Nuclear fusion in stars
... • If R increases by a factor of 4, r does the same by factor of 8. This means that a collapsing cloud can fragment ! into smaller collapsing clouds. • This process ends with star formation or when rotational speed becomes too high (conservation of angular momentum) • Hierarchical collapse can produc ...
... • If R increases by a factor of 4, r does the same by factor of 8. This means that a collapsing cloud can fragment ! into smaller collapsing clouds. • This process ends with star formation or when rotational speed becomes too high (conservation of angular momentum) • Hierarchical collapse can produc ...
Gizmos: H-R Diagrams
... Gizmo Warm-up In the early 1900s, astronomers were able to identify many star characteristics such as color, size, temperature, and luminosity—or how bright a star is. However, astronomers did not yet understand exactly how these characteristics were related. Using the H-R Diagram Gizmo™, you will d ...
... Gizmo Warm-up In the early 1900s, astronomers were able to identify many star characteristics such as color, size, temperature, and luminosity—or how bright a star is. However, astronomers did not yet understand exactly how these characteristics were related. Using the H-R Diagram Gizmo™, you will d ...
Astronomical Distance Ladder
... This proper motion technique is capable of giving reliable distances up to around 800 parsecs. With the distances to many stars in the galaxy calculated by parallax different ways to calculate distance was needed to extend the astronomical distance ladder. It was also discovered that stars radiated ...
... This proper motion technique is capable of giving reliable distances up to around 800 parsecs. With the distances to many stars in the galaxy calculated by parallax different ways to calculate distance was needed to extend the astronomical distance ladder. It was also discovered that stars radiated ...
Two-Gyro Performance, Scheduling and Acquisitions
... Our TGM average failure rate (Fine-Lock Backup not considered a failure) is 5.01%. ...
... Our TGM average failure rate (Fine-Lock Backup not considered a failure) is 5.01%. ...
stars and beyond - Math/Science Nucleus
... A celestial globe shows the complete northern and southern hemispheres and the main stars of each hemisphere. It is divided into 88 regions called constellations. The purple band that runs around the globe is the Milky Way Galaxy. The dotted line within this band is the galactic equator. There is a ...
... A celestial globe shows the complete northern and southern hemispheres and the main stars of each hemisphere. It is divided into 88 regions called constellations. The purple band that runs around the globe is the Milky Way Galaxy. The dotted line within this band is the galactic equator. There is a ...
Constellation
... constellation has alpha in its name, because it’s the first letter of the Greek alphabet. The brightest star in the constellation Perseus is called Alpha Persei. The second brightest is Beta Persei. (Beta is the second letter in the Greek alphabet.) The star closest to the Sun is Alpha Centauri. Thi ...
... constellation has alpha in its name, because it’s the first letter of the Greek alphabet. The brightest star in the constellation Perseus is called Alpha Persei. The second brightest is Beta Persei. (Beta is the second letter in the Greek alphabet.) The star closest to the Sun is Alpha Centauri. Thi ...
Measuring the Stars pages 813-820
... the winter, because they are on the ether side of the sun. ...
... the winter, because they are on the ether side of the sun. ...
Outside the Solar System Outside the Solar System OUTSIDE THE
... The Milky Way Galaxy is just one of more than 125 billion galaxies in the universe. Some galaxies have a few million stars. Others have billions of stars. Still others have trillions of stars. The Milky Way has more than 100 billion stars. ...
... The Milky Way Galaxy is just one of more than 125 billion galaxies in the universe. Some galaxies have a few million stars. Others have billions of stars. Still others have trillions of stars. The Milky Way has more than 100 billion stars. ...
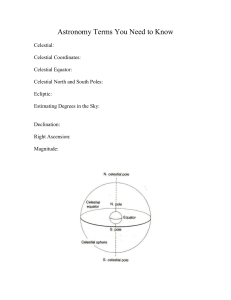
Astronomy Terms You Need to Know
... The Geminids are usually the strongest meteor shower of the year and meteor enthusiasts are certain to circle December 13 and 14 on their calendars. This is the one major shower that provides good activity prior to midnight as the constellation of Gemini is well placed from 10pm onward. The Geminids ...
... The Geminids are usually the strongest meteor shower of the year and meteor enthusiasts are certain to circle December 13 and 14 on their calendars. This is the one major shower that provides good activity prior to midnight as the constellation of Gemini is well placed from 10pm onward. The Geminids ...
Section 3: Three Periodicities - Wobble, Tilt, and
... King) will be the Pole Star (Love). Next will be Vega, then Thuban, and then Polaris again -- each star taking its turn in the 26,000-year precessional cycle. So it is correct to say that there is no one single North Star -- or that Polaris is just the current pole star. ...
... King) will be the Pole Star (Love). Next will be Vega, then Thuban, and then Polaris again -- each star taking its turn in the 26,000-year precessional cycle. So it is correct to say that there is no one single North Star -- or that Polaris is just the current pole star. ...
Wazzat Mean - Peterborough Astronomical Association
... at tremendous speed (typically 20 to 40 miles per second or 32 to 64 kilometres per second ). Also called a “shooting star.” If material survives the trip through the atmosphere, it’s called a meteorite after landing on Earth’s surface. Meteor Shower An increase in meteor activity at certain times o ...
... at tremendous speed (typically 20 to 40 miles per second or 32 to 64 kilometres per second ). Also called a “shooting star.” If material survives the trip through the atmosphere, it’s called a meteorite after landing on Earth’s surface. Meteor Shower An increase in meteor activity at certain times o ...
