Leaving the Main Sequence
... • Degenerate-electron pressure is independent of temperature. • He heats up, He burning happens faster. • Without having a “ pressure safety valve”, temperature becomes too high to make the ...
... • Degenerate-electron pressure is independent of temperature. • He heats up, He burning happens faster. • Without having a “ pressure safety valve”, temperature becomes too high to make the ...
Notes
... Zanstra temperature - Measure brightness of star compared to brightness of nebula in optical hydrogen emission lines to estimate the uv/optical flux ratio to get temperature ...
... Zanstra temperature - Measure brightness of star compared to brightness of nebula in optical hydrogen emission lines to estimate the uv/optical flux ratio to get temperature ...
10 New Constellations
... Also known as Alpha Persei, Mirfak is located around 500 light years from Earth and is the brightest star in the constellation, it's a white supergiant with a diameter around 30 times larger than the sun. Algol Also known as Beta Persei, Algol is actually a three star system located around 90 light ...
... Also known as Alpha Persei, Mirfak is located around 500 light years from Earth and is the brightest star in the constellation, it's a white supergiant with a diameter around 30 times larger than the sun. Algol Also known as Beta Persei, Algol is actually a three star system located around 90 light ...
Measuring Distances - Stockton University
... appears to follow a fairly consistent light-curve, peaking at an absolute magnitude of about Mv -19. This makes them 23.8 magnitudes more luminous than the Sun, equivalent to a factor of 1023.8/2.5 = 3.3 x 109 . • These are now playing an important role in modern cosmology as there are large proje ...
... appears to follow a fairly consistent light-curve, peaking at an absolute magnitude of about Mv -19. This makes them 23.8 magnitudes more luminous than the Sun, equivalent to a factor of 1023.8/2.5 = 3.3 x 109 . • These are now playing an important role in modern cosmology as there are large proje ...
Slide 1
... The Chandrasekhar (chan-druh-SAY-kar) limit is the maximum nonrotating mass which can be supported against gravitational collapse by electron degeneracy pressure. It is commonly given as being about 1.4 solar masses. Computed values for the limit will vary depending on the approximations used, the n ...
... The Chandrasekhar (chan-druh-SAY-kar) limit is the maximum nonrotating mass which can be supported against gravitational collapse by electron degeneracy pressure. It is commonly given as being about 1.4 solar masses. Computed values for the limit will vary depending on the approximations used, the n ...
June - Magic Valley Astronomical Society
... La Caille, Blanchinus, and Purbach, is predicted to occur at 12:07; the equation of time - the difference between apparent time and mean time - is zero at 17:00 6/13 Mars is at heliocentric conjunction with Saturn at 7:00; Mercury is 6.7° south-southeast of M45 at 16:00 6/14 The earliest sunrise of ...
... La Caille, Blanchinus, and Purbach, is predicted to occur at 12:07; the equation of time - the difference between apparent time and mean time - is zero at 17:00 6/13 Mars is at heliocentric conjunction with Saturn at 7:00; Mercury is 6.7° south-southeast of M45 at 16:00 6/14 The earliest sunrise of ...
Mark Rubin
... and the He II lines can be observed with R > 3000 spectroscopy using a GSMT. Observations can focus on the region in which He II is expected (e.g., at 1.44 microns or Hband, for the z ~ 7.7 window). • If a He II (1640 A) feature is discovered that is strong relative to the UV continuum limits from J ...
... and the He II lines can be observed with R > 3000 spectroscopy using a GSMT. Observations can focus on the region in which He II is expected (e.g., at 1.44 microns or Hband, for the z ~ 7.7 window). • If a He II (1640 A) feature is discovered that is strong relative to the UV continuum limits from J ...
The Sun and the Stars
... If stars radiated like blackbodies then a colour-colour plot would be unique and follow a straight line ...
... If stars radiated like blackbodies then a colour-colour plot would be unique and follow a straight line ...
The Northern Winter Constellations
... quickly lifted him to the heavens and made him immortal, where he now hunts eternally with his two dogs, Canis Major and Canis Minor. In front of him is his prey Taurus the Bull. The myths surrounding Auriga the Charioteer vary, but it is an ancient constellation dating back to at least to the Ancie ...
... quickly lifted him to the heavens and made him immortal, where he now hunts eternally with his two dogs, Canis Major and Canis Minor. In front of him is his prey Taurus the Bull. The myths surrounding Auriga the Charioteer vary, but it is an ancient constellation dating back to at least to the Ancie ...
Time From the Perspective of a Particle Physicist
... • Stars “move” East to West over the course of one Night (in circle about the North Star) • Stars “move” East to West by 2 hours per month and “return” to the same position after one Year • It’s just caused by Earth’s daily spin and yearly orbit about the Sun • Star wheel depends on latitude: northe ...
... • Stars “move” East to West over the course of one Night (in circle about the North Star) • Stars “move” East to West by 2 hours per month and “return” to the same position after one Year • It’s just caused by Earth’s daily spin and yearly orbit about the Sun • Star wheel depends on latitude: northe ...
20_LectureOutline
... is now blue-white. Why? Could there have been an intervening dust cloud? (Then where is it?) Could its companion have been a red giant? (It became a white dwarf very quickly, then!) ...
... is now blue-white. Why? Could there have been an intervening dust cloud? (Then where is it?) Could its companion have been a red giant? (It became a white dwarf very quickly, then!) ...
Lecture 15, PPT version
... At their maximum brightness, supernovae are as bright as an entire galaxy. ...
... At their maximum brightness, supernovae are as bright as an entire galaxy. ...
