File
... •Stars twinkle because the light is distorted by Earth’s atmosphere. •All stars have one thing in common, the way they produce energy. •The energy comes from nuclear reactions that change hydrogen into helium. It is as if millions of atomic bombs were going off every second inside the star. •Unlike ...
... •Stars twinkle because the light is distorted by Earth’s atmosphere. •All stars have one thing in common, the way they produce energy. •The energy comes from nuclear reactions that change hydrogen into helium. It is as if millions of atomic bombs were going off every second inside the star. •Unlike ...
Magnitudes lesson plan
... that he could see from his latitude into six classes of brightness. His idea of six classes probably came from the Babylonians whose base number was six. The formal introduction of six magnitudes has been credited to Ptolemy (100-150 A.D.) who was a Greek/Egyptian astronomer. He simply advanced the ...
... that he could see from his latitude into six classes of brightness. His idea of six classes probably came from the Babylonians whose base number was six. The formal introduction of six magnitudes has been credited to Ptolemy (100-150 A.D.) who was a Greek/Egyptian astronomer. He simply advanced the ...
Double Stars Discovered by IOTA Predicted Occultations July, 2010
... event, with the brighter of the two stars occulted first. A double asteroid is precluded by the fact that the magnitude drops are different between the two events. Two light curves are shown to verify the ‘events’ were not affected by other non-occultation variations. ...
... event, with the brighter of the two stars occulted first. A double asteroid is precluded by the fact that the magnitude drops are different between the two events. Two light curves are shown to verify the ‘events’ were not affected by other non-occultation variations. ...
Stars, Galaxies & Universe
... • Stars use up their hydrogen and expand their atmosphere. • Stars that are less than 1.4 solar masses will shrink to a white dwarf. • Stars between 1.4 -3.0 solar masses will produce a supernova and leave a neutron star. • Stars more than 3.0 solar masses will produce a supernova and collapse into ...
... • Stars use up their hydrogen and expand their atmosphere. • Stars that are less than 1.4 solar masses will shrink to a white dwarf. • Stars between 1.4 -3.0 solar masses will produce a supernova and leave a neutron star. • Stars more than 3.0 solar masses will produce a supernova and collapse into ...
HR DIAGRAM[1] Star Human Comparison Are all stars the same
... From the birth of a star through most of adulthood, the star burns (fuses) hydrogen in order to maintain equilibrium. There are small adjustments made to maintain Main Sequence status, but these changes are only to maintain balance between gravity and gas pressure. A star spends most of its life in ...
... From the birth of a star through most of adulthood, the star burns (fuses) hydrogen in order to maintain equilibrium. There are small adjustments made to maintain Main Sequence status, but these changes are only to maintain balance between gravity and gas pressure. A star spends most of its life in ...
Quiz Chapter 10 Answers
... they are surrounded by clouds of gas and dust X c) they only emit infrared radiation d) they are all moving away from Earth so fast that their visible light is Doppler shifted into the infrared ...
... they are surrounded by clouds of gas and dust X c) they only emit infrared radiation d) they are all moving away from Earth so fast that their visible light is Doppler shifted into the infrared ...
Star Birth
... What kind of matter exists in the spaces between the stars? Where do new stars form? What steps are involved in forming a star like the Sun? When a star forms, why does it end up with only a fraction of the available matter? What do star clusters tell us about the formation of stars? Where in the Ga ...
... What kind of matter exists in the spaces between the stars? Where do new stars form? What steps are involved in forming a star like the Sun? When a star forms, why does it end up with only a fraction of the available matter? What do star clusters tell us about the formation of stars? Where in the Ga ...
The Solar System
... – supernova remnants, expanding at 10,000 km/s – may trigger future star formation? – Neutron stars: mass star but just 10 km across. • Teaspoon weighs 100 million tons! • Seen as Pulsars, flashing beacons in space. ...