Mass and the Properties of Main Sequence Stars
... Evolution of Low-Mass Star – II The time it takes to reach the red giant state depends on the mass of the star • For star with lower mass then the Sun, it takes longer. • As the shell hydrogen fusion stops, the helium core of the low mass stars may never a temperature high enough for helium fusion ...
... Evolution of Low-Mass Star – II The time it takes to reach the red giant state depends on the mass of the star • For star with lower mass then the Sun, it takes longer. • As the shell hydrogen fusion stops, the helium core of the low mass stars may never a temperature high enough for helium fusion ...
AST 301 Test #3 Friday Nov. 12 Name: 1. a) The Sun is in
... Water flowing into a bucket balances water flowing out through a hole. When supply and demand are equal the price is stable. The floor pushes me up to balance gravity pulling me down. 2. If I want to use the Doppler technique to search for a planet orbiting around a star, what measurements or observ ...
... Water flowing into a bucket balances water flowing out through a hole. When supply and demand are equal the price is stable. The floor pushes me up to balance gravity pulling me down. 2. If I want to use the Doppler technique to search for a planet orbiting around a star, what measurements or observ ...
Stars (Ch. 13)
... • At this distance it takes light 4.3 years to travel from this star. In other words the star is 4.3 light years away. • The space shuttle travels 17,500 miles/hour, at this ...
... • At this distance it takes light 4.3 years to travel from this star. In other words the star is 4.3 light years away. • The space shuttle travels 17,500 miles/hour, at this ...
Astronomy
... constellation is hidden in the daylight sky. As the night hours pass and the Earth turns on its axis, the stars turn in circles around Polaris, which appears to stand still. Some constellations are close enough to Polaris that they never set below the horizon. These are the circumpolar stars. Most s ...
... constellation is hidden in the daylight sky. As the night hours pass and the Earth turns on its axis, the stars turn in circles around Polaris, which appears to stand still. Some constellations are close enough to Polaris that they never set below the horizon. These are the circumpolar stars. Most s ...
The Stars education kit - Student activities 5-10
... blue flame from a Bunsen burner is hotter and more dangerous than a red/yellow flame. The metal rod and the gas in the Bunsen burner have no colour of their own but change colour depending on their temperature. This is the same with stars. Cooler stars (with temperatures around 3,000K) glow red, whi ...
... blue flame from a Bunsen burner is hotter and more dangerous than a red/yellow flame. The metal rod and the gas in the Bunsen burner have no colour of their own but change colour depending on their temperature. This is the same with stars. Cooler stars (with temperatures around 3,000K) glow red, whi ...
H-RDiagramSE
... diagram and become giants or supergiants. Giants and supergiants form when the center of a star collapses and its outer parts expand outwards. What are the characteristics of giants and supergiants? _____________________________ ...
... diagram and become giants or supergiants. Giants and supergiants form when the center of a star collapses and its outer parts expand outwards. What are the characteristics of giants and supergiants? _____________________________ ...
AGN-Hubble
... That’s because if you know how fast we are expanding, you can run the movie backwards and see when everything crunches together. If the Universe is slowing its expansion, you get a younger age. You can compare the age gotten this way with the oldest globular ...
... That’s because if you know how fast we are expanding, you can run the movie backwards and see when everything crunches together. If the Universe is slowing its expansion, you get a younger age. You can compare the age gotten this way with the oldest globular ...
QDSpaperFred1.tex
... between the infrared excess of space colonies and naturally occurring dust or debris. There are two approaches to this discrimination: the temperature range of the source and the age of the star. The temperature of the dust is determined by the distance from the star and the size and composition of ...
... between the infrared excess of space colonies and naturally occurring dust or debris. There are two approaches to this discrimination: the temperature range of the source and the age of the star. The temperature of the dust is determined by the distance from the star and the size and composition of ...
Perseus (constellation)

Perseus, named after the Greek mythological hero Perseus, is a constellation in the northern sky. It was one of 48 listed by the 2nd-century astronomer Ptolemy and among the 88 modern constellations defined by the International Astronomical Union (IAU). It is located in the northern celestial hemisphere near several other constellations named after legends surrounding Perseus, including Andromeda to the west and Cassiopeia to the north. Perseus is also bordered by Aries and Taurus to the south, Auriga to the east, Camelopardalis to the north, and Triangulum to the west.The galactic plane of the Milky Way passes through Perseus but is mostly obscured by molecular clouds. The constellation's brightest star is the yellow-white supergiant Alpha Persei (also called Mirfak), which shines at magnitude 1.79. It and many of the surrounding stars are members of an open cluster known as the Alpha Persei Cluster. The best-known star, however, is Algol (Beta Persei), linked with ominous legends because of its variability, which is noticeable to the naked eye. Rather than being an intrinsically variable star, it is an eclipsing binary. Other notable star systems in Perseus include X Persei, a binary system containing a neutron star, and GK Persei, a nova that peaked at magnitude 0.2 in 1901. The Double Cluster, comprising two open clusters quite near each other in the sky, was known to the ancient Chinese. The constellation gives its name to the Perseus Cluster (Abell 426), a massive galaxy cluster located 250 million light-years from Earth. It hosts the radiant of the annual Perseids meteor shower—one of the most prominent meteor showers in the sky.