A Brief History of Planetary Science
... Each spectral type is divided into 10 sub classes 0 - 9 (from high to low T) ...
... Each spectral type is divided into 10 sub classes 0 - 9 (from high to low T) ...
Astronomy 162 Lab 4: Stars
... Magnitude is measured so that the smaller numbers correspond to the brightest objects. The Sun is by far the brightest object in the sky and has an Apparent Magnitude of about -30. The Apparent Magnitude of any object is determined by two things: the object's intrinsic brightness, and the object's d ...
... Magnitude is measured so that the smaller numbers correspond to the brightest objects. The Sun is by far the brightest object in the sky and has an Apparent Magnitude of about -30. The Apparent Magnitude of any object is determined by two things: the object's intrinsic brightness, and the object's d ...
Topic E: Astrophysics
... ellipses and moons orbit planets. (Details of Kepler’s laws are not required.) Students should also know the names of the planets, their approximate comparative sizes and comparative distances from the Sun, the nature of comets, and the nature and position of the asteroid belt. ...
... ellipses and moons orbit planets. (Details of Kepler’s laws are not required.) Students should also know the names of the planets, their approximate comparative sizes and comparative distances from the Sun, the nature of comets, and the nature and position of the asteroid belt. ...
White Dwarf star. Are
... of energy, it is finished. Our sun will run out of energy and it will be finished too. But this will not happen for another 5 billion years! ...
... of energy, it is finished. Our sun will run out of energy and it will be finished too. But this will not happen for another 5 billion years! ...
Quiz Solution: 1 April 2013 What does it mean when an astronomer
... What does it mean when an astronomer says that a star "moves" from one place to another on an H-R Diagram? Can you provide an example of this? As stars evolve and change structure, their radii and temperatures also change. Since a star's luminosity is dependent on both temperature and radius, the lu ...
... What does it mean when an astronomer says that a star "moves" from one place to another on an H-R Diagram? Can you provide an example of this? As stars evolve and change structure, their radii and temperatures also change. Since a star's luminosity is dependent on both temperature and radius, the lu ...
KOI-54 Claude Plymate There is a star system about 45 light years
... close binary system, consisting of nearly twin A stars in highly eccentric (e = 0.83) 41.8 day orbits about their mutual center of mass. These main sequence stars reside right at the bottom of the instability strip on the H-R diagram. The instability strip is a nearly vertical region in the H-R diag ...
... close binary system, consisting of nearly twin A stars in highly eccentric (e = 0.83) 41.8 day orbits about their mutual center of mass. These main sequence stars reside right at the bottom of the instability strip on the H-R diagram. The instability strip is a nearly vertical region in the H-R diag ...
solution
... for visual (the visible range includes visual and spans B V G R) which lets light in the range 551 nm ± 88 nm through. So for a star to be bright at U and V, but dim at B, means that the spectrum has a big dip in it in-between the two bands. This is very unlikely, since stars are blackbody radiators ...
... for visual (the visible range includes visual and spans B V G R) which lets light in the range 551 nm ± 88 nm through. So for a star to be bright at U and V, but dim at B, means that the spectrum has a big dip in it in-between the two bands. This is very unlikely, since stars are blackbody radiators ...
Life Cycles of Stars
... Fate of High Mass Stars • After Helium is exhausted, core collapses again until it becomes hot enough to fuse Carbon into Magnesium or Oxygen. • Through a combination of processes, successively heavier elements are formed and burned. ...
... Fate of High Mass Stars • After Helium is exhausted, core collapses again until it becomes hot enough to fuse Carbon into Magnesium or Oxygen. • Through a combination of processes, successively heavier elements are formed and burned. ...
Problem set 2
... specific intensity), you do not need to know the distance or luminosity, but only the temperature and angle subtended! Both of these are direct observables, unlike distance and luminosity . . . (c) Show that the answer to the previous part is the same as you would get by the more obvious but unneces ...
... specific intensity), you do not need to know the distance or luminosity, but only the temperature and angle subtended! Both of these are direct observables, unlike distance and luminosity . . . (c) Show that the answer to the previous part is the same as you would get by the more obvious but unneces ...
constellations[1]
... above the North Pole. This star appears in the same place every night all year long. In the Northern Hemisphere, if you find Polaris you will be able to tell which direction is north. ...
