PHYS 390 Lectures 1/2 - The Big Picture 1/2
... Knowing the radius of the Earth’s orbit Res, distances to nearby stars can be found through parallax, the apparent motion of nearby stars caused by the motion of the Earth in its orbit around the Sun (first used in 1838 by Freidrich Wilhelm Bessel). Below, the Earth is shown in its orbit at two extr ...
... Knowing the radius of the Earth’s orbit Res, distances to nearby stars can be found through parallax, the apparent motion of nearby stars caused by the motion of the Earth in its orbit around the Sun (first used in 1838 by Freidrich Wilhelm Bessel). Below, the Earth is shown in its orbit at two extr ...
March 2017 - Shasta Astronomy Club
... that is constantly under development. Phylogenetic trees add an extra dimension to our endeavours which is why this approach is so special. The branches of the tree serve to inform us about the stars’ shared history,” she says. The team picked 22 stars, including the Sun, to study. The chemical elem ...
... that is constantly under development. Phylogenetic trees add an extra dimension to our endeavours which is why this approach is so special. The branches of the tree serve to inform us about the stars’ shared history,” she says. The team picked 22 stars, including the Sun, to study. The chemical elem ...
Supernovae Gamma-Ray Bursts and and some of their uses
... surrounding interstellar medium at V > 104 km/s, compresses it, intermingles with it, enriches it with freshly synthesized heavy elements, and forms what is called a supernova remnant • Supernova remnants may be observed for hundreds of thousands of years as often beautiful, visual objects, but also ...
... surrounding interstellar medium at V > 104 km/s, compresses it, intermingles with it, enriches it with freshly synthesized heavy elements, and forms what is called a supernova remnant • Supernova remnants may be observed for hundreds of thousands of years as often beautiful, visual objects, but also ...
http://webcache.googleusercontent.com/search?q=cache
... aspect, the native is reduced to being a door-keeper, admitting and saluting guests. [2] Ptolemy attributes a mercurial-saturnine nature to the constellation as a whole, but notes the principal star Arcturus (from Arktouros 'Bear Guard': arktos, bear + ouros, guard - from its position behind Ursa Ma ...
... aspect, the native is reduced to being a door-keeper, admitting and saluting guests. [2] Ptolemy attributes a mercurial-saturnine nature to the constellation as a whole, but notes the principal star Arcturus (from Arktouros 'Bear Guard': arktos, bear + ouros, guard - from its position behind Ursa Ma ...
lab 11 only - Penn State University
... spherical cloud of stars that surrounds the entire galaxy). The halo is much larger than the bulge. Our Milky Way Galaxy is made up of mostly stars, gas, and dust. The dust blocks out light from distant stars, and makes it hard to see a lot of the galaxy, especially the bulge and parts of the disk. ...
... spherical cloud of stars that surrounds the entire galaxy). The halo is much larger than the bulge. Our Milky Way Galaxy is made up of mostly stars, gas, and dust. The dust blocks out light from distant stars, and makes it hard to see a lot of the galaxy, especially the bulge and parts of the disk. ...
THE SPECTRA OF FIVE IRREGULAR VARIABLE STARS George H
... emission objects associated with nebulosity. 3. V567 Sagittarii.—This object was discovered by Miss Henrietta Swope,4 who stated : "The spectrum is given as Pd in Harvard Circular 231, where it is called a gaseous nebula. . . . The variation is real and apparently irregular with no distinctive chara ...
... emission objects associated with nebulosity. 3. V567 Sagittarii.—This object was discovered by Miss Henrietta Swope,4 who stated : "The spectrum is given as Pd in Harvard Circular 231, where it is called a gaseous nebula. . . . The variation is real and apparently irregular with no distinctive chara ...
1 Introduction - High Point University
... they reach their peak brightness and begin to fade. They are only useful as distance indicators if it is possible to calibrate them—to relate their observed brightness profile to absolute magnitudes. Type I supernovae are very uniform—the light curves and spectra for Type I supernovae are all fairly ...
... they reach their peak brightness and begin to fade. They are only useful as distance indicators if it is possible to calibrate them—to relate their observed brightness profile to absolute magnitudes. Type I supernovae are very uniform—the light curves and spectra for Type I supernovae are all fairly ...