The double-degenerate, super-Chandrasekhar nucleus of the
... They showed a photometric variability as large as ∼0.36 mag between series, so the system was monitored for a single, 4-hour interval on the night of September 2, 2009, and an orbital period was determined. Another similar 4-hour time-series was covered in the Johnson B-band with the SAAO 1m telesco ...
... They showed a photometric variability as large as ∼0.36 mag between series, so the system was monitored for a single, 4-hour interval on the night of September 2, 2009, and an orbital period was determined. Another similar 4-hour time-series was covered in the Johnson B-band with the SAAO 1m telesco ...
Oct 06, 2001
... C. It is moving away from the Earth. D. It will live longer than a B spectral class main sequence star. E. It is the same size as a red giant star of the same temperature. 28. There are reported to be about 6,000 stars visible to the naked eye. How many of those stars would you expect to be part of ...
... C. It is moving away from the Earth. D. It will live longer than a B spectral class main sequence star. E. It is the same size as a red giant star of the same temperature. 28. There are reported to be about 6,000 stars visible to the naked eye. How many of those stars would you expect to be part of ...
answer key
... 16. What do these super large stars produce? 17. What happens when 2 neutron stars collide? What is produced? 18. What is the chance of a collision between the sun and another star? Failed Stars (After 5th intro frame) 19. What are “blue stragglers”? 20. Which types of stars are known as “failed sta ...
... 16. What do these super large stars produce? 17. What happens when 2 neutron stars collide? What is produced? 18. What is the chance of a collision between the sun and another star? Failed Stars (After 5th intro frame) 19. What are “blue stragglers”? 20. Which types of stars are known as “failed sta ...
10.1 Introduction
... Figure 10.6). At a distance of only 2.4 pc, Wolf 359 is the fifth closest star to the Sun, after the three stars that make up the α Centauri system and Barnard’s star. Its spectral type is M6.0 V and its luminosity is 0.001L ; ...
... Figure 10.6). At a distance of only 2.4 pc, Wolf 359 is the fifth closest star to the Sun, after the three stars that make up the α Centauri system and Barnard’s star. Its spectral type is M6.0 V and its luminosity is 0.001L ; ...
Science East Meteor Radiant Worksheet finished
... Meteors: Pieces of this dust or debris that enter the atmosphere and burns up. These are also known as ‘shooting stars’ or ‘falling stars’. Most burn up and never land at the surface. Fireball: Is simply a very bright meteor, generated by a larger chunk or rock. Fireballs can make it to the ground, ...
... Meteors: Pieces of this dust or debris that enter the atmosphere and burns up. These are also known as ‘shooting stars’ or ‘falling stars’. Most burn up and never land at the surface. Fireball: Is simply a very bright meteor, generated by a larger chunk or rock. Fireballs can make it to the ground, ...
Galaxies and the Universe
... • Red galaxies have lots of red stars (both giants and main sequence). • Blue galaxies have both blue and red main sequence… but probably not a lot of red giants yet. – Blue MS are much more luminous than red MS so a population with both would appear mostly blue. ...
... • Red galaxies have lots of red stars (both giants and main sequence). • Blue galaxies have both blue and red main sequence… but probably not a lot of red giants yet. – Blue MS are much more luminous than red MS so a population with both would appear mostly blue. ...
PARALLAX EXERCISE1 The goal of this exercise is to introduce the
... The measurements that you made above are quite similar to those made by astronomers in order to measure the distances to nearby stars. The big difference is that even the nearest stars are quite far away compared to the diameter of the Earth’s orbit around the Sun. Because the stars are so far away, ...
... The measurements that you made above are quite similar to those made by astronomers in order to measure the distances to nearby stars. The big difference is that even the nearest stars are quite far away compared to the diameter of the Earth’s orbit around the Sun. Because the stars are so far away, ...
parallax
... The measurements that you made above are quite similar to those made by astronomers in order to measure the distances to nearby stars. The big difference is that even the nearest stars are quite far away compared to the diameter of the Earth’s orbit around the Sun. Because the stars are so far away, ...
... The measurements that you made above are quite similar to those made by astronomers in order to measure the distances to nearby stars. The big difference is that even the nearest stars are quite far away compared to the diameter of the Earth’s orbit around the Sun. Because the stars are so far away, ...
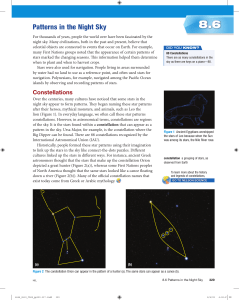
Patterns in the Night Sky
... Although we can mark out the same constellations our ancient ancestors saw thousands of years ago, their component stars are not in exactly the same location as they were then. Precise observations of stars reveal that they move relative to each other in space, but these changes in position occur s ...
... Although we can mark out the same constellations our ancient ancestors saw thousands of years ago, their component stars are not in exactly the same location as they were then. Precise observations of stars reveal that they move relative to each other in space, but these changes in position occur s ...
Boötes

Boötes /boʊˈoʊtiːz/ is a constellation in the northern sky, located between 0° and +60° declination, and 13 and 16 hours of right ascension on the celestial sphere. The name comes from the Greek Βοώτης, Boōtēs, meaning herdsman or plowman (literally, ox-driver; from βοῦς bous “cow”). The ""ö"" in the name is a diaeresis, not an umlaut, meaning that each 'o' is to be pronounced separately.One of the 48 constellations described by the 2nd century astronomer Ptolemy, Boötes is now one of the 88 modern constellations. It contains the fourth brightest star in the night sky, the orange-hued Arcturus. Boötes is home to many other bright stars, including eight above the fourth magnitude and an additional 21 above the fifth magnitude, making a total of 29 stars easily visible to the naked eye.