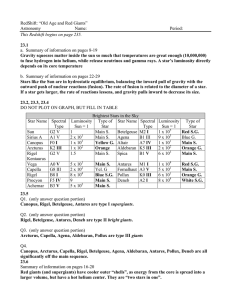
Stellar Spectral Classes
... For which two spectral classes are these lines the prominent feature? ...
... For which two spectral classes are these lines the prominent feature? ...
Chemical Composition of Stars II
... • Students will put on the glasses provided and take note of the spectral lines that appear on the right (3:00 position) • Students should write notes as to what colors are being observed and in which order the colors appear • Students will reproduce what they observed using colored pencils on the s ...
... • Students will put on the glasses provided and take note of the spectral lines that appear on the right (3:00 position) • Students should write notes as to what colors are being observed and in which order the colors appear • Students will reproduce what they observed using colored pencils on the s ...
Hertzsprung2 - courses.psu.edu
... A final word about the stars in the night sky: * Majority of stars in the galaxy are low-luminosity cool stars (“red dwarfs”) ...
... A final word about the stars in the night sky: * Majority of stars in the galaxy are low-luminosity cool stars (“red dwarfs”) ...
Astronomy Review revised Key
... yellow, 5000-6000 degrees C in temperature, average in brightness, main sequence, average star. ...
... yellow, 5000-6000 degrees C in temperature, average in brightness, main sequence, average star. ...
3. Stellar Formation and Evolution
... the star's core starts to collapse and heat up. This causes the outer layers of the star to expand and cool, similar to the process that occurred after the star ran out of hydrogen fuel and left the main sequence. As the star becomes larger and larger, it eventually becomes a red supergiant. • Extre ...
... the star's core starts to collapse and heat up. This causes the outer layers of the star to expand and cool, similar to the process that occurred after the star ran out of hydrogen fuel and left the main sequence. As the star becomes larger and larger, it eventually becomes a red supergiant. • Extre ...
Temperature
... • Since gases ionize at different temperatures, the lines tell the temperature of the star. ...
... • Since gases ionize at different temperatures, the lines tell the temperature of the star. ...
chapter10
... Degenerate stellar remnant (C,O core) Extremely dense: 1 teaspoon of white dwarf material: mass ≈ 16 tons!!! Chunk of white dwarf material the size of a beach ball would outweigh an ocean liner! ...
... Degenerate stellar remnant (C,O core) Extremely dense: 1 teaspoon of white dwarf material: mass ≈ 16 tons!!! Chunk of white dwarf material the size of a beach ball would outweigh an ocean liner! ...
Redshift - Old Age and Red Giants
... Aldebaran (K5 III) and Pollux (K0 III) are orange giants that will cool into red giants like the sun. 23.8 (OMIT THIS SECTION) Q12. Q13. Q14. Q15. Q16. Conclusion Describe what you learned about the path a star takes after it moves off the main sequence. The path is complex and depends on the star’s ...
... Aldebaran (K5 III) and Pollux (K0 III) are orange giants that will cool into red giants like the sun. 23.8 (OMIT THIS SECTION) Q12. Q13. Q14. Q15. Q16. Conclusion Describe what you learned about the path a star takes after it moves off the main sequence. The path is complex and depends on the star’s ...
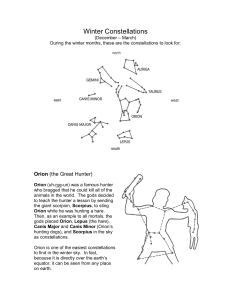
seven winter constellations
... Orion (uh-rye-un) was a famous hunter who bragged that he could kill all of the animals in the world. The gods decided to teach the hunter a lesson by sending the giant scorpion, Scorpius, to sting Orion while he was hunting a hare. Then, as an example to all mortals, the gods placed Orion, Lepus (t ...
... Orion (uh-rye-un) was a famous hunter who bragged that he could kill all of the animals in the world. The gods decided to teach the hunter a lesson by sending the giant scorpion, Scorpius, to sting Orion while he was hunting a hare. Then, as an example to all mortals, the gods placed Orion, Lepus (t ...
What`s Up - April 2016
... same distance, Canopus would appear far brighter than Sirius. Canopus is 15000 times as luminous as the sun, a rare yellow-white supergiant 313 light years away. If placed at the center of our solar system, its surface would be three quarters of the distance from the centre to the orbit of Mercury, ...
... same distance, Canopus would appear far brighter than Sirius. Canopus is 15000 times as luminous as the sun, a rare yellow-white supergiant 313 light years away. If placed at the center of our solar system, its surface would be three quarters of the distance from the centre to the orbit of Mercury, ...
White Dwarfs
... Globular clusters formed 12-14 billion years ago. Useful info for studying the history of the Milky Way Galaxy. ...
... Globular clusters formed 12-14 billion years ago. Useful info for studying the history of the Milky Way Galaxy. ...
WebQuest-The-Life-Cycle-of-Stars-1
... 2. You will investigate the process of nuclear fusion explained by Einstein's famous equation E = MC2 and learn how mass in the form of hydrogen atoms is converted to helium and causes a release of energy that makes stars shine. 3. You will also begin to understand the forces involved in stars that ...