... above the North Pole. This star appears in the same place every night all year long. In the Northern Hemisphere, if you find Polaris you will be able to tell which direction is north. ...
Constellations 1
... above the North Pole. This star appears in the same place every night all year long. In the Northern Hemisphere, if you find Polaris you will be able to tell which direction is north. ...
... above the North Pole. This star appears in the same place every night all year long. In the Northern Hemisphere, if you find Polaris you will be able to tell which direction is north. ...
Constellations 1
... above the North Pole. This star appears in the same place every night all year long. In the Northern Hemisphere, if you find Polaris you will be able to tell which direction is north. ...
... above the North Pole. This star appears in the same place every night all year long. In the Northern Hemisphere, if you find Polaris you will be able to tell which direction is north. ...
Astronomers classify stars according to their physical characteristics
... called its _apparent magnitude__ or brightness. •A star’s _apparent_ brightness depends upon how bright it _actually is and its _distance_ from Earth. •A star’s actual brightness (or _absolute magnitude) usually depends on the star’s _size_ and temperature__. •Because stars with _more mass ___ have ...
... called its _apparent magnitude__ or brightness. •A star’s _apparent_ brightness depends upon how bright it _actually is and its _distance_ from Earth. •A star’s actual brightness (or _absolute magnitude) usually depends on the star’s _size_ and temperature__. •Because stars with _more mass ___ have ...
ISP 205 Review Questions, Week 10
... density (the number of atoms per unit volume), and also to the average speed of the atoms (measured by the gas temperature). 3. Using the Hertzprung-Russell diagram in Figure ...
... density (the number of atoms per unit volume), and also to the average speed of the atoms (measured by the gas temperature). 3. Using the Hertzprung-Russell diagram in Figure ...
Document
... The Milky Way Galaxy is a giant disk of stars 160,000 light-years across and 1,000 light-years thick. The Sun is located at the edge of a spiral arm, 30,000 light-years from the center It takes 250 Million years for the Sun to complete one orbit ...
... The Milky Way Galaxy is a giant disk of stars 160,000 light-years across and 1,000 light-years thick. The Sun is located at the edge of a spiral arm, 30,000 light-years from the center It takes 250 Million years for the Sun to complete one orbit ...
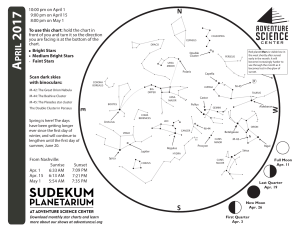
Night Sky Checklist July–August–September Unaided Eye Astronomy
... roughly around the time of the American Revolution. Most deep sky objects look like “faint fuzzies” to the unaided eye, and many are attractive in binoculars or a low power telescope.) M6 is a faint, fairly small open cluster barely visible to the unaided eye under clear, dark skies. About 1600 ligh ...
... roughly around the time of the American Revolution. Most deep sky objects look like “faint fuzzies” to the unaided eye, and many are attractive in binoculars or a low power telescope.) M6 is a faint, fairly small open cluster barely visible to the unaided eye under clear, dark skies. About 1600 ligh ...
19Nov_2014
... • The core collapses, and the layers above fall rapidly toward the center, where they collide with the core material and “bounce” • The “bounced material collides with the remaining infalling gas, raising temperatures high enough to set off a massive fusion reaction. The star then ...
... • The core collapses, and the layers above fall rapidly toward the center, where they collide with the core material and “bounce” • The “bounced material collides with the remaining infalling gas, raising temperatures high enough to set off a massive fusion reaction. The star then ...
Astronomy Test Review
... 19. SuperGiants and some Red giant stars end their lives as supernovas. (and some Blue giants) 20. A pulsar is a spinning neutron star that gives off pulses of energy. (radio waves) 21. It takes our solar system 200 million years to orbit the Milky Way. 22. Greater red shifts mean the universe ...
