Document
... Birth of the Solar System We know how the Earth and Solar System are today and this allows us to work backwards and determine how the Earth and Solar System were formed Plus we can look out into the universe for clues on how stars and planets are currently being formed ...
... Birth of the Solar System We know how the Earth and Solar System are today and this allows us to work backwards and determine how the Earth and Solar System were formed Plus we can look out into the universe for clues on how stars and planets are currently being formed ...
Yukon Grade One Earth and Space Science: Daily And Seasonal
... Create a chart that records how constellations change position in the sky at different times of the year. GRADE 9 Earth and Space Science: Space Exploration D1 Explain how a variety of technologies have advanced understanding of the universe and solar system. Identify and describe a range of instrum ...
... Create a chart that records how constellations change position in the sky at different times of the year. GRADE 9 Earth and Space Science: Space Exploration D1 Explain how a variety of technologies have advanced understanding of the universe and solar system. Identify and describe a range of instrum ...
The Earth in Perspective
... Jupiter is about 1 pixel in size. Earth is invisible at this scale. ...
... Jupiter is about 1 pixel in size. Earth is invisible at this scale. ...
Humanism for Secondary School Pupils S4 – 6
... the Big Bang. You can hear it yourself – it is the static you get when you try to tune in a radio or TV station. It is important to realise that this was the beginning of space and time. To ask, “what was there before the Big Bang?” is meaningless because time did not exist. What Can We See? Powerfu ...
... the Big Bang. You can hear it yourself – it is the static you get when you try to tune in a radio or TV station. It is important to realise that this was the beginning of space and time. To ask, “what was there before the Big Bang?” is meaningless because time did not exist. What Can We See? Powerfu ...
Mechanical Systems Topics 1 and 2
... When measuring the diameter of the sun, we use an indirect method, so that we can determine the diameter without actually measuring it directly. To calculate the accuracy of your measured value, this is calculated to show how far from the real value your measured value is … A. actual error B. estima ...
... When measuring the diameter of the sun, we use an indirect method, so that we can determine the diameter without actually measuring it directly. To calculate the accuracy of your measured value, this is calculated to show how far from the real value your measured value is … A. actual error B. estima ...
Astronomy from the ancients to the Renaissance
... The Greeks had a notion that because the planets were located in the heavens, their motions must be “perfect”. Uniform, circular motion was regarded as perfect. So the planets must move through space uniformly on circles. But – the planets do not move uniformly to the east against the stars. Theref ...
... The Greeks had a notion that because the planets were located in the heavens, their motions must be “perfect”. Uniform, circular motion was regarded as perfect. So the planets must move through space uniformly on circles. But – the planets do not move uniformly to the east against the stars. Theref ...
Lecture #2 - Personal.psu.edu
... Astronomical unit: mean distance from Earth to Sun First measured during transits of Mercury and Venus, using triangulation ...
... Astronomical unit: mean distance from Earth to Sun First measured during transits of Mercury and Venus, using triangulation ...
Homework 2
... Earth is closer to the Sun in January than in July. Therefore, in accord with Kepler’s second law: (a) Earth travels faster in its orbit around the Sun in July than in January. (b) Earth travels faster in its orbit around the Sun in January than in July. (c) It is summer in January and winter in Jul ...
... Earth is closer to the Sun in January than in July. Therefore, in accord with Kepler’s second law: (a) Earth travels faster in its orbit around the Sun in July than in January. (b) Earth travels faster in its orbit around the Sun in January than in July. (c) It is summer in January and winter in Jul ...
Quiz # 2
... C) planets move in circular epicycles around the Sun while the Sun moves in a circular orbit around the Earth. D) planets move in circular epicycles while the centers of the epicycles move in circular orbits around the Earth. ...
... C) planets move in circular epicycles around the Sun while the Sun moves in a circular orbit around the Earth. D) planets move in circular epicycles while the centers of the epicycles move in circular orbits around the Earth. ...
Ch. 28 Sec. 1
... F is the force measured in newtons, G is the universal gravitation constant (6.6726 × 10–11 m3/ kg•s2), m1 and m2 are the masses of the bodies in kilograms, and r is the distance between the two bodies in meters. ...
... F is the force measured in newtons, G is the universal gravitation constant (6.6726 × 10–11 m3/ kg•s2), m1 and m2 are the masses of the bodies in kilograms, and r is the distance between the two bodies in meters. ...
astronomy review sheet2
... The diagram below represents a plastic hemisphere upon which lines have been drawn to show the apparent paths of the Sun on four days at one locate on in the Northern Hemisphere. Two of the paths are dated. The protractor is placed over the north-south line. X represents the position of a vertical p ...
