1 WHY DO THE STARS IN ORION LOOK SO DIFFERENT FROM
... Remember that we said the apparent magnitude of a star is as we observe it from earth and that it is not reflective of a stars true physical character. We can understand more about a stars’ brightness by understanding the relationship of a stars’ luminosity and size. Luminosity shows the relationshi ...
... Remember that we said the apparent magnitude of a star is as we observe it from earth and that it is not reflective of a stars true physical character. We can understand more about a stars’ brightness by understanding the relationship of a stars’ luminosity and size. Luminosity shows the relationshi ...
Integrative Studies 410 Our Place in the Universe
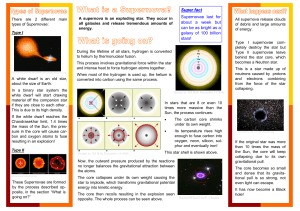
... • A shock wave travels through the star and blows off the outer layers, including the heavy elements – a supernova • A million times brighter than a nova!! • The actual explosion takes less than a second ...
... • A shock wave travels through the star and blows off the outer layers, including the heavy elements – a supernova • A million times brighter than a nova!! • The actual explosion takes less than a second ...
Lecture 12
... The magnitude system • Astronomers quantify the intensity of light produced by a source with the unit magnitudes • Magnitudes are a logarithmic representation of the spectral flux density of a source. – Allows for easy comparison of sources with immense ranges in ...
... The magnitude system • Astronomers quantify the intensity of light produced by a source with the unit magnitudes • Magnitudes are a logarithmic representation of the spectral flux density of a source. – Allows for easy comparison of sources with immense ranges in ...
Solutions
... Problem 1 (12 points): Five of the following celestial objects represent (or likely contain) a solar mass star at some point in its evolution. We associate the sixth object with an evolutionary stage of a much more massive star. Place a 1, 2, 3, 4, or 5 in age order (youngest to oldest) for the fiv ...
... Problem 1 (12 points): Five of the following celestial objects represent (or likely contain) a solar mass star at some point in its evolution. We associate the sixth object with an evolutionary stage of a much more massive star. Place a 1, 2, 3, 4, or 5 in age order (youngest to oldest) for the fiv ...
Chapter 27 Stars and Galaxies
... 2. Elliptical: nearly spherical with very bright centers; no spiral arms No young stars, dust, or gas ...
... 2. Elliptical: nearly spherical with very bright centers; no spiral arms No young stars, dust, or gas ...
Linking Asteroids and Meteorites through Reflectance
... • We identify a star cluster that is close enough to determine its distance by parallax • We plots its H-R diagram • Since we know the distances to the cluster stars • We can determine their luminosities ...
... • We identify a star cluster that is close enough to determine its distance by parallax • We plots its H-R diagram • Since we know the distances to the cluster stars • We can determine their luminosities ...
What is a supernova - University of Warwick
... If the white dwarf reaches the Chandrasekhar limit, 1.4 times the mass of the Sun, the pressure in the core will cause carbon and oxygen atoms to fuse resulting in an explosion! ...
... If the white dwarf reaches the Chandrasekhar limit, 1.4 times the mass of the Sun, the pressure in the core will cause carbon and oxygen atoms to fuse resulting in an explosion! ...
Lab 5 Takehome
... Figure 2 shows the same stars, but here what’s plotted is the apparent brightness of the star as seen from the Earth, instead of the luminosity. The vertical axis is scaled so that 1.0 represe ...
... Figure 2 shows the same stars, but here what’s plotted is the apparent brightness of the star as seen from the Earth, instead of the luminosity. The vertical axis is scaled so that 1.0 represe ...
Astronomy Quiz #1 Answers
... showing stars are moving away from us/each other -diagram should be of 2 visible spectra with lines; first one is the original, second one should show that they shifted towards the red end of the spectrum a. What does a large red shift indicate about a galaxy’s motion? -it indicates that the galaxy’ ...
... showing stars are moving away from us/each other -diagram should be of 2 visible spectra with lines; first one is the original, second one should show that they shifted towards the red end of the spectrum a. What does a large red shift indicate about a galaxy’s motion? -it indicates that the galaxy’ ...
the stars
... Stars have different colors and luminosities. Following this tutorial we will learn what star luminosity and color are, and which information about stellar evolution we can obtain from them. 2 Stars: magnitude and color Looking at the sky with naked eye most stars appear of the same color. We see st ...
... Stars have different colors and luminosities. Following this tutorial we will learn what star luminosity and color are, and which information about stellar evolution we can obtain from them. 2 Stars: magnitude and color Looking at the sky with naked eye most stars appear of the same color. We see st ...
GIZMO H-RDiagramSE
... Gizmo Warm-up In the early 1900s, astronomers were able to identify many star characteristics such as color, size, temperature, and luminosity—or how bright a star is. However, astronomers did not yet understand exactly how these characteristics were related. Using the H-R Diagram Gizmo™, you will d ...
