sunmoon - University of Glasgow
... The two end stars are the ‘Pointers’, and point towards the Pole Star, (which is in the Little Bear). ...
... The two end stars are the ‘Pointers’, and point towards the Pole Star, (which is in the Little Bear). ...
SigAssignment
... M=mass. This is usually measured in the metric of kilograms, and this is also a variable. C^2= the speed of light squared. This is a constant. C^2 is 89,875,517,900,000,000 meters a second or 449,726,663,100,000,000 miles per hour. 3) In the equation E=mc^2 mass and energy are related. The reason wh ...
... M=mass. This is usually measured in the metric of kilograms, and this is also a variable. C^2= the speed of light squared. This is a constant. C^2 is 89,875,517,900,000,000 meters a second or 449,726,663,100,000,000 miles per hour. 3) In the equation E=mc^2 mass and energy are related. The reason wh ...
Chapter105.ppt
... • Planets are made from planetesimals; originally the rings of gas and dusk surrounding a protostar. The Moon formed when another celestial body collided with the Earth to create a massive cloud of dust and debris that coalesced to form the Moon. ...
... • Planets are made from planetesimals; originally the rings of gas and dusk surrounding a protostar. The Moon formed when another celestial body collided with the Earth to create a massive cloud of dust and debris that coalesced to form the Moon. ...
Chapter 9 Gravitation Beyond Earth’s surface
... But it is the Gravitational Force (definition of weight) that makes both the elevator and the body free-fall with the same acceleration. FEELING weightless and BEING weightless are VERY different. ...
... But it is the Gravitational Force (definition of weight) that makes both the elevator and the body free-fall with the same acceleration. FEELING weightless and BEING weightless are VERY different. ...
LECTURE 2: I.Our Place in the Universe
... phenomenon in a way that is consistent with laws, observations, and experiments. ...
... phenomenon in a way that is consistent with laws, observations, and experiments. ...
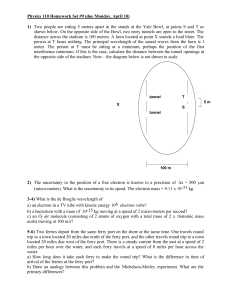
Physics 110 Homework Set #9 (due Monday, April 10) 1) Two
... returns to earth. Except for brief intervals of time when he is accelerating or decelerating, his spaceship travels at the incredible speed of v = 0.995 c relative to the earth. The star is 30 lightyears away. (A light-year is the distance light travels in 1 year.) a. Show that the factor γ for this ...
... returns to earth. Except for brief intervals of time when he is accelerating or decelerating, his spaceship travels at the incredible speed of v = 0.995 c relative to the earth. The star is 30 lightyears away. (A light-year is the distance light travels in 1 year.) a. Show that the factor γ for this ...
5.3 Most objects in the solar system are in a regular and predictable
... spin (rotate) and they change positions relative to each other (revolve). 2. The sun is a star that produces light that travels in straight lines away from the sun in all directions. Light from the sun illuminates objects that reflect light, including Earth and its moon. The side of the earth that i ...
... spin (rotate) and they change positions relative to each other (revolve). 2. The sun is a star that produces light that travels in straight lines away from the sun in all directions. Light from the sun illuminates objects that reflect light, including Earth and its moon. The side of the earth that i ...
The Planets in the Solar System There are an uncountable number
... from huge stars to tiny particles of dust. Somewhere between the two extremes are planets. For example, Ida, Jupiter, and Mercury are all big enough to be seen from Earth, but should we classify all three of these objects as planets? This question has made many people wonder: How many planets are th ...
... from huge stars to tiny particles of dust. Somewhere between the two extremes are planets. For example, Ida, Jupiter, and Mercury are all big enough to be seen from Earth, but should we classify all three of these objects as planets? This question has made many people wonder: How many planets are th ...
Time
... The measurement of time passage probably began with the concepts of past, present, and future. Throughout history humans have used various celestial bodies—that is, the Sun, the Moon, the planets, and the stars—to measure the passage of time. Ancient peoples used the apparent motion of these bodies ...
... The measurement of time passage probably began with the concepts of past, present, and future. Throughout history humans have used various celestial bodies—that is, the Sun, the Moon, the planets, and the stars—to measure the passage of time. Ancient peoples used the apparent motion of these bodies ...
Grade 5 - Morgan County Schools
... Matter of any type can be subdivided into particles that are too small to see, but even then the matter still exists and can be detected by other means. A model shows that gases are made from matter particles that are too small to see and are moving freely around in space can explain many observat ...
