Star - Uplift Education
... Eclipsing binary: (Rare) binary-star system in which the two stars are too close to be seen separately but is aligned in such a way that from Earth we periodically observe changes in brightness as each star successively passes in front of the other, that is, eclipses the other ...
... Eclipsing binary: (Rare) binary-star system in which the two stars are too close to be seen separately but is aligned in such a way that from Earth we periodically observe changes in brightness as each star successively passes in front of the other, that is, eclipses the other ...
ASTR2050 Spring 2005 • In this class we will cover: Brief review
... Interlude: Naming stars Ordinary stars Greek letter (in order of brightness) then constellation e.g. α-Orionis is brightest star in Orion (aka Betelgeuse) δ-Cephei is fourth brightest star in Cepheus Variable stars Listed in order of discovery, starting with “R”, then “S” and on through “Z”, then “ ...
... Interlude: Naming stars Ordinary stars Greek letter (in order of brightness) then constellation e.g. α-Orionis is brightest star in Orion (aka Betelgeuse) δ-Cephei is fourth brightest star in Cepheus Variable stars Listed in order of discovery, starting with “R”, then “S” and on through “Z”, then “ ...
After Dark in Allenspark
... January 22: Last quarter moon. January 27: Saturn at opposition (on the opposite side of the Earth from the Sun), so it's the brightest and closest it will be all year and up all night. You can spot it, shining brightly, low in the East in the evening sky. January 29: New moon. And, as I promised, a ...
... January 22: Last quarter moon. January 27: Saturn at opposition (on the opposite side of the Earth from the Sun), so it's the brightest and closest it will be all year and up all night. You can spot it, shining brightly, low in the East in the evening sky. January 29: New moon. And, as I promised, a ...
Stellar Evolution
... We do not know that all stars, regardless of their size, eventually run out of fuel and collapse due to gravity Low Mass Stars – consume fuel at a slow rate, may remain on main-sequence for up to 100 billion years, end up collapsing into white dwarfs Medium Mass Stars – go into red-giant stage, foll ...
... We do not know that all stars, regardless of their size, eventually run out of fuel and collapse due to gravity Low Mass Stars – consume fuel at a slow rate, may remain on main-sequence for up to 100 billion years, end up collapsing into white dwarfs Medium Mass Stars – go into red-giant stage, foll ...
Stellar Evolution
... Formation of Stars • Begins with interstellar gas and dust called a nebula • Collapses on self as a result of gravity • Rotates and flattens with hot condensed object at center called a protostar ...
... Formation of Stars • Begins with interstellar gas and dust called a nebula • Collapses on self as a result of gravity • Rotates and flattens with hot condensed object at center called a protostar ...
The Sun . . .
... Main Sequence: Average, ordinary stars. ~ 90% of stars are main sequence. Supergiant: 20 to 200 times larger than the Sun, but also much brighter, cooler and less dense. Dwarf: Small stars; fairly hot but very dim. Diameter is about the same as Earth, but their mass is equal to the sun . . . ...
... Main Sequence: Average, ordinary stars. ~ 90% of stars are main sequence. Supergiant: 20 to 200 times larger than the Sun, but also much brighter, cooler and less dense. Dwarf: Small stars; fairly hot but very dim. Diameter is about the same as Earth, but their mass is equal to the sun . . . ...
The Life Cycle of Stars
... exhausted its ability to fuse other elements like carbon and oxygen, it will become a red giant and expand in size to envelope the Earth. And surprisingly, the larger the mass of the star, the quicker it burns its fuel sources and the shorter its lifespan. Also see and read about Hubble Space Telesc ...
... exhausted its ability to fuse other elements like carbon and oxygen, it will become a red giant and expand in size to envelope the Earth. And surprisingly, the larger the mass of the star, the quicker it burns its fuel sources and the shorter its lifespan. Also see and read about Hubble Space Telesc ...
What are stars?
... How are absolute magnitude and apparent magnitude similar? ________________ ___________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________ ...
... How are absolute magnitude and apparent magnitude similar? ________________ ___________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________ ...
Chapter 8, Lesson 4, 2nd Packet, pdf
... How are absolute magnitude and apparent magnitude similar? ________________ ___________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________ ...
... How are absolute magnitude and apparent magnitude similar? ________________ ___________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________ ...
Scientists classify stars by
... would look the same because the two lights are exactly the same. Their absolute magnitude is the same. Distance makes them look different. The same is true for stars. Two stars could be the same brightness but their distance from us makes their brightness different. ...
... would look the same because the two lights are exactly the same. Their absolute magnitude is the same. Distance makes them look different. The same is true for stars. Two stars could be the same brightness but their distance from us makes their brightness different. ...
Stars
... Color of Stars • Look at the candle and Bunsen burner. Which is hotter? • The blue flame of the Bunsen burner is much hotter than the yellow flame of the candle. • Stars are different colors too, so we know they are different ...
... Color of Stars • Look at the candle and Bunsen burner. Which is hotter? • The blue flame of the Bunsen burner is much hotter than the yellow flame of the candle. • Stars are different colors too, so we know they are different ...