... 19. SuperGiants and some Red giant stars end their lives as supernovas. (and some Blue giants) 20. A pulsar is a spinning neutron star that gives off pulses of energy. (radio waves) 21. It takes our solar system 200 million years to orbit the Milky Way. 22. Greater red shifts mean the universe ...
How it works:
... How it works: On the reverse of this sheet are four constellations, all of which can be seen on summer nights in Colorado. Each constellation has five stars. For every book read, fill in one star. Each time you complete a constellation, bring this sheet to the teenseen to receive a prize and a raffl ...
... How it works: On the reverse of this sheet are four constellations, all of which can be seen on summer nights in Colorado. Each constellation has five stars. For every book read, fill in one star. Each time you complete a constellation, bring this sheet to the teenseen to receive a prize and a raffl ...
1704 chart front - Adventure Science Center
... the Bull. Still further beyond Aldebaran, you may find another orange-red dot, the red planet Mars. Mars will be much fainter. If you can’t find it, try scanning with binoculars. Like Orion and Taurus, Mars will be gone by the end of the month. Look high in the north for the Big Dipper. As famous as t ...
... the Bull. Still further beyond Aldebaran, you may find another orange-red dot, the red planet Mars. Mars will be much fainter. If you can’t find it, try scanning with binoculars. Like Orion and Taurus, Mars will be gone by the end of the month. Look high in the north for the Big Dipper. As famous as t ...
The Hertzsprung – Russell Diagram
... 4. List the four categories of information you can determine about a star by using the H-R Diagram? 5. If you know a star’s color, what other information can you determine? 6. What is the relationship between the X and Y values for main sequence stars? 7. 90% of stars belong to which category? 8. Wh ...
... 4. List the four categories of information you can determine about a star by using the H-R Diagram? 5. If you know a star’s color, what other information can you determine? 6. What is the relationship between the X and Y values for main sequence stars? 7. 90% of stars belong to which category? 8. Wh ...
LT 9: I can describe how a protostar becomes a star.
... – Pulsating stars: change in brightness as they expand (cool, dim) and contract (hot, bright) – Cepheid variables: the longer their cycle is the larger their absolute magnitude is – Eclipsing binary: 2 stars of unequal brightness that revolve around each other and appear to change brightness Pulsa ...
... – Pulsating stars: change in brightness as they expand (cool, dim) and contract (hot, bright) – Cepheid variables: the longer their cycle is the larger their absolute magnitude is – Eclipsing binary: 2 stars of unequal brightness that revolve around each other and appear to change brightness Pulsa ...
Perseus (constellation)

Perseus, named after the Greek mythological hero Perseus, is a constellation in the northern sky. It was one of 48 listed by the 2nd-century astronomer Ptolemy and among the 88 modern constellations defined by the International Astronomical Union (IAU). It is located in the northern celestial hemisphere near several other constellations named after legends surrounding Perseus, including Andromeda to the west and Cassiopeia to the north. Perseus is also bordered by Aries and Taurus to the south, Auriga to the east, Camelopardalis to the north, and Triangulum to the west.The galactic plane of the Milky Way passes through Perseus but is mostly obscured by molecular clouds. The constellation's brightest star is the yellow-white supergiant Alpha Persei (also called Mirfak), which shines at magnitude 1.79. It and many of the surrounding stars are members of an open cluster known as the Alpha Persei Cluster. The best-known star, however, is Algol (Beta Persei), linked with ominous legends because of its variability, which is noticeable to the naked eye. Rather than being an intrinsically variable star, it is an eclipsing binary. Other notable star systems in Perseus include X Persei, a binary system containing a neutron star, and GK Persei, a nova that peaked at magnitude 0.2 in 1901. The Double Cluster, comprising two open clusters quite near each other in the sky, was known to the ancient Chinese. The constellation gives its name to the Perseus Cluster (Abell 426), a massive galaxy cluster located 250 million light-years from Earth. It hosts the radiant of the annual Perseids meteor shower—one of the most prominent meteor showers in the sky.








![constellations[1]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/008081352_2-f872c73597ccdde4cfed49c9b322d3b2-300x300.png)