OSP2016Level 3 Map - Oregon Star Party
... What is it? V404 Cyg is a black hole (12+/- 3 solar masses) with late K or early G type stellar companion that’s slightly smaller than the Sun, orbiting each other in less than 6.5 days. They are approximately 7800 light years away. Why you want to see it: The stellar companion is distorted into a ...
... What is it? V404 Cyg is a black hole (12+/- 3 solar masses) with late K or early G type stellar companion that’s slightly smaller than the Sun, orbiting each other in less than 6.5 days. They are approximately 7800 light years away. Why you want to see it: The stellar companion is distorted into a ...
here - ESA Science
... spiral arms. The times that these traverses occurred appear to coincide with extended cold periods on Earth. Perhaps the densely-filled star and gas environment of the spiral arms have an effect on the Earth’s climate. Mapping the positions and motions of stars allows astronomers to develop a frame ...
... spiral arms. The times that these traverses occurred appear to coincide with extended cold periods on Earth. Perhaps the densely-filled star and gas environment of the spiral arms have an effect on the Earth’s climate. Mapping the positions and motions of stars allows astronomers to develop a frame ...
Lecture 16
... Life Stages of High-Mass Star 1. Main Sequence: H fuses to He in core 2. Red Supergiant: H fuses to He in shell around He core 3. Helium Core Fusion: He fuses to C in core while H fuses to He in shell 4. Multiple Shell Fusion: many elements fuse in shells 5. Supernova leaves neutron star behind and ...
... Life Stages of High-Mass Star 1. Main Sequence: H fuses to He in core 2. Red Supergiant: H fuses to He in shell around He core 3. Helium Core Fusion: He fuses to C in core while H fuses to He in shell 4. Multiple Shell Fusion: many elements fuse in shells 5. Supernova leaves neutron star behind and ...
Evolution of our Sun
... About how long does our star live as a main sequence star? Explain why a massive star only lives a short time? What elements are created in a sun-like star? What elements are created in a massive star? Evolution of the Sun – Part 2 Name and briefly describe the stages that our sun will go through as ...
... About how long does our star live as a main sequence star? Explain why a massive star only lives a short time? What elements are created in a sun-like star? What elements are created in a massive star? Evolution of the Sun – Part 2 Name and briefly describe the stages that our sun will go through as ...
Letot STELLAR EVOLUTION By Kyle Letot Grade Level: 6
... covering of rubber on the balloon is holding the air in. (I will include that stars do NOT have a membrane such as the balloon, rather the balloon has visual similarities that students can see and touch without the harming effects of an actual star.) Next I will point out how the air we used to blow ...
... covering of rubber on the balloon is holding the air in. (I will include that stars do NOT have a membrane such as the balloon, rather the balloon has visual similarities that students can see and touch without the harming effects of an actual star.) Next I will point out how the air we used to blow ...
1. - TeacherWeb
... • We learn about stars by studying energy. – Stars produce a full range of electromagnetic radiation, from high-energy X-rays to low-energy radio waves. – Scientists use optical telescopes to study visible light and radio telescopes to study radio waves emitted from astronomical objects. – Earth’s a ...
... • We learn about stars by studying energy. – Stars produce a full range of electromagnetic radiation, from high-energy X-rays to low-energy radio waves. – Scientists use optical telescopes to study visible light and radio telescopes to study radio waves emitted from astronomical objects. – Earth’s a ...
Small images
... they were handed down through the Greeks and Arabs. Few pictorial records of the ancient constellation figures have survived, but in the Almagest AD 150, Ptolemy catalogued the positions of 1,022 of the brightest stars both in terms of celestial latitude and longitude, and of their places in 48 cons ...
... they were handed down through the Greeks and Arabs. Few pictorial records of the ancient constellation figures have survived, but in the Almagest AD 150, Ptolemy catalogued the positions of 1,022 of the brightest stars both in terms of celestial latitude and longitude, and of their places in 48 cons ...
E N 1”=140 AU
... ・Accretion from the circumstellar disk around the primary is very active(White & Ghez 2001). ・The primary is an EXor, which periodically undergo outbursts (Coffey et al. 2004). ...
... ・Accretion from the circumstellar disk around the primary is very active(White & Ghez 2001). ・The primary is an EXor, which periodically undergo outbursts (Coffey et al. 2004). ...
How far away are the Stars?
... • If distance to an object is known, we can measure its size. Diameter 2 Dis tan ce ...
... • If distance to an object is known, we can measure its size. Diameter 2 Dis tan ce ...
Chapter21
... close pair are close enough together to do so. 2. Binaries with periods less than a few years are usually only a few AU apart. This is too close together for their images to be separated so that they would be seen as a visual binary. 3. If the binary doesn’t appear to obey Kepler’s laws, the orbit m ...
... close pair are close enough together to do so. 2. Binaries with periods less than a few years are usually only a few AU apart. This is too close together for their images to be separated so that they would be seen as a visual binary. 3. If the binary doesn’t appear to obey Kepler’s laws, the orbit m ...
Explores Angular Size - Chandra X
... smaller - only about 1/60 of a degree. This small angle is called the arc-minute. There are 60 arcminutes in one degree. What we really would like to know is, physically, how big something is in kilometers, instead of how big it appears to be in angular measure. To get this information, all we need ...
... smaller - only about 1/60 of a degree. This small angle is called the arc-minute. There are 60 arcminutes in one degree. What we really would like to know is, physically, how big something is in kilometers, instead of how big it appears to be in angular measure. To get this information, all we need ...