... 2. You will investigate the process of nuclear fusion explained by Einstein's famous equation E = MC2 and learn how mass in the form of hydrogen atoms is converted to helium and causes a release of energy that makes stars shine. 3. You will also begin to understand the forces involved in stars that ...
Exam Study Guide
... under the mirror to control its shape of in order to correct for distortions caused by a variety of things including the mirror’s weight and position. 37. The technique called ______________ uses a high speed computer to monitor atmospheric distortion (often with a laser generated false star) and ad ...
... under the mirror to control its shape of in order to correct for distortions caused by a variety of things including the mirror’s weight and position. 37. The technique called ______________ uses a high speed computer to monitor atmospheric distortion (often with a laser generated false star) and ad ...
Handout from Allaire Star Party
... Among the most spectacular objects in the sky are emission nebulae. A nebula is a region of gas and dust that is held together by its own gravity. Stars form in nebulae when pockets of gas in these nebulae collapse and heat up enough to ignite nuclear fires in their cores. Our own Sun formed in such ...
... Among the most spectacular objects in the sky are emission nebulae. A nebula is a region of gas and dust that is held together by its own gravity. Stars form in nebulae when pockets of gas in these nebulae collapse and heat up enough to ignite nuclear fires in their cores. Our own Sun formed in such ...
Studying the Stars
... Pogson assigned the brightest stars the first order of magnitude (magnitude = 1), and dimmer stars were 2nd, 3rd, 4th order, etc. (magnitudes = 2, 3, 4, etc.) Now that we can be more accurate in our measurements, stars can have more specific magnitudes like 1.5, 6.73, etc. and even negative numbers ...
... Pogson assigned the brightest stars the first order of magnitude (magnitude = 1), and dimmer stars were 2nd, 3rd, 4th order, etc. (magnitudes = 2, 3, 4, etc.) Now that we can be more accurate in our measurements, stars can have more specific magnitudes like 1.5, 6.73, etc. and even negative numbers ...
Chapter 21
... • radii of 20 to several hundred solar radii (they are about the size of Jupiter's orbit!!!!) • two types are red supergiants (Betelgeuse and Antares) and blue supergiants (Rigel) ...
... • radii of 20 to several hundred solar radii (they are about the size of Jupiter's orbit!!!!) • two types are red supergiants (Betelgeuse and Antares) and blue supergiants (Rigel) ...
Telephone Quizzes for ASTR 200 1999 Revision
... a large mirror is more attractive to look at than a large lens. there is no chromatic aberration and large sizes are more feasible at relatively better cost. large telescope mirrors may be made from inexpensive metal rather than costly glass. they have chromatic aberration making it easier to obtain ...
... a large mirror is more attractive to look at than a large lens. there is no chromatic aberration and large sizes are more feasible at relatively better cost. large telescope mirrors may be made from inexpensive metal rather than costly glass. they have chromatic aberration making it easier to obtain ...
Stellar Evolution - Hays High Indians
... – Small low mass stars can take billions of years to form – More massive stars can completely form in a few hundred thousand years ...
... – Small low mass stars can take billions of years to form – More massive stars can completely form in a few hundred thousand years ...
INV 12B MOTION WITH CHANGING SPEED DRY LAB DATA
... e. galaxy we are in f. the only planet with Goldilocks conditions g. planet with hot, heavily-cratered surface h. space object that causes craters i. the force that exists between any two bodies in the universe j. process that developed the three layers of Earth and Moon’s interior k. a large cloud ...
... e. galaxy we are in f. the only planet with Goldilocks conditions g. planet with hot, heavily-cratered surface h. space object that causes craters i. the force that exists between any two bodies in the universe j. process that developed the three layers of Earth and Moon’s interior k. a large cloud ...
Perseus (constellation)

Perseus, named after the Greek mythological hero Perseus, is a constellation in the northern sky. It was one of 48 listed by the 2nd-century astronomer Ptolemy and among the 88 modern constellations defined by the International Astronomical Union (IAU). It is located in the northern celestial hemisphere near several other constellations named after legends surrounding Perseus, including Andromeda to the west and Cassiopeia to the north. Perseus is also bordered by Aries and Taurus to the south, Auriga to the east, Camelopardalis to the north, and Triangulum to the west.The galactic plane of the Milky Way passes through Perseus but is mostly obscured by molecular clouds. The constellation's brightest star is the yellow-white supergiant Alpha Persei (also called Mirfak), which shines at magnitude 1.79. It and many of the surrounding stars are members of an open cluster known as the Alpha Persei Cluster. The best-known star, however, is Algol (Beta Persei), linked with ominous legends because of its variability, which is noticeable to the naked eye. Rather than being an intrinsically variable star, it is an eclipsing binary. Other notable star systems in Perseus include X Persei, a binary system containing a neutron star, and GK Persei, a nova that peaked at magnitude 0.2 in 1901. The Double Cluster, comprising two open clusters quite near each other in the sky, was known to the ancient Chinese. The constellation gives its name to the Perseus Cluster (Abell 426), a massive galaxy cluster located 250 million light-years from Earth. It hosts the radiant of the annual Perseids meteor shower—one of the most prominent meteor showers in the sky.