... – supernova remnants, expanding at 10,000 km/s – may trigger future star formation? – Neutron stars: mass star but just 10 km across. • Teaspoon weighs 100 million tons! • Seen as Pulsars, flashing beacons in space. ...
NAME_______________________________________
... D) warmer gas in front of a source that emits a continuous spectrum ____ 16. The apparent shift in a star’s position caused by the motion of the observer is called ____. A) luminosity C) absolute magnitude B) apparent magnitude D) parallax ...
... D) warmer gas in front of a source that emits a continuous spectrum ____ 16. The apparent shift in a star’s position caused by the motion of the observer is called ____. A) luminosity C) absolute magnitude B) apparent magnitude D) parallax ...
Astronomy 114 Problem Set # 7 Due: 30 Apr 2007 SOLUTIONS 1
... from very nearby standard candles. One example is the Cepheid Variable that we often use to determine the distance of galaxies. By accurately measuring the parallax of nearby Cepheid Variables we can then determine the correlation between their luminosity and luminosity variability period. Using thi ...
... from very nearby standard candles. One example is the Cepheid Variable that we often use to determine the distance of galaxies. By accurately measuring the parallax of nearby Cepheid Variables we can then determine the correlation between their luminosity and luminosity variability period. Using thi ...
Slide 1
... processes within the body of the star itself. Stars typically range in mass between 0.08 and 100 solar masses. A Hertzprung-Russell diagram is a very useful illustration of the relationship between various key stellar properties, namely the luminosity and the effective temperature (related to both s ...
... processes within the body of the star itself. Stars typically range in mass between 0.08 and 100 solar masses. A Hertzprung-Russell diagram is a very useful illustration of the relationship between various key stellar properties, namely the luminosity and the effective temperature (related to both s ...
Stars & Constellations
... Some constellations could be spotted, e.g. Ursa Minor contain Polaris, the North Star (which always points North). Once navigators had found North, they could observe its height in the sky and hence work out their latitude (how far North / South they are). Now they know how far North they are + the ...
... Some constellations could be spotted, e.g. Ursa Minor contain Polaris, the North Star (which always points North). Once navigators had found North, they could observe its height in the sky and hence work out their latitude (how far North / South they are). Now they know how far North they are + the ...
Unit 60 to 79
... 6) For a white dwarf to become a nova it is necessary for it to a. Have a companion star (be a member of a binary) b. Exceed its Chandrasekhar limit c. Have begun life as a high-mass star d. Continue the fusion cycle until its core is completely composed of iron 7) Which of the following events wil ...
... 6) For a white dwarf to become a nova it is necessary for it to a. Have a companion star (be a member of a binary) b. Exceed its Chandrasekhar limit c. Have begun life as a high-mass star d. Continue the fusion cycle until its core is completely composed of iron 7) Which of the following events wil ...
NASAexplores 9-12 Lesson: Classified Stars - Science
... American Henry Russell, determined a pattern in the life of stars. They arranged stars on a chart according to their color and brightness. The most amazing thing is that they did not even know one other, and did their experiments completely independent of each other. Therefore, this chart is called ...
... American Henry Russell, determined a pattern in the life of stars. They arranged stars on a chart according to their color and brightness. The most amazing thing is that they did not even know one other, and did their experiments completely independent of each other. Therefore, this chart is called ...
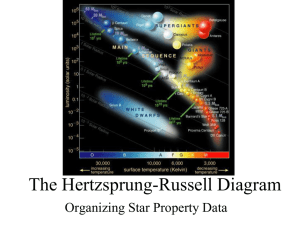
The Hertzsprung-Russell Diagram
... expect stars of the same size but different temperatures to form a diagonal line called an equal radius line. Equal Radius lines can be added to an H-R diagram ...
... expect stars of the same size but different temperatures to form a diagonal line called an equal radius line. Equal Radius lines can be added to an H-R diagram ...
Study Guide for 3RD Astronomy Exam
... Solve problems relating to the relative brightness or luminosity of two stars given their m or M values. Determine the hottest and coolest stars from a list of stars with their spectral types. Interpret the luminosity class of a star by naming the luminosity class and identifying if the star is in t ...