... Gizmo Warm-up In the early 1900s, astronomers were able to identify many star characteristics such as color, size, temperature, and luminosity—or how bright a star is. However, astronomers did not yet understand exactly how these characteristics were related. Using the H-R Diagram Gizmo™, you will d ...
Stellar Evolution - Hays High School
... – Small low mass stars can take billions of years to form – More massive stars can completely form in a few hundred thousand years ...
... – Small low mass stars can take billions of years to form – More massive stars can completely form in a few hundred thousand years ...
Multiple choice test questions 2, Winter Semester
... C) If enough mass is accreted by a white dwarf star that it exceeds the 1.4 solar mass limit, it will undergo a supernova explosion and leave behind a black-hole remnant. D) If enough mass is accreted by a neutron star, it will undergo a supernova explosion and leave behind a black-hole remnant. E) ...
... C) If enough mass is accreted by a white dwarf star that it exceeds the 1.4 solar mass limit, it will undergo a supernova explosion and leave behind a black-hole remnant. D) If enough mass is accreted by a neutron star, it will undergo a supernova explosion and leave behind a black-hole remnant. E) ...
astronomy practice Answers - hhs-snc1d
... Practice Astronomy Questions Answers 1) If something were to happen to the sun, it would take __________ for us to know about it. a) 8 seconds b) 8 minutes c) 8 hours d) 8 days ...
... Practice Astronomy Questions Answers 1) If something were to happen to the sun, it would take __________ for us to know about it. a) 8 seconds b) 8 minutes c) 8 hours d) 8 days ...
Kinds of Stars
... size. Include blue-white RIGEL, Whiteyellow CANOPUS, red SuperGiants ANTARES & BETELGUESE. REDSUPERGIANTS- Largest of all stars ...
... size. Include blue-white RIGEL, Whiteyellow CANOPUS, red SuperGiants ANTARES & BETELGUESE. REDSUPERGIANTS- Largest of all stars ...
Exploring the Universe
... but very dim signals in the form of microwaves that are emitted all over the sky i. Scientists believe that these microwaves are the remains of the radiation produced during the Big ...
... but very dim signals in the form of microwaves that are emitted all over the sky i. Scientists believe that these microwaves are the remains of the radiation produced during the Big ...
The Life Cycle of a Star
... the Carbon into Iron, there is no more fuel left to consume. The Core of the supergiant will then collapse in less than a second, causing a massive explosion called a supernova. In a supernova, a massive shockwave is produced that blows away the outer layers of the star. ...
... the Carbon into Iron, there is no more fuel left to consume. The Core of the supergiant will then collapse in less than a second, causing a massive explosion called a supernova. In a supernova, a massive shockwave is produced that blows away the outer layers of the star. ...
Using Star Charts Introduction A Digression on Star Names
... At 9PM Central Daylight Time tonight, where in the sky would you look to find the constellation Capricornus? …………………………………………………. The celestial coordinates of Mars in the middle of September, 2007, are RA = 5h32m, Dec = +22d51m. Find its position , and write down the constellation in which it is and ...
... At 9PM Central Daylight Time tonight, where in the sky would you look to find the constellation Capricornus? …………………………………………………. The celestial coordinates of Mars in the middle of September, 2007, are RA = 5h32m, Dec = +22d51m. Find its position , and write down the constellation in which it is and ...
Stars Notes - Yonkers Public Schools
... • Very luminous • Low Temperature • Late evolution of medium-sized main sequence stars when they greatly expand in size ...
... • Very luminous • Low Temperature • Late evolution of medium-sized main sequence stars when they greatly expand in size ...
Perseus (constellation)

Perseus, named after the Greek mythological hero Perseus, is a constellation in the northern sky. It was one of 48 listed by the 2nd-century astronomer Ptolemy and among the 88 modern constellations defined by the International Astronomical Union (IAU). It is located in the northern celestial hemisphere near several other constellations named after legends surrounding Perseus, including Andromeda to the west and Cassiopeia to the north. Perseus is also bordered by Aries and Taurus to the south, Auriga to the east, Camelopardalis to the north, and Triangulum to the west.The galactic plane of the Milky Way passes through Perseus but is mostly obscured by molecular clouds. The constellation's brightest star is the yellow-white supergiant Alpha Persei (also called Mirfak), which shines at magnitude 1.79. It and many of the surrounding stars are members of an open cluster known as the Alpha Persei Cluster. The best-known star, however, is Algol (Beta Persei), linked with ominous legends because of its variability, which is noticeable to the naked eye. Rather than being an intrinsically variable star, it is an eclipsing binary. Other notable star systems in Perseus include X Persei, a binary system containing a neutron star, and GK Persei, a nova that peaked at magnitude 0.2 in 1901. The Double Cluster, comprising two open clusters quite near each other in the sky, was known to the ancient Chinese. The constellation gives its name to the Perseus Cluster (Abell 426), a massive galaxy cluster located 250 million light-years from Earth. It hosts the radiant of the annual Perseids meteor shower—one of the most prominent meteor showers in the sky.