sections 16-18 instructor notes
... v. by determining the peculiar velocity of the Sun relative to nearby galaxies in the Local Group. It is not as simple a task as it might seem, owing to the intrinsic velocities of other galaxies in the system. An estimate of the local circular velocity from such an analysis is that of Arp (A&A, 15 ...
... v. by determining the peculiar velocity of the Sun relative to nearby galaxies in the Local Group. It is not as simple a task as it might seem, owing to the intrinsic velocities of other galaxies in the system. An estimate of the local circular velocity from such an analysis is that of Arp (A&A, 15 ...
The Science of Astronomy - Ohio Wesleyan University
... – The equator is an example of a great circle: a circle that divides a sphere into 2 equal parts (northern and southern hemisphere in this case) – For historical reasons, the exact location of the origin on the equator is due south of the former location of the Royal Observatory in Greenwich, Englan ...
... – The equator is an example of a great circle: a circle that divides a sphere into 2 equal parts (northern and southern hemisphere in this case) – For historical reasons, the exact location of the origin on the equator is due south of the former location of the Royal Observatory in Greenwich, Englan ...
Today in Astronomy 102: observations of stellar
... Discovery of “stellar” black holes: GRO J1655-40 GRO J1655-40 is an X-ray transient source discovered by NASA’s Compton Gamma-Ray Observatory (GRO) in 1994. Rapidly-variable emission in its X-ray bursts: the X-ray object is a few hundred km around. The X-ray source has a stellar companion, a st ...
... Discovery of “stellar” black holes: GRO J1655-40 GRO J1655-40 is an X-ray transient source discovered by NASA’s Compton Gamma-Ray Observatory (GRO) in 1994. Rapidly-variable emission in its X-ray bursts: the X-ray object is a few hundred km around. The X-ray source has a stellar companion, a st ...
Complete Lecture Notes (pdf file)
... stars are both observed to be 7.5, but their blue magnitudes are B1 = 7.2 and B2 = 8.65. (a) What are the colour indices of the two stars. (b) Which star is the bluer and by what factor is it brighter at blue wavelength. (c) Making reasonable assumptions, deduce as many of the physical properties of ...
... stars are both observed to be 7.5, but their blue magnitudes are B1 = 7.2 and B2 = 8.65. (a) What are the colour indices of the two stars. (b) Which star is the bluer and by what factor is it brighter at blue wavelength. (c) Making reasonable assumptions, deduce as many of the physical properties of ...
Direct Detection of Galactic Halo Dark Matter
... to harbor a substantial amount of unseen matter. Recent observations indirectly suggest that as much as half of this “dark matter” may be in the form of old, very cool white dwarfs, the remnants of an ancient population of stars as old as the galaxy itself. We conducted a survey to find faint, cool ...
... to harbor a substantial amount of unseen matter. Recent observations indirectly suggest that as much as half of this “dark matter” may be in the form of old, very cool white dwarfs, the remnants of an ancient population of stars as old as the galaxy itself. We conducted a survey to find faint, cool ...
The Royal Arch of the Heavens
... On a band of sky which lies roughly 8 either side of the Ecliptic is where we find the constellations of the zodiac circle of animals. This thin band of sky is divided into twelve segments of 30 each, with one constellation contained, or at least mostly contained, within each segment. As far as we ...
... On a band of sky which lies roughly 8 either side of the Ecliptic is where we find the constellations of the zodiac circle of animals. This thin band of sky is divided into twelve segments of 30 each, with one constellation contained, or at least mostly contained, within each segment. As far as we ...
How we know black holes exist
... emission shifts slightly toward the red end of the electromagnetic spectrum; as it speeds toward our planet, its emission shifts to the blue end. From the amount the spectrum shifts, astronomers can determine how fast the visible star is moving and how long it takes to complete one orbit. Then, usin ...
... emission shifts slightly toward the red end of the electromagnetic spectrum; as it speeds toward our planet, its emission shifts to the blue end. From the amount the spectrum shifts, astronomers can determine how fast the visible star is moving and how long it takes to complete one orbit. Then, usin ...