... Solve problems relating to the relative brightness or luminosity of two stars given their m or M values. Determine the hottest and coolest stars from a list of stars with their spectral types. Interpret the luminosity class of a star by naming the luminosity class and identifying if the star is in t ...
P10263v1.2 Lab 6 Text
... parsecs away, the Small Magellanic Cloud (a small satellite galaxy orbiting our own Milky Way) is about 53,000 parsecs away, making observations of individual stars much more difficult. Thus, we cannot use the Pleiades method with the Small Magellanic Cloud since the only individual stars we can suc ...
... parsecs away, the Small Magellanic Cloud (a small satellite galaxy orbiting our own Milky Way) is about 53,000 parsecs away, making observations of individual stars much more difficult. Thus, we cannot use the Pleiades method with the Small Magellanic Cloud since the only individual stars we can suc ...
Aging nearby spiral galaxies using H
... » Combine theories of physical stellar proerties: mass loss, spectral output, plasma/gas dynamics &c. » Different options to cover most types of conditions: ...
... » Combine theories of physical stellar proerties: mass loss, spectral output, plasma/gas dynamics &c. » Different options to cover most types of conditions: ...
Stars and Stellar Evolution
... Ex: Sun = apparent magnitude: -26.7, absolute magnitude: 5 More negative = brighter, more positive = dimmer ...
... Ex: Sun = apparent magnitude: -26.7, absolute magnitude: 5 More negative = brighter, more positive = dimmer ...
The Hertzsprung-Russell Diagram
... (individual masses can be gotten if you have a signal from both stars) The orbital period comes from watching the stars, or the periodic variation of their velocity or brightness. To get orbital semimajor axis, you need either the parallax to a visual system or the velocity from a spectroscopic syst ...
... (individual masses can be gotten if you have a signal from both stars) The orbital period comes from watching the stars, or the periodic variation of their velocity or brightness. To get orbital semimajor axis, you need either the parallax to a visual system or the velocity from a spectroscopic syst ...
Beyond the Solar System Homework for Geology 8
... stars can be additional colors as well, depending upon their surface temperatures. 47. Only the most massive stars evolve to become black dwarfs. 48. Hot stars evolve much more quickly than do cool stars. 49. Degenerate matter is highly condensed material, where even the electrons of atoms are pushe ...
... stars can be additional colors as well, depending upon their surface temperatures. 47. Only the most massive stars evolve to become black dwarfs. 48. Hot stars evolve much more quickly than do cool stars. 49. Degenerate matter is highly condensed material, where even the electrons of atoms are pushe ...
Neutron Stars
... Upper mass limit of Neutron Stars • In Neutron stars the gravity is balanced by two forces. – Degenerate neutron pressure – Strong nuclear force. ...
... Upper mass limit of Neutron Stars • In Neutron stars the gravity is balanced by two forces. – Degenerate neutron pressure – Strong nuclear force. ...
Boötes

Boötes /boʊˈoʊtiːz/ is a constellation in the northern sky, located between 0° and +60° declination, and 13 and 16 hours of right ascension on the celestial sphere. The name comes from the Greek Βοώτης, Boōtēs, meaning herdsman or plowman (literally, ox-driver; from βοῦς bous “cow”). The ""ö"" in the name is a diaeresis, not an umlaut, meaning that each 'o' is to be pronounced separately.One of the 48 constellations described by the 2nd century astronomer Ptolemy, Boötes is now one of the 88 modern constellations. It contains the fourth brightest star in the night sky, the orange-hued Arcturus. Boötes is home to many other bright stars, including eight above the fourth magnitude and an additional 21 above the fifth magnitude, making a total of 29 stars easily visible to the naked eye.



![HR DIAGRAM[1] Star Human Comparison Are all stars the same](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/010665051_1-e4f26b4aee29f3f3aaab891d368963d6-300x300.png)