The Milky Way Galaxy
... the Galaxy, where extinction effects are much less than that found along the Milky Way ...
... the Galaxy, where extinction effects are much less than that found along the Milky Way ...
Implications of the Search and Discovery
... Number of Intelligent Civilizations = Number of Stars in the Galaxy (400 billion) x Fraction of Stars with Planets (1/4?) x Number of suitable planets per star (2?) x Fraction of planets where life appears (1/2??) x Fraction of planets with intelligence (???) x Fraction of planets with technology (? ...
... Number of Intelligent Civilizations = Number of Stars in the Galaxy (400 billion) x Fraction of Stars with Planets (1/4?) x Number of suitable planets per star (2?) x Fraction of planets where life appears (1/2??) x Fraction of planets with intelligence (???) x Fraction of planets with technology (? ...
The H-R Diagram
... • Parallax, the only direct method of finding distances to stars, except for rare eclipsing binaries • Spectral types are a Temperature sequence: OBAFGKM hot to cool. • 90% of all stars are on Main Sequence= hydrogen burning stars • Main Sequence is a mass sequence, lower right to upper left is risi ...
... • Parallax, the only direct method of finding distances to stars, except for rare eclipsing binaries • Spectral types are a Temperature sequence: OBAFGKM hot to cool. • 90% of all stars are on Main Sequence= hydrogen burning stars • Main Sequence is a mass sequence, lower right to upper left is risi ...
ASTR 101 Final Study Guide Use as a guide to the topics as you
... 4. In a sample of nearby stars, about what percentage will lie on the main sequence? 90% 5. In what part of the H-R diagram do white dwarfs lie? Upper right 6. This statement is true about stellar luminosities…luminosities have a smaller ranger than masses. 7. If two stars have the same luminosity, ...
... 4. In a sample of nearby stars, about what percentage will lie on the main sequence? 90% 5. In what part of the H-R diagram do white dwarfs lie? Upper right 6. This statement is true about stellar luminosities…luminosities have a smaller ranger than masses. 7. If two stars have the same luminosity, ...
colour
... • Individual stars • Binary systems • Star clusters....these reveal how stars evolve with time • Nuclear physics...energy source, synthesis of heavy elements No direct information about physical conditions in stellar interiors (except from helioseismology and solar neutrinos) No direct evidence for ...
... • Individual stars • Binary systems • Star clusters....these reveal how stars evolve with time • Nuclear physics...energy source, synthesis of heavy elements No direct information about physical conditions in stellar interiors (except from helioseismology and solar neutrinos) No direct evidence for ...
here - ESA Science
... Information from Hipparcos has enabled astronomers to trace the Sun’s passage through the Galaxy back in time. This has shown that over the last 500 million years the Sun has passed through four of the Milky Way’s spiral arms. The times that these traverses occurred appear to coincide with extended ...
... Information from Hipparcos has enabled astronomers to trace the Sun’s passage through the Galaxy back in time. This has shown that over the last 500 million years the Sun has passed through four of the Milky Way’s spiral arms. The times that these traverses occurred appear to coincide with extended ...
STELLAR STRUCTURE AND EVOLUTION
... • Individual stars • Binary systems • Star clusters....these reveal how stars evolve with time • Nuclear physics...energy source, synthesis of heavy elements No direct information about physical conditions in stellar interiors (except from helioseismology and solar neutrinos) No direct evidence for ...
... • Individual stars • Binary systems • Star clusters....these reveal how stars evolve with time • Nuclear physics...energy source, synthesis of heavy elements No direct information about physical conditions in stellar interiors (except from helioseismology and solar neutrinos) No direct evidence for ...
Stellar balancing act — dynamic equilibrium. A star spends most of
... Standing shock – a strong pressure wave that forms due to neutron-star bounce, but which stalls a certain distance from the neutron star as outer material rains down on it. All core-collapse supernovae measured to date, Type Ib, Ic, and II, are not spherical. They may be “football” shaped or “pancak ...
... Standing shock – a strong pressure wave that forms due to neutron-star bounce, but which stalls a certain distance from the neutron star as outer material rains down on it. All core-collapse supernovae measured to date, Type Ib, Ic, and II, are not spherical. They may be “football” shaped or “pancak ...