Shapes in the Sky
... Post-visit Discussion & Activities: 1. Make up your own constellations from existing star patterns. From there students can create their own myths and stories. 2. Find Polaris in the night sky and measure its altitude. This may be accomplished by either using your fist (a fist held at arm's length i ...
... Post-visit Discussion & Activities: 1. Make up your own constellations from existing star patterns. From there students can create their own myths and stories. 2. Find Polaris in the night sky and measure its altitude. This may be accomplished by either using your fist (a fist held at arm's length i ...
March
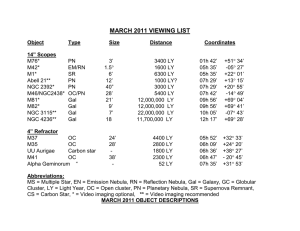
... refractor. Since NGC 4236 is a so-called starburst galaxy, the light is unevenly spread along the major axis and appears clumpy through larger scopes.. M37 in the constellation Auriga (awe-RYE-gah) is a rich open cluster with an apparent diameter of about 24 moa. It is about 27 light years in diamet ...
... refractor. Since NGC 4236 is a so-called starburst galaxy, the light is unevenly spread along the major axis and appears clumpy through larger scopes.. M37 in the constellation Auriga (awe-RYE-gah) is a rich open cluster with an apparent diameter of about 24 moa. It is about 27 light years in diamet ...
Notes- Stars
... – Smaller stars will live on for billions of years because they burn their fuel much more slowly ...
... – Smaller stars will live on for billions of years because they burn their fuel much more slowly ...
Life Cycle of Stars
... • Eventually, fusion begins in hydrogen gas at the core and the star begins its life. ...
... • Eventually, fusion begins in hydrogen gas at the core and the star begins its life. ...
September Evening Skies
... SOUTH No planets are above the horizon at map time. Seven objects of first magnitude or brighter are visible. In order of brightness they are: Arcturus, Vega, Capella, Altair, Antares, Fomalhaut, and Deneb. In addition to stars, other objects that should be visible to the unaided eye are labeled on ...
... SOUTH No planets are above the horizon at map time. Seven objects of first magnitude or brighter are visible. In order of brightness they are: Arcturus, Vega, Capella, Altair, Antares, Fomalhaut, and Deneb. In addition to stars, other objects that should be visible to the unaided eye are labeled on ...
22 Stellar Remnant/HR Diagram
... Star Clusters All stars formed at the same time Match the shape of the main sequence Compare age to MS lifetime Gives spectral type of MS “turnoff” stars Spectral type gives absolute magnitude! Yields a distance! ...
... Star Clusters All stars formed at the same time Match the shape of the main sequence Compare age to MS lifetime Gives spectral type of MS “turnoff” stars Spectral type gives absolute magnitude! Yields a distance! ...
Stellar Evolution
... blasted into space to create a new nebula (starts the cycle over) • The core collapses to form a neutron star ...
... blasted into space to create a new nebula (starts the cycle over) • The core collapses to form a neutron star ...
Stars: the Hertzsprung
... line from the upper left to the lower right. – Hotter is brighter – Cooler is dimmer • Red giant stars – Upper right hand corner (big, bright, and cool) • White dwarf stars – Lower left hand corner (small, dim, and hot) ...
... line from the upper left to the lower right. – Hotter is brighter – Cooler is dimmer • Red giant stars – Upper right hand corner (big, bright, and cool) • White dwarf stars – Lower left hand corner (small, dim, and hot) ...
Roy - WordPress.com
... The Hyades is the nearest open star cluster to the Solar System at about 150 lightyears away and thus, one of the beststudied of all star clusters. It consists of hundreds of stars sharing the same age, place of origin, chemical content, and motion through space. In the constellation Taurus, its b ...
... The Hyades is the nearest open star cluster to the Solar System at about 150 lightyears away and thus, one of the beststudied of all star clusters. It consists of hundreds of stars sharing the same age, place of origin, chemical content, and motion through space. In the constellation Taurus, its b ...
Barred Spiral Galaxy
... • Large amounts of electrically charged gas are ejected suddenly from the Sun’s corona. ...
... • Large amounts of electrically charged gas are ejected suddenly from the Sun’s corona. ...
Boötes

Boötes /boʊˈoʊtiːz/ is a constellation in the northern sky, located between 0° and +60° declination, and 13 and 16 hours of right ascension on the celestial sphere. The name comes from the Greek Βοώτης, Boōtēs, meaning herdsman or plowman (literally, ox-driver; from βοῦς bous “cow”). The ""ö"" in the name is a diaeresis, not an umlaut, meaning that each 'o' is to be pronounced separately.One of the 48 constellations described by the 2nd century astronomer Ptolemy, Boötes is now one of the 88 modern constellations. It contains the fourth brightest star in the night sky, the orange-hued Arcturus. Boötes is home to many other bright stars, including eight above the fourth magnitude and an additional 21 above the fifth magnitude, making a total of 29 stars easily visible to the naked eye.