established. • The Landolt system, based on A0 stars has become the sta ...
Survey of Astrophysics A110 The Milky Way Galaxy
... – 5. They have long main sequences on the HR diagram which indicate that they are young (e.g., many contain young hot O and B type Population I stars). ...
... – 5. They have long main sequences on the HR diagram which indicate that they are young (e.g., many contain young hot O and B type Population I stars). ...
Senior thesis - University of Texas Astronomy Home Page
... every field of astronomy. Using precision asteroseismology, we can explore, for example, a star’s mass, rotation rate, equation of state, and nuclear reaction rates. By studying the rate of change of WD pulsations we can explore galactic time measurements, orbiting planets, dark matter theories, or ...
... every field of astronomy. Using precision asteroseismology, we can explore, for example, a star’s mass, rotation rate, equation of state, and nuclear reaction rates. By studying the rate of change of WD pulsations we can explore galactic time measurements, orbiting planets, dark matter theories, or ...
HET603-M05A01: Colours and Spectral Types: Learning about stars
... • hot stars will have a high spectrum peaked towards the blue end; • cool stars will have a low, flat spectrum peaked towards the red end; • if a star is moving rapidly towards us (or away from us), then the entire spectrum is shifted towards the blue (or the red) end of the spectrum; • that very ho ...
... • hot stars will have a high spectrum peaked towards the blue end; • cool stars will have a low, flat spectrum peaked towards the red end; • if a star is moving rapidly towards us (or away from us), then the entire spectrum is shifted towards the blue (or the red) end of the spectrum; • that very ho ...
CH. 7 - science1d
... With enough time and a fast enough spacecraft to transport us on this imaginary journey, we would eventually travel among the stars. The next nearest star to Earth after the Sun is actually part of a group of three stars that orbit each other. This group is called the Centauri system (Figure 7.8). I ...
... With enough time and a fast enough spacecraft to transport us on this imaginary journey, we would eventually travel among the stars. The next nearest star to Earth after the Sun is actually part of a group of three stars that orbit each other. This group is called the Centauri system (Figure 7.8). I ...
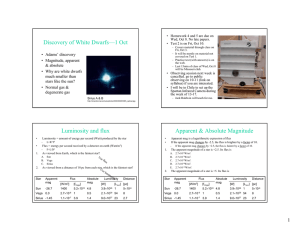
Discovery of White Dwarfs—1 Oct • Adams’ discovery
... • If the apparent mag changes by −2.5, the flux is brighter by a factor of 10. • Fluxes and magnitudes of two stars A and B ...
... • If the apparent mag changes by −2.5, the flux is brighter by a factor of 10. • Fluxes and magnitudes of two stars A and B ...
Chapter15.1
... – An H-R diagram plots stellar luminosity of stars versus surface temperature (or color or spectral type). ...
... – An H-R diagram plots stellar luminosity of stars versus surface temperature (or color or spectral type). ...
Cataclysmic Cosmic Events and How to Observe Them www.springer.com/series/5338
... their violence and energy output. Active galaxies, containing supermassive black holes at their centers, can swallow a solar mass every month, releasing huge amounts of energy that amateur astronomers can observe as a fluctuation in light output. The luminosity of some of these objects is truly mind ...
... their violence and energy output. Active galaxies, containing supermassive black holes at their centers, can swallow a solar mass every month, releasing huge amounts of energy that amateur astronomers can observe as a fluctuation in light output. The luminosity of some of these objects is truly mind ...
Clusters as laboratories for the study of galaxy evolution
... The DEEP Groth Strip Survey. IX. Evolution of the Fundamental Plane of Field Galaxies – Gebhardt et al., 2003 ApJ 537, 239. Velocity dispersions and optical photometry for 21 “early-type” galaxies in the Groth strip. “The difference in the degree of evolution between our field sample and published ...
... The DEEP Groth Strip Survey. IX. Evolution of the Fundamental Plane of Field Galaxies – Gebhardt et al., 2003 ApJ 537, 239. Velocity dispersions and optical photometry for 21 “early-type” galaxies in the Groth strip. “The difference in the degree of evolution between our field sample and published ...
Perseus (constellation)

Perseus, named after the Greek mythological hero Perseus, is a constellation in the northern sky. It was one of 48 listed by the 2nd-century astronomer Ptolemy and among the 88 modern constellations defined by the International Astronomical Union (IAU). It is located in the northern celestial hemisphere near several other constellations named after legends surrounding Perseus, including Andromeda to the west and Cassiopeia to the north. Perseus is also bordered by Aries and Taurus to the south, Auriga to the east, Camelopardalis to the north, and Triangulum to the west.The galactic plane of the Milky Way passes through Perseus but is mostly obscured by molecular clouds. The constellation's brightest star is the yellow-white supergiant Alpha Persei (also called Mirfak), which shines at magnitude 1.79. It and many of the surrounding stars are members of an open cluster known as the Alpha Persei Cluster. The best-known star, however, is Algol (Beta Persei), linked with ominous legends because of its variability, which is noticeable to the naked eye. Rather than being an intrinsically variable star, it is an eclipsing binary. Other notable star systems in Perseus include X Persei, a binary system containing a neutron star, and GK Persei, a nova that peaked at magnitude 0.2 in 1901. The Double Cluster, comprising two open clusters quite near each other in the sky, was known to the ancient Chinese. The constellation gives its name to the Perseus Cluster (Abell 426), a massive galaxy cluster located 250 million light-years from Earth. It hosts the radiant of the annual Perseids meteor shower—one of the most prominent meteor showers in the sky.