General Astrophysics And Comparative Planetology
... task, the TPF missions could easily undertake a broad range of further scientific investigations. This document discusses the potential of TPF for general astrophysics beyond its base mission, focusing on science obtainable with no or minimal modifications to the mission design, but also exploring p ...
... task, the TPF missions could easily undertake a broad range of further scientific investigations. This document discusses the potential of TPF for general astrophysics beyond its base mission, focusing on science obtainable with no or minimal modifications to the mission design, but also exploring p ...
Lab: Inverse Square Law
... Introduction: As light travels from a source it spreads out equally in all directions. The brightness of the light is the power (energy per second) per area. We all know that a light, such as a candle or a streetlight, looks dimmer the farther away from it we get. But how does the brightness change ...
... Introduction: As light travels from a source it spreads out equally in all directions. The brightness of the light is the power (energy per second) per area. We all know that a light, such as a candle or a streetlight, looks dimmer the farther away from it we get. But how does the brightness change ...
Local Horizon View
... lines up from the East, and loosing those low in the West. So a fixed degree system based on the Pole and the Equator just won't work. They need to be tied into the fact that Earth rotates every 24 hours and this is an amount of time. ...
... lines up from the East, and loosing those low in the West. So a fixed degree system based on the Pole and the Equator just won't work. They need to be tied into the fact that Earth rotates every 24 hours and this is an amount of time. ...
Structure of Neutron Stars
... progenitors of NSs (see for example, Ergma, van den Heuvel 1998 A&A 331, L29). For example, an interesting estimate was obtained for GX 301-2. The progenitor mass is >50 solar masses. On the other hand, for several other systems with both NSs and BHs progenitor masses a smaller: from 20 up to 50. Fi ...
... progenitors of NSs (see for example, Ergma, van den Heuvel 1998 A&A 331, L29). For example, an interesting estimate was obtained for GX 301-2. The progenitor mass is >50 solar masses. On the other hand, for several other systems with both NSs and BHs progenitor masses a smaller: from 20 up to 50. Fi ...
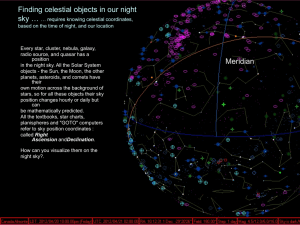
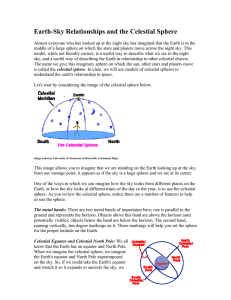
Earth-Sky Relationships and the Celestial Sphere
... NCP. (By the way, Polaris is not the brightest star in the night sky, contrary to much popular belief. It is approximately the 20th brightest star in the night sky, but is the brightest star near the NCP.) Lines of Celestial Latitude and Longitude: If you look carefully at the celestial spheres, you ...
... NCP. (By the way, Polaris is not the brightest star in the night sky, contrary to much popular belief. It is approximately the 20th brightest star in the night sky, but is the brightest star near the NCP.) Lines of Celestial Latitude and Longitude: If you look carefully at the celestial spheres, you ...
Basic principles of celestial navigation
... through" the observer’s meridian from east to west at intervals of 23 hour, 56 minute, 4 second of mean solar time, also called the sidereal rotational period of the Earth or the sidereal day. The observer’s zenith is defined by the outward extension of the line from the center of the Earth through ...
... through" the observer’s meridian from east to west at intervals of 23 hour, 56 minute, 4 second of mean solar time, also called the sidereal rotational period of the Earth or the sidereal day. The observer’s zenith is defined by the outward extension of the line from the center of the Earth through ...
Basic principles of celestial navigation
... through" the observer’s meridian from east to west at intervals of 23 hour, 56 minute, 4 second of mean solar time, also called the sidereal rotational period of the Earth or the sidereal day. The observer’s zenith is defined by the outward extension of the line from the center of the Earth through ...
... through" the observer’s meridian from east to west at intervals of 23 hour, 56 minute, 4 second of mean solar time, also called the sidereal rotational period of the Earth or the sidereal day. The observer’s zenith is defined by the outward extension of the line from the center of the Earth through ...