... The diagram below represents a plastic hemisphere upon which lines have been drawn to show the apparent paths of the Sun on four days at one locate on in the Northern Hemisphere. Two of the paths are dated. The protractor is placed over the north-south line. X represents the position of a vertical p ...
asteroid -- a large rock in outer space that orbits the sun (Many
... gravity. The gravitational pull of the sun causes the Earth to revolve (orbit) around it. The gravitational pull of the Earth causes the moon to revolve (orbit) around it. inner planets -- the planets closest to the sun (Mercury, Venus, Earth, and Mars) moon -- a natural satellite of a planet becaus ...
... gravity. The gravitational pull of the sun causes the Earth to revolve (orbit) around it. The gravitational pull of the Earth causes the moon to revolve (orbit) around it. inner planets -- the planets closest to the sun (Mercury, Venus, Earth, and Mars) moon -- a natural satellite of a planet becaus ...
Solar system junior
... are solid bodies which, unlike the stars, do not have their own light, but receive the same from the Sun. Obviously the planets that are closest to the Sun are those with the highest temperature, and those which are further away from the Sun, instead, are colder. The planet we live on is the Earth. ...
... are solid bodies which, unlike the stars, do not have their own light, but receive the same from the Sun. Obviously the planets that are closest to the Sun are those with the highest temperature, and those which are further away from the Sun, instead, are colder. The planet we live on is the Earth. ...
Homework 3
... 5. [2 points] Explain why we on Earth only see one side of the moon. If you were on the near side of the Moon, would you see only one side of the Earth? Would you see the Earth at all? Explain. ...
... 5. [2 points] Explain why we on Earth only see one side of the moon. If you were on the near side of the Moon, would you see only one side of the Earth? Would you see the Earth at all? Explain. ...
ParalStellarDist.V2doc
... relationship between the amount of movement of the observer and the amount of parallax observed: the more the observer moves, the greater the parallax shift. A person experiences parallax in a moving car when they observe the nearby road signs appearing to move by much faster than a distant mountain ...
... relationship between the amount of movement of the observer and the amount of parallax observed: the more the observer moves, the greater the parallax shift. A person experiences parallax in a moving car when they observe the nearby road signs appearing to move by much faster than a distant mountain ...
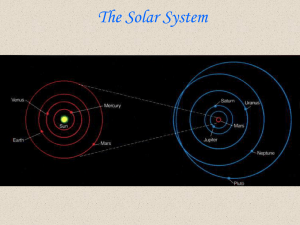
Solar System
... The Sun • The Sun is the closest star to Earth. • The Sun is made out of helium and hydrgen. ...
... The Sun • The Sun is the closest star to Earth. • The Sun is made out of helium and hydrgen. ...
CelestialSphere
... fact that the Earth moves around the Sun faster than they do, causing us to overtake them periodically, during which time they appear to move “backwards” in the sky. This caused a lot of headaches for those trying to explain the apparent motion of the planets. The “S” shape is due to the fact that t ...
... fact that the Earth moves around the Sun faster than they do, causing us to overtake them periodically, during which time they appear to move “backwards” in the sky. This caused a lot of headaches for those trying to explain the apparent motion of the planets. The “S” shape is due to the fact that t ...
CelestialSphere02
... fact that the Earth moves around the Sun faster than they do, causing us to overtake them periodically, during which time they appear to move “backwards” in the sky. This caused a lot of headaches for those trying to explain the apparent motion of the planets. The “S” shape is due to the fact that t ...
... fact that the Earth moves around the Sun faster than they do, causing us to overtake them periodically, during which time they appear to move “backwards” in the sky. This caused a lot of headaches for those trying to explain the apparent motion of the planets. The “S” shape is due to the fact that t ...
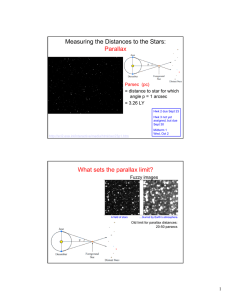
Measuring the Distances to the Stars: Parallax What sets the parallax limit?
... MW Rotation Curve • In principle, for stars, clusters, etc: ...
... MW Rotation Curve • In principle, for stars, clusters, etc: ...
quiz 2
... a) That the tilt of the Earth’s axis was 90 degrees b) That the seasons were caused by the distance between the Earth and the Sun. c) That the seasons were caused by the varying tilt of the Earth’s axis d) That the seasons were caused by the moon intercepting some of the light from the sun. For Ques ...
... a) That the tilt of the Earth’s axis was 90 degrees b) That the seasons were caused by the distance between the Earth and the Sun. c) That the seasons were caused by the varying tilt of the Earth’s axis d) That the seasons were caused by the moon intercepting some of the light from the sun. For Ques ...