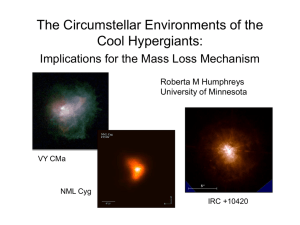
Circumstellar
... with spectral types A to M, high mass loss rates, photometric and spectroscopic variability, large infrared excess, ...
... with spectral types A to M, high mass loss rates, photometric and spectroscopic variability, large infrared excess, ...
What To See Telescope(Jul-Sept) v1 - One
... remarkably like a miniature version of the constellation Cassiopeia. The stars of this group are just aligned by chance. The stars are unrelated and moving in different directions through interstellar space. But they are a lovely sight. At magnitude 7 to 9, the stars exhibit a range of colors. The b ...
... remarkably like a miniature version of the constellation Cassiopeia. The stars of this group are just aligned by chance. The stars are unrelated and moving in different directions through interstellar space. But they are a lovely sight. At magnitude 7 to 9, the stars exhibit a range of colors. The b ...
The Hubble Ultra Deep Field Project Overview
... Exercise 1: Galaxy morphology over cosmic time In this exercise you will consider a variety of galaxies over a range of redshifts in order to derive any morphological trends which may arise in the HUDF, over cosmic timescales. Though it is a far from perfect classification system, the morphology (or ...
... Exercise 1: Galaxy morphology over cosmic time In this exercise you will consider a variety of galaxies over a range of redshifts in order to derive any morphological trends which may arise in the HUDF, over cosmic timescales. Though it is a far from perfect classification system, the morphology (or ...
Astronomy 1 – Introductory Astronomy Spring 2014
... Part I: The Changing Sky Most people know that the Sun, Moon, and stars appear to move through the sky over the course of a 24-hour day as the Earth turns on its axis. However, careful observation shows that Earth’s rotation is not enough to account for all the movements in the celestial sphere. In ...
... Part I: The Changing Sky Most people know that the Sun, Moon, and stars appear to move through the sky over the course of a 24-hour day as the Earth turns on its axis. However, careful observation shows that Earth’s rotation is not enough to account for all the movements in the celestial sphere. In ...
A Stargazers Guide to Astronomy
... Our Solar System The Sun Earth's Moon Planets Asteroids Meteoroids Comets Kuiper Belt Beyond Our Solar System Stars Constellations Find The Stars In The Sky Introducing 3DAstronomer ...
... Our Solar System The Sun Earth's Moon Planets Asteroids Meteoroids Comets Kuiper Belt Beyond Our Solar System Stars Constellations Find The Stars In The Sky Introducing 3DAstronomer ...
12-1 - Piscataway High School
... visual magnitude a star would have if it were 10 pc away as its absolute visual magnitude (MV). This is an expression of the intrinsic brightness of the star. The symbol for absolute visual magnitude is a capital M with a subscript V. The subscript reminds you it is a visual magnitude based only on ...
... visual magnitude a star would have if it were 10 pc away as its absolute visual magnitude (MV). This is an expression of the intrinsic brightness of the star. The symbol for absolute visual magnitude is a capital M with a subscript V. The subscript reminds you it is a visual magnitude based only on ...
When we look at a neighboring galaxy (such as M31, the
... measuring the radial velocities of the stars. M31 is barreling towards us at -300 km/sec (about -670,000 miles/hr), where the minus sign serves as a reminder that the velocity is towards us. (Truth be told: most of this apparent motion is actually due to the sun's motion around the center of the Mil ...
... measuring the radial velocities of the stars. M31 is barreling towards us at -300 km/sec (about -670,000 miles/hr), where the minus sign serves as a reminder that the velocity is towards us. (Truth be told: most of this apparent motion is actually due to the sun's motion around the center of the Mil ...
Brown dwarfs: Failed stars, super Jupiters
... representative M, L, and T brown dwarfs and the gas giant Jupiter. M and L dwarfs are the hottest, youngest, and most massive brown dwarfs. T dwarfs are the coldest currently known and have spectra that are more similar to those of gas giant planets than to those of stars. The complex spectra of bro ...
... representative M, L, and T brown dwarfs and the gas giant Jupiter. M and L dwarfs are the hottest, youngest, and most massive brown dwarfs. T dwarfs are the coldest currently known and have spectra that are more similar to those of gas giant planets than to those of stars. The complex spectra of bro ...
prehistoric constellations on swedish rock
... After 3 years the phase of the moon was shifted forward in the Leo-Cancer ship by 32.6 days if the length of the year was 365 ¼, or 31.9 days if the year had just 365 days. In the first case there had been an excess of 3.1 days compared with one lunar month and in the second case the excess was 2.4 ...
... After 3 years the phase of the moon was shifted forward in the Leo-Cancer ship by 32.6 days if the length of the year was 365 ¼, or 31.9 days if the year had just 365 days. In the first case there had been an excess of 3.1 days compared with one lunar month and in the second case the excess was 2.4 ...
CENTRAL TEXAS COLLEGE
... provide a sense of the mystery and majesty of the universe. As with our ancestors back beyond recorded time, we can’t help but wonder what kind of Universe is this? What are its fundamental laws? How old is it? How big? What does it contain? How has it changed with time, and what may be its future? ...
... provide a sense of the mystery and majesty of the universe. As with our ancestors back beyond recorded time, we can’t help but wonder what kind of Universe is this? What are its fundamental laws? How old is it? How big? What does it contain? How has it changed with time, and what may be its future? ...
Word - Stefan`s Florilegium
... pulley. The other end of the string was connected to a weight while a shaft connected the pulley to a pointer. As the water level in the collection container rose, so too would the float. This would cause the weight at the other end of the string to fall and the pulley, with the attached pointer, to ...