PH607lec08
... • When examined with sufficient resolution, 25% to more than 40% of E galaxies show features due to dust absorption. • The dust lanes seen in E galaxies imply that the absorbing material is distributed in rings or disks. Dust lanes may be aligned with either the major or minor axes, or they may be w ...
... • When examined with sufficient resolution, 25% to more than 40% of E galaxies show features due to dust absorption. • The dust lanes seen in E galaxies imply that the absorbing material is distributed in rings or disks. Dust lanes may be aligned with either the major or minor axes, or they may be w ...
Lecture21 - Michigan State University
... wavelengths They were all moving away from us at high speed ...
... wavelengths They were all moving away from us at high speed ...
–1– 2. Milky Way We know a great deal, perhaps more than any
... is about 27 pc above the Galactic plane. Furthermore, the vertical distribution of stars in the solar neighborhood can be approximated by the sum of two exponentials. These were identified as a thin disk and a thick disk components. The stars in the thin and thick disks appear to have different ages ...
... is about 27 pc above the Galactic plane. Furthermore, the vertical distribution of stars in the solar neighborhood can be approximated by the sum of two exponentials. These were identified as a thin disk and a thick disk components. The stars in the thin and thick disks appear to have different ages ...
1. INTRODUCTION
... using Keck I with the HIRES echelle spectrometer (Vogt et al. 1994). The spectra have resolution, R \ 80,000 and span wavelengths from 3900 to 6200 A . Wavelength calibration is carried out by means of an iodine absorption cell (Marcy & Butler 1992 ; Butler et al. 1996), which superimposes a refere ...
... using Keck I with the HIRES echelle spectrometer (Vogt et al. 1994). The spectra have resolution, R \ 80,000 and span wavelengths from 3900 to 6200 A . Wavelength calibration is carried out by means of an iodine absorption cell (Marcy & Butler 1992 ; Butler et al. 1996), which superimposes a refere ...
Moro_Martin`s Talk - CIERA
... The clearing of dust inside the planet’s orbit has a clear signature in the disk SED SEDs are sensitive to the presence and location of massive planets. Spitzer Space Telescope observations of debris disks: Debris disks and planets co-exist. Cold KB-like disks are more common than AB-like disks. Ind ...
... The clearing of dust inside the planet’s orbit has a clear signature in the disk SED SEDs are sensitive to the presence and location of massive planets. Spitzer Space Telescope observations of debris disks: Debris disks and planets co-exist. Cold KB-like disks are more common than AB-like disks. Ind ...
Part2
... o Individual clouds only resolved inside the Local Group by the 30m. o Individual low mass clouds only detectable inside Local Group. o Individual high mass clouds detectable with effort in nearest other groups. o Observing distant galaxies requires averaging many clouds inside a beam (that’s okay, ...
... o Individual clouds only resolved inside the Local Group by the 30m. o Individual low mass clouds only detectable inside Local Group. o Individual high mass clouds detectable with effort in nearest other groups. o Observing distant galaxies requires averaging many clouds inside a beam (that’s okay, ...
Searching for the oldest, most metal-poor stars in the SkyMapper Survey
... 1. Normalize the spectra. The processed and reduced echelle spectra from the MagellanClay telescope for each star are high-resolution (0.7” slit R = λ/∆λ ∼ 30, 000 and 1.0” slit R ∼ 35, 000) line spectra. Each spectrum possess ∼ 30 orders, which are small pieces of the spectrum. The wavelength rang ...
... 1. Normalize the spectra. The processed and reduced echelle spectra from the MagellanClay telescope for each star are high-resolution (0.7” slit R = λ/∆λ ∼ 30, 000 and 1.0” slit R ∼ 35, 000) line spectra. Each spectrum possess ∼ 30 orders, which are small pieces of the spectrum. The wavelength rang ...
Corvus (constellation)

Corvus is a small constellation in the Southern Celestial Hemisphere. Its name comes from the Latin word ""raven"" or ""crow"". It includes only 11 stars with brighter than 4.02 magnitudes. One of the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd-century astronomer Ptolemy, it remains one of the 88 modern constellations. The four brightest stars, Gamma, Delta, Epsilon, and Beta Corvi from a distinctive quadrilateral in the night sky. The young star Eta Corvi has been found to have two debris disks.