DTU 8e Chap 11 Characterizing Stars
... stars are plotted against their spectral types. Each dot on this graph represents a star whose luminosity and spectral type have been determined. The data points are grouped in just a few regions of the diagram, revealing that luminosity and spectral type are correlated: Mainsequence stars fall alon ...
... stars are plotted against their spectral types. Each dot on this graph represents a star whose luminosity and spectral type have been determined. The data points are grouped in just a few regions of the diagram, revealing that luminosity and spectral type are correlated: Mainsequence stars fall alon ...
Chapter 8 powerpoint presentation
... How many of the H atoms are in each of the excitation levels, n=1, n=2, etc, described by the Boltzmann equation and secondly, how many of the H atoms are completely ionized, for if the H atoms are ionized they can not produce any absorption lines. This is described by the Saha equation. ...
... How many of the H atoms are in each of the excitation levels, n=1, n=2, etc, described by the Boltzmann equation and secondly, how many of the H atoms are completely ionized, for if the H atoms are ionized they can not produce any absorption lines. This is described by the Saha equation. ...
Photosphere
... • 3 clicker points for 10 best answers that can be repeated in class. • Enter in Angel before ...
... • 3 clicker points for 10 best answers that can be repeated in class. • Enter in Angel before ...
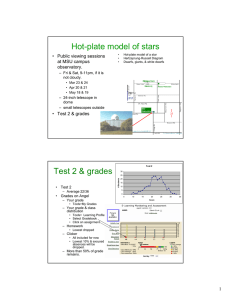
Hot-plate model of stars Test 2 & grades • Public viewing sessions
... • 3 clicker points for 10 best answers that can be repeated in class. • Enter in Angel before ...
... • 3 clicker points for 10 best answers that can be repeated in class. • Enter in Angel before ...
Today in Astronomy 142: observations of stars
... ! RA (right ascension) tells you when your object is up. • 12 hours is up highest Mar 21 • 0 hours is up highest Sept 21 ! DEC (declination) tells you how far away from the north pole. Polaris is at +90. Anything below 0 degrees is hard to observe from the northern hemisphere. ! Spectral types and ...
... ! RA (right ascension) tells you when your object is up. • 12 hours is up highest Mar 21 • 0 hours is up highest Sept 21 ! DEC (declination) tells you how far away from the north pole. Polaris is at +90. Anything below 0 degrees is hard to observe from the northern hemisphere. ! Spectral types and ...
Evolution of low
... stars in many of the evolutionary phases. Can test timescale, surface temperature and luminosity predictions. After 30 years of testing, it looks like we understand the basic evolution of stars very well. (2) My personal favorite test is the measurement of radioactive Tc in AGB stars. ...
... stars in many of the evolutionary phases. Can test timescale, surface temperature and luminosity predictions. After 30 years of testing, it looks like we understand the basic evolution of stars very well. (2) My personal favorite test is the measurement of radioactive Tc in AGB stars. ...
Perseus (constellation)

Perseus, named after the Greek mythological hero Perseus, is a constellation in the northern sky. It was one of 48 listed by the 2nd-century astronomer Ptolemy and among the 88 modern constellations defined by the International Astronomical Union (IAU). It is located in the northern celestial hemisphere near several other constellations named after legends surrounding Perseus, including Andromeda to the west and Cassiopeia to the north. Perseus is also bordered by Aries and Taurus to the south, Auriga to the east, Camelopardalis to the north, and Triangulum to the west.The galactic plane of the Milky Way passes through Perseus but is mostly obscured by molecular clouds. The constellation's brightest star is the yellow-white supergiant Alpha Persei (also called Mirfak), which shines at magnitude 1.79. It and many of the surrounding stars are members of an open cluster known as the Alpha Persei Cluster. The best-known star, however, is Algol (Beta Persei), linked with ominous legends because of its variability, which is noticeable to the naked eye. Rather than being an intrinsically variable star, it is an eclipsing binary. Other notable star systems in Perseus include X Persei, a binary system containing a neutron star, and GK Persei, a nova that peaked at magnitude 0.2 in 1901. The Double Cluster, comprising two open clusters quite near each other in the sky, was known to the ancient Chinese. The constellation gives its name to the Perseus Cluster (Abell 426), a massive galaxy cluster located 250 million light-years from Earth. It hosts the radiant of the annual Perseids meteor shower—one of the most prominent meteor showers in the sky.