File
... • A star enters its third stage when about 20% of the hydrogen atoms within its core have fused into helium atoms. Giant Stars • A star’s shell of gases grows cooler as it expands. As the gases in the outer shell become cooler, they begin to glow with a reddish color. These stars are known as giants ...
... • A star enters its third stage when about 20% of the hydrogen atoms within its core have fused into helium atoms. Giant Stars • A star’s shell of gases grows cooler as it expands. As the gases in the outer shell become cooler, they begin to glow with a reddish color. These stars are known as giants ...
Multiple Choice, continued
... • A star enters its third stage when about 20% of the hydrogen atoms within its core have fused into helium atoms. Giant Stars • A star’s shell of gases grows cooler as it expands. As the gases in the outer shell become cooler, they begin to glow with a reddish color. These stars are known as giants ...
... • A star enters its third stage when about 20% of the hydrogen atoms within its core have fused into helium atoms. Giant Stars • A star’s shell of gases grows cooler as it expands. As the gases in the outer shell become cooler, they begin to glow with a reddish color. These stars are known as giants ...
Lecture 6: Stellar Distances and Brightness
... Apparent Brightness of Stars The apparent brightness of stars is what we can measure How bright any given star will appear depends on 2 things: How bright it is physically (Luminosity) How far away it is (Distance) Related through the inverse square law ...
... Apparent Brightness of Stars The apparent brightness of stars is what we can measure How bright any given star will appear depends on 2 things: How bright it is physically (Luminosity) How far away it is (Distance) Related through the inverse square law ...
Chapter 13
... • As helium burns in the star’s core, its radius shrinks, but never enough to heat it to carbon-fusing temperatures • Increased luminosity, expands outer surface to red supergiant sizes and temperature down to 2500 K • Carbon and silicon flakes (grains) form in this cool environment and are driven o ...
... • As helium burns in the star’s core, its radius shrinks, but never enough to heat it to carbon-fusing temperatures • Increased luminosity, expands outer surface to red supergiant sizes and temperature down to 2500 K • Carbon and silicon flakes (grains) form in this cool environment and are driven o ...
CS3_Ch 3 - Leon County Schools
... Life Cycle of a Star (cont.) • When a star’s hydrogen supply is nearly gone, the star leaves the main sequence and begins the next stage of its life cycle. • All stars form in the same way, but stars die in different ways, depending on their masses. • Massive stars eventually become red ...
... Life Cycle of a Star (cont.) • When a star’s hydrogen supply is nearly gone, the star leaves the main sequence and begins the next stage of its life cycle. • All stars form in the same way, but stars die in different ways, depending on their masses. • Massive stars eventually become red ...
Measuring The Parallax of Barnard's Star
... to worry about the fact that at low altitude stars of different colors are refracted differently by the atmosphere. I had taken the images using a broad-band luminance filter and so this refraction issue could be a problem especially given that the sixth image was acquired when Barnard’s star was so ...
... to worry about the fact that at low altitude stars of different colors are refracted differently by the atmosphere. I had taken the images using a broad-band luminance filter and so this refraction issue could be a problem especially given that the sixth image was acquired when Barnard’s star was so ...
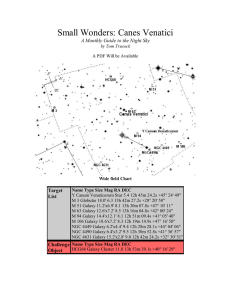
Small Wonders: Canes Venatici
... Canes Venatici is a somewhat small constellation, and may be difficult to find. Flanked on by both Ursa Major and Bootes, Canes is located in a somewhat barren section of the night sky. Canes (whose name means The Hunting Dogs) has been seen as Bootes pets for at least several hundred years, but the ...
... Canes Venatici is a somewhat small constellation, and may be difficult to find. Flanked on by both Ursa Major and Bootes, Canes is located in a somewhat barren section of the night sky. Canes (whose name means The Hunting Dogs) has been seen as Bootes pets for at least several hundred years, but the ...
HR Diagram, Star Clusters, and Stellar Evolution
... surface (akin to the Sun's solar wind, but much stronger), and, in the course of the star's RG life, carries away most of the H envelope • During the final shedding of its envelope, when the mass loss is the greatest, the star becomes unstable and pulsates, with periods ~ few months to > 1 yr. Such ...
... surface (akin to the Sun's solar wind, but much stronger), and, in the course of the star's RG life, carries away most of the H envelope • During the final shedding of its envelope, when the mass loss is the greatest, the star becomes unstable and pulsates, with periods ~ few months to > 1 yr. Such ...
Boötes

Boötes /boʊˈoʊtiːz/ is a constellation in the northern sky, located between 0° and +60° declination, and 13 and 16 hours of right ascension on the celestial sphere. The name comes from the Greek Βοώτης, Boōtēs, meaning herdsman or plowman (literally, ox-driver; from βοῦς bous “cow”). The ""ö"" in the name is a diaeresis, not an umlaut, meaning that each 'o' is to be pronounced separately.One of the 48 constellations described by the 2nd century astronomer Ptolemy, Boötes is now one of the 88 modern constellations. It contains the fourth brightest star in the night sky, the orange-hued Arcturus. Boötes is home to many other bright stars, including eight above the fourth magnitude and an additional 21 above the fifth magnitude, making a total of 29 stars easily visible to the naked eye.