... Matter of any type can be subdivided into particles that are too small to see, but even then the matter still exists and can be detected by other means. A model shows that gases are made from matter particles that are too small to see and are moving freely around in space can explain many observat ...
Structure of the Universe
... We can then find the distance from: i.e., the closer the object, the greater flux we will will measure for a given luminosity ...
... We can then find the distance from: i.e., the closer the object, the greater flux we will will measure for a given luminosity ...
Intro to Astronomy
... Typically, spacecraft will use the gravity of the Earth or other planets to send them farther out into space. The method is called “gravity assist” or “sling-shot”. Otherwise, spacecraft would have to be much larger to carry enough fuel and more powerful engines to get anywhere. Sling-shotting throu ...
... Typically, spacecraft will use the gravity of the Earth or other planets to send them farther out into space. The method is called “gravity assist” or “sling-shot”. Otherwise, spacecraft would have to be much larger to carry enough fuel and more powerful engines to get anywhere. Sling-shotting throu ...
Quiz Lecture 3
... a. The Laws were developed by Kepler prior to the condemnation and imprisonment of Galileo. b. A line from the Sun to a planet sweeps out equal areas in equal intervals of time. c. The square of a planet's orbital period around the Sun is proportional to its average distance from the Sun cubed. d. T ...
... a. The Laws were developed by Kepler prior to the condemnation and imprisonment of Galileo. b. A line from the Sun to a planet sweeps out equal areas in equal intervals of time. c. The square of a planet's orbital period around the Sun is proportional to its average distance from the Sun cubed. d. T ...
Astronomy 1010 final review sample topics
... stars are slightly displaced relative to where they were the night before b.) stars do not move in the sky during a single night, but instead each successive night the stars are slightly displaced relative to where they were the night before c.) stars do not move in the sky during a single night and ...
... stars are slightly displaced relative to where they were the night before b.) stars do not move in the sky during a single night, but instead each successive night the stars are slightly displaced relative to where they were the night before c.) stars do not move in the sky during a single night and ...
Solar System
... • Nucleus = solid portion of a comet (inner layer). • Coma = halo of dust and gas that forms around the nucleus of a comet. Comets have “tails” that may extend millions of km into space! They face away from the sun. • Like other objects in space, comets orbit the sun. Comets have an elliptical shape ...
... • Nucleus = solid portion of a comet (inner layer). • Coma = halo of dust and gas that forms around the nucleus of a comet. Comets have “tails” that may extend millions of km into space! They face away from the sun. • Like other objects in space, comets orbit the sun. Comets have an elliptical shape ...
The Year and The Seasons
... • Homework # 1 will start on Tuesday, Sept. 20th, and will be due on Thursday Sept. 29th. ...
... • Homework # 1 will start on Tuesday, Sept. 20th, and will be due on Thursday Sept. 29th. ...
September 2013 - Joliet Junior College
... The Autumnal Equinox is at 3:44 pm on September 22nd. It is the end of astronomical summer and the beginning of fall. On that date, the sun is directly above the equator and will continue to move southward over the southern hemisphere to 23 degrees below the equator. Here in the Midwest, it means th ...
... The Autumnal Equinox is at 3:44 pm on September 22nd. It is the end of astronomical summer and the beginning of fall. On that date, the sun is directly above the equator and will continue to move southward over the southern hemisphere to 23 degrees below the equator. Here in the Midwest, it means th ...
The Solar System - Teachers TryScience
... • A solar system consists of a star and objects that revolve around it. • Our Solar System consists of the Sun and nine known planets and the moons that orbit those planets. • The force of gravity keeps planets in orbit around the sun. ...
... • A solar system consists of a star and objects that revolve around it. • Our Solar System consists of the Sun and nine known planets and the moons that orbit those planets. • The force of gravity keeps planets in orbit around the sun. ...
science - Amazon Web Services
... Bode’s Law. Although the distances in Figure 1 have been computed accurately with scientific precision, some two hundred years ago an astronomer named Bode developed a mathematical relationship for the distances of the then known planets from the sun, which has been popularized as Bode’s Law. His la ...
... Bode’s Law. Although the distances in Figure 1 have been computed accurately with scientific precision, some two hundred years ago an astronomer named Bode developed a mathematical relationship for the distances of the then known planets from the sun, which has been popularized as Bode’s Law. His la ...