... pulley. The other end of the string was connected to a weight while a shaft connected the pulley to a pointer. As the water level in the collection container rose, so too would the float. This would cause the weight at the other end of the string to fall and the pulley, with the attached pointer, to ...
Latitudes and Longitudes
... We now know how to determine locations further north or further south on the Earth, in other words, we can determine the latitude of a location. To pinpoint our position on Earth, we need to know if we are further east or west. This means that we need to know the longitude. Now the Sun and the star ...
... We now know how to determine locations further north or further south on the Earth, in other words, we can determine the latitude of a location. To pinpoint our position on Earth, we need to know if we are further east or west. This means that we need to know the longitude. Now the Sun and the star ...
an Educator`s GuidE
... observing the effects they have on their parent stars. These effects, driven by gravity and line-of-sight, are visible to us as either periodic dimming (called “transits”) or shifting wavelengths within the electromagnetic spectrum (referred to as a “wobble”). To find a world capable of supporting l ...
... observing the effects they have on their parent stars. These effects, driven by gravity and line-of-sight, are visible to us as either periodic dimming (called “transits”) or shifting wavelengths within the electromagnetic spectrum (referred to as a “wobble”). To find a world capable of supporting l ...
... the finite speed of light to measure distances. However, stars are so far away and such poor reflectors that this approach is impractical (though it is used to determine distances to planets in our solar system). The question of measuring star distances has occupied astronomers at least since the ti ...
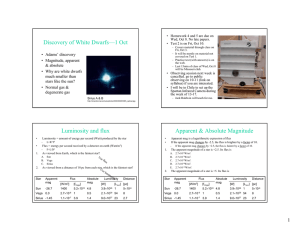
Discovery of White Dwarfs—1 Oct • Adams’ discovery
... • Apparent mag is a logarithmetic expression of flux • If the apparent mag changes by −2.5, the flux is brighter by a factor of 10. • Fluxes and magnitudes of two stars A and B ...
... • Apparent mag is a logarithmetic expression of flux • If the apparent mag changes by −2.5, the flux is brighter by a factor of 10. • Fluxes and magnitudes of two stars A and B ...
Planets in the Sky
... It was finally solved by Johannes Kepler in early 17th century, who discovered the elliptical nature of planetary orbits. ...
... It was finally solved by Johannes Kepler in early 17th century, who discovered the elliptical nature of planetary orbits. ...
Open clusters in the Third Galactic Quadrant III. Alleged binary
... the appropriate isochrone. Notice that in cases like this one, we can simultaneously obtain the color excess, the distance modulus and also the age of the cluster. In one case, given the large amount of internal reddening (see Sect. 4.2.1), the range of distance modulus is so large that we only indi ...
... the appropriate isochrone. Notice that in cases like this one, we can simultaneously obtain the color excess, the distance modulus and also the age of the cluster. In one case, given the large amount of internal reddening (see Sect. 4.2.1), the range of distance modulus is so large that we only indi ...
Moitinho et al. - Wiley Online Library
... (Martı́nez-Delgado et al. 2005). The youth of the BP also explains why no 1–2 Gyr red clump is evident at 8 kpc. Fig. 2 also reveals the presence of a few other BPs. These would also be considered a non-Galactic population, but in this case they are much closer than the proposed distance to the CMa ...
... (Martı́nez-Delgado et al. 2005). The youth of the BP also explains why no 1–2 Gyr red clump is evident at 8 kpc. Fig. 2 also reveals the presence of a few other BPs. These would also be considered a non-Galactic population, but in this case they are much closer than the proposed distance to the CMa ...
The Discovery of Planets beyond the Solar System
... There is a planet going around its star in only 3 days, there is another that takes 4.5 years. The planet closest to its star moves at only 0.04 of the Earth-Sun distance. The planet moving the farthest away is at 2.8 times the EarthSun distance from its star. In the Solar System, all planets move i ...
... There is a planet going around its star in only 3 days, there is another that takes 4.5 years. The planet closest to its star moves at only 0.04 of the Earth-Sun distance. The planet moving the farthest away is at 2.8 times the EarthSun distance from its star. In the Solar System, all planets move i ...
Larger, high-res file, best for printing
... just prior to the explosion. After core collapse, the optical luminosity of the supernova is powered by radioactive decay of nickel-56 and its daughter element cobalt-56. Meanwhile, in the less dense outer layers of the supernova remnant, the rare titanium-44, apparently an exclusive product of type ...
... just prior to the explosion. After core collapse, the optical luminosity of the supernova is powered by radioactive decay of nickel-56 and its daughter element cobalt-56. Meanwhile, in the less dense outer layers of the supernova remnant, the rare titanium-44, apparently an exclusive product of type ...
sections 16-18 instructor notes
... v. by determining the peculiar velocity of the Sun relative to nearby galaxies in the Local Group. It is not as simple a task as it might seem, owing to the intrinsic velocities of other galaxies in the system. An estimate of the local circular velocity from such an analysis is that of Arp (A&A, 15 ...
... v. by determining the peculiar velocity of the Sun relative to nearby galaxies in the Local Group. It is not as simple a task as it might seem, owing to the intrinsic velocities of other galaxies in the system. An estimate of the local circular velocity from such an analysis is that of Arp (A&A, 15 ...
Corvus (constellation)

Corvus is a small constellation in the Southern Celestial Hemisphere. Its name comes from the Latin word ""raven"" or ""crow"". It includes only 11 stars with brighter than 4.02 magnitudes. One of the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd-century astronomer Ptolemy, it remains one of the 88 modern constellations. The four brightest stars, Gamma, Delta, Epsilon, and Beta Corvi from a distinctive quadrilateral in the night sky. The young star Eta Corvi has been found to